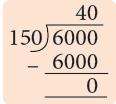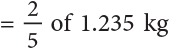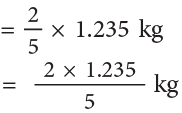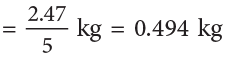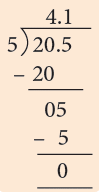Measurement of Length, Mass and Capacity Class 5 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Measurement? |

|
| 1. Length |

|
| 2. Mass (Weight) |

|
| 3.Capacity |

|
| Decimals and Measurements |

|
| Basic Operations on Measurements |

|
| Finding Fractions of Quantities |

|
Introduction
Imagine you are going on an adventure! ️To make it a success, you’ll need to measure a lot of things
- How far can you travel?
- How much water you need to carry, and even how much time you have before the sun sets!
That’s exactly what we will learn in this chapter – Measurement!
What is Measurement?
Measurement means determining the size, length, capacity, weight, or time of something using standard units.
Types of Measurements
1. Length
Length tells us how long or tall something is.
- The standard unit of length is the meter (m).
- Other units of length, along with their conversion in meters, are given below:
- Kilometer (km) = 1000 m
- Hectometer (hm) = 100 m
- Decameter (dam) = 10 m
- Meter (m) = 1 m
- Decimeter (dm) = 110 m = 0.1 m
- Centimeter (cm) = 1100 m = 0.01 m
- Millimeter (mm) = 11000 m = 0.001 m
Follow the diagram to do the conversions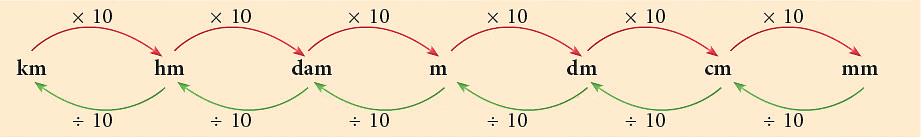
Examples including conversions are given below
Example 1: Convert 3 km into meter.
Sol: We know that 1 km = 1000 m
hence, 3 km = 3 x 1000
= (3 × 1000) m
= 3000 m
Example 2: Convert 370 m into hectometer.
Sol: We know that 1 Hectometer (hm) = 100 m
(i) 1001 m = 1 hm
(ii) 1100 m = 1 hm
(iii) 370 m = 370 × 1100 hm = 370100 hm = 3.7 hm
Example 3: Convert 2000 mm into meter.
Sol: As We know that: 1 mm = 11000 meters = 0.001m
So, 2000 mm = 20001000 meters = 2 meters.
Example 4: Convert 12000 cm to dam.
Sol: 1 cm = 11000 dam
=Therefore 12000 cm = 120001000 dam
= 12 dam
2. Mass (Weight)
Mass tells us how heavy an object is.
- The standard unit of mass is a Kilogram (kg)
- Other Units of mass along with their conversion in grams are given below
1. Kilogram (kg) = 1000 g
2. Hectogram (hg) = 100 g
3. Decagram (dag) = 10 g
4. Gram (g) = 1 g
5. Decigram (dg) = 110 g = 0.1 g
6. Centigram (cg) = 1100 g = 0.01 g
7. Milligram (mg) = 11000 g = 0.001 g
Follow the diagram to do the conversions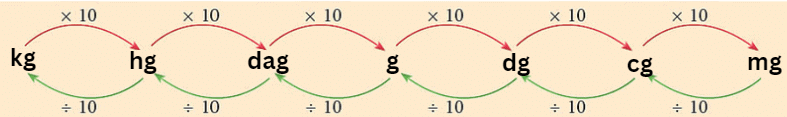
Example 1: Conversion of various units to grams and vice versa.
(i) 24 kg = (24 × 1000) g = 24000 g
(ii) 1.217 g = (1.217 × 1000) mg = 1217 mg
(iii) 3200 mg = (3200 ÷ 1000) g = 3.2 g
(iv) 315 cg = (315 ÷ 100) g = 3.15 g
Example 2: Conversion between Units
(i) 14 mg = (14 ÷ 10) cg = 1.4 cg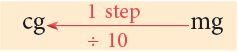 (ii) 300 dg = (300 ÷ 100) dag = 3 dag
(ii) 300 dg = (300 ÷ 100) dag = 3 dag
(iii) 2417 cg = (2417 ÷ 1000) dag = 2.417 dag
(iv) 38 kg = (38 × 100) dag = 3800 dag
(v) 23.7 dg = (23.7 × 10) cg = 237 cg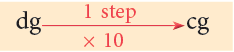
(vi) 4 hg = (4 × 1000) dg = 4000 dg
Example 3: A basket of apples weighs 2.5 kg. How much is that in g?
Sol: 2.5 × 1000 = 2500 g
The basket of apples weighs 2500 g.
3.Capacity
Capacity tells us how much a container can hold (liquid).
- The standard unit of capacity is a litre (l)
- Other units of capacity along with their conversion in litres are given below
1. Kilolitre (kL) = 1000 L
2. Hectolitre (hL) = 100 L
3. Decalitre (daL) = 10 L
4. Litre (L) = 1 L
5. Decilitre (dL) = 110 L = 0.1 L
6. Centilitre (cL) = 1100 L = 0.01 L
7. Millilitre (mL) = 11000 L = 0.001 L
Follow the diagram to do the conversions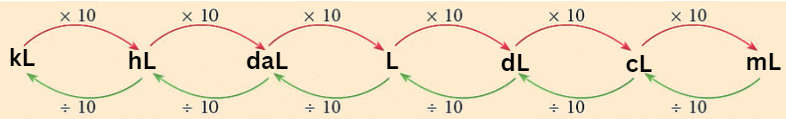
Examples of the conversions are given below
Example 1: Conversion of various units to litres and litres to various units
(i) 2.3 kL = (2.3 × 1000) L = 2300 L
(ii) 1.8 cL = (1.8 ÷ 100) L = 0.018 L
(iii) 64 hL = (64 × 100) L = 6400 L
(iv) 600 L = (600 ÷ 100) hL = 6 hL
(v) 7315 mL = (7315 ÷ 1000) L = 7.315 L
(vi) 11.9 L = (11.9 × 1000) mL = 11900 mL
Example 2: Conversions between Units.
(i) 25 hL = (25 × 10) daL = 250 daL
(ii) 13.8 dL = (13.8 × 100) mL = 1380 mL
(iii) 500 daL = (500 ÷ 100) kL = 5 kL
(iv) 3.117 hL = (3.117 × 1000) dL = 3117 dL
Decimals and Measurements
- Decimals are commonly used in measurements to give more precise values.
- For example, when measuring length, weight, or capacity, we often need to express measurements that are not whole numbers.
- Now we will understand how decimals are being used to express Length, Weight and Capacity.
1. Using Decimals to Express Length
- If you travel 7 kilometres and 500 meters, we can write it as 7500 meters.
- Using decimals, we can also write 7500 meters as 7.500 kilometres (Why?)
- Because, as we have studied earlier, 1 km = 1000 m
=> 1000 m = 1 km
=> 1 m = 1100 m
Therefore, 7500m = 75001000 km = 7.500 km
Example: Convert 5.45 meters into centimetres.
Sol: 1meter=100 centimeters
5.45 × 100 = 545 centimeters
2. Using Decimals to Express Mass(Weight)
- If the weight of a rice sack is 4 kilograms and 500 grams, we can write it as 4500 grams.
- Using Decimals, we can also write 4550 grams as 4.500 kilograms ( Why?)
- Because, as we have studied earlier, 1 kg = 1000 g
=> 1000 g = 1 kg
=> 1 g = 11000 kg
=> 4500 g = 45001000 kg = 4.500 kg
Example: Convert 2.85 kilograms into grams.
Sol:
1 kilogram = 1000 grams
2.85 Kg = 2.85 × 1000=2850 gram
3. Using Decimals to Express Capacity
- Decimals help us show how much liquid something can hold using bigger units.
- For example, if you made 1 litre and 200 millilitres of lemonade, we can write it as 1200 millilitres.
- Using decimals, we can also write 1200 millilitres as 1.200 litres (Why?)
- Because, as we have studied earlier, 1 L = 1000 mL
=> 1000 mL = 1 L
=> 1 mL = 11000 L
=> 1200 mL = 12001000 L = 1.200 L
Example: Convert 3.5 litres into millilitres.
Sol: As we know,
=> 1 litre =1000 millilitres
=> 3.5×1000 = 3500 millilitres
=> 3500 milliliters
Basic Operations on Measurements
1. Addition and Subtraction
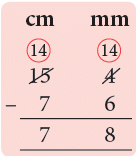
Example 1: Ritu drew a line segment of length 15 cm 4 mm. Then, she erased a portion of it. The remaining line segment measured 7 cm 6 mm. What is the length in mm of the erased line segment?
Sol: Length of the line segment in the beginning = 15 cm 4 mm
Length of line segment left after erasing = 7 cm 6 mm
Length of line segment erased = 15 cm 4 mm – 7 cm 6 mm
= 7 cm 8 m m
= 7 + 810 cm = 7.8 cm.
Example 2: Add 3 cm 4 mm and 9 cm 8 mm.
Sol:
12 mm
= 10 mm + 2 mm
= 1 cm + 2 mm
= 13 cm 2 mm = 13.2 cm.
Example 3: Subtract 8 kL 150 L – 4 kL 850 L.
Sol:
150 L < 850 L
Borrow 1 kL = 1000 L
1000 L + 150 L
= 1150 L
= 3.300 kL.
2. Multiplication
- Arrange numbers in columns unit wise and then multiply as you would multiply whole numbers.
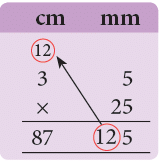
Example 1: Find the height of a pile of 25 books, if each book is 3 cm, 5 mm thick (in centimetres).
Sol: Thickness of 1 book = 3 cm 5 mm = 3.5 cm
Height of 25 books = 3.5 cm × 25
= 87.5 cm
Thus, height of the pile of 25 books
= 87.5 cm.
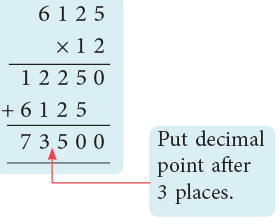
Example 2: A carton full of fruits weighs 6 kg 125 g. What is the weight of 12 such cartons in kg?
Sol: Weight of one carton = 6 kg 125 g
= 6.125 kg
∴ Weight of 12 cartons = (6.125 × 12) kg
= 73.500 kg
= 73 kg 500 g.
Division
- In division also arrange the numbers in columns unit wise and then divide like whole numbers.
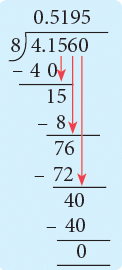
Example 1: Reena prepared 4 L 156 mL of orange juice. Distribute it equally among 8 children. How many mL of orange juice each child gets?
Sol: Juice Reena prepared = 4 L 156 mL = 4.156 L
When distributed among 8 children,
juice each child gets = (4.156 ÷ 8) L
= 0.51 95 L
= 519 .5 mL.
Example 2: How many 150 mL glasses can I fill with 5 bottles of soft drinks each holding 1.2 litres?
Sol: Total soft drink in 5 bottles = 1.2 L × 5 = 6.0 = 6 L
∵ 1 L = 1000 mL
Total soft drink = 6 L = 6 × 1000 = 6000 mL
Number of 150 mL of glasses that can be filled = 6000 mL ÷ 150 mL = 40
Thus, with 6 L of soft drink, I can fill 40 glasses of 150 mL.
Finding Fractions of Quantities
Example 1: A basket contains 3 kg 705 g of mangoes. 23 of the mangoes are eaten by Mr Bhasin. Lata, his daughter, gets 25 of the remaining mangoes. What is her share in grams?
Sol: Total weight of mangoes = 3 kg 705 g
Mangoes eaten by Mr Bhasin
= 23 of 3 kg 705 g= 23 of 3.705 g
= 23 x 3.705 g
= 2 x 3.7053 kg
= 7.413 kg = 2.47 kg
Mangoes left = 3.705 kg – 2.47 kg
= 1.235 kg
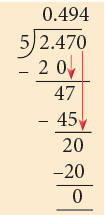
Mangoes eaten by Lata
= (0.494 × 1000) g
= 494 g
So, Lata ate 494 g of the mangoes.
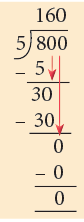
Example 2: Anshul had 45 kg of wafers. He packed all the wafers equally into 5 small packets. How many grams of wafers were there in each packet?
Sol: Total wafers with Anshul = 45 kg
= 45 x 1000 g
= 800 g
800 g wafers are filled in 5 small packets.
∴ Wafers in one packet = 800 ÷ 5
= 8005 = 160 g
So, each packet contains 160 g of wafers.
Example 3: Madhuri drew a line segment of length 20 cm 5 mm. She accidentally erased 2 / 5 of it. What is the length of the remaining line segment in cm?
Sol: Length of the line segment drawn = 20 cm 5 mm = 20.5 cm
Length of the erased line segment = 25 of 20.5 cm
= (2 × 4.1) cm
= 8.2 cm
Length of the remaining line segment = 20.5 cm – 8.2 cm
= 12.3 cm.
|
95 videos|462 docs|47 tests
|
FAQs on Measurement of Length, Mass and Capacity Class 5 Notes Maths
| 1. What is the difference between length and mass? |  |
| 2. How do you convert between different units of length? |  |
| 3. What are some common units of capacity and how are they related? |  |
| 4. How do decimals relate to measurements? |  |
| 5. How can I find a fraction of a quantity in measurements? |  |