A.C. Generator | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
AC Generator
An AC generator is an electric generator that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy in form of alternative emf or alternating current. AC generator works on the principle of ”Electromagnetic Induction”.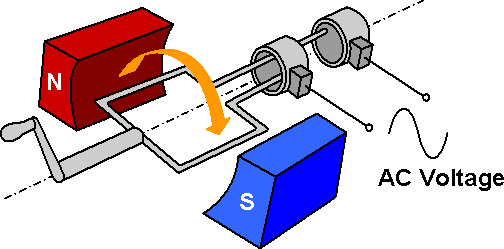
Parts of an AC Generator
An Ac generator consists of two poles i.e is the north pole and south pole of a magnet so that we can have a uniform magnetic field. There is also a coil which is rectangular in shape that is the armature. These coils are connected to the slip rings and attached to them are carbon brushes.
The slip rings are made of metal and are insulated from each other. The brushes are carbon brushes and one end of each brush connects to the ring and other connects to the circuit. The rectangular coils rotate about an axis which is perpendicular to the magnetic field. There is also a shaft which rotates rapidly.
Working of an AC Generator
When the armature rotates between the poles of the magnet upon an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field, the flux which links with the armature changes continuously. Due to this, an emf is induced in the armature. This produces an electric current through the galvanometer and the slip rings and brushes.
The galvanometer swings between the positive and negative values. This indicates that there is an alternating current flowing through the galvanometer.
Emf induced in an AC generator
If the coil of N turn and area A is rotated at v revolutions per second in a uniform magnetic field B, then the motional emf produced is e = NBA(2πv)sin(2πv)t, where we assume that at time t = 0 s, the coil is perpendicular to the field. The direction of the induced emf is given by Fleming’s right-hand rule or the Lenz’s law.
Fleming’s right-hand rule states that, stretch the forefinger, the middle finger and the thumb of the right hand such that they are manually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger indicates the direction of the magnetic field, rhumb indicates the direction of the motion of the conductor. The middle finger indicates the direction of the induced current in the conductor.
3-Phase AC generator
In a symmetric three-phase power supply system, three conductors each carry an alternating current of the same frequency and voltage amplitude relative to a common reference but with a phase difference of one third the period. The common reference usually connects to ground and often to a current-carrying conductor that is neutral.
Due to the phase difference, the voltage on any conductor reaches its peak at one-third of a cycle after one of the other conductors and one-third of a cycle before the remaining conductor. This phase delay gives constant power transfer to a balanced linear load. It also makes it possible to produce a rotating magnetic field in an electric motor and generate other phase arrangements using transformers.
Solve Questions
Q.1. What replacement is required to convert an AC generator to DC generator
(a) Armature with coil
(b) Concave magnets with horseshoe magnet
(c) Slip rings with split rings
(d) All of the above
Ans: (c)
Solution: The slip rings in an AC generator maintain a connection between a moving rotor and the stationary rotor results in the periodic change of current in the loop making it an alternate current. However, the DC generator is consisting of split rings makes the current change direction every half rotation which causes no change in direction of the current.
Q.2. What determines the frequency of a.c. produced by a generator?
(a) The number of rotations of coil in one-second
(b) A speed of rotation coil
(c) Both A and B
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Solution: A frequency of ac, v= w/2π, where w is the speed of rotation.
|
289 videos|635 docs|179 tests
|
FAQs on A.C. Generator - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is an AC generator? |  |
| 2. How does an AC generator work? |  |
| 3. What are the main components of an AC generator? |  |
| 4. What are the applications of AC generators? |  |
| 5. How is the output voltage controlled in an AC generator? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|

















