Weather and Climate Class 5 Notes SST
What is Weather?
The day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere at a place with respect to elements like humidity, temperature, wind speed, rainfall, etc. is called the weather of that place.
- Weather is something that doesn't stay the same. It can change every day, and sometimes, it even changes within the same day.
- For example, a day that starts sunny might become cloudy or windy by the evening. We often check the weather report on TV or read forecasts in the newspaper to know what to expect.
- Weather includes things like the air condition, temperature, wind, humidity, and rainfall at a specific place and time.
- Weather can be cloudy, sunny, rainy, stormy, or clear. It is a part of the natural phenomenon which maintains the equilibrium in the atmosphere.

- But conditions can be worse sometimes. When the atmospheric conditions are extreme or intense enough to cause property loss or life loss, such weather is termed severe weather.
- Changes in weather conditions give rise to seasons.
- In India, we enjoy three seasons: Summer, Winter & Monsoon.
 Seasons of India
Seasons of India
What is Climate?
The weather conditions that prevail over a large area and for a long period of time is called climate.
- The climate of a place remains more or less the same, year after year. Different parts of the world have different types of climate.
- Based on the prevailing climatic conditions, the world can be divided into seven major climatic regions.
- Different places in the world have different types of climates. Countries like Canada, Norway, Sweden, and Russia are very cold, while several parts of India, Myanmar, China, Bangladesh, and Indonesia are hot and humid. The regions with similar climatic conditions have similar ways of life too.
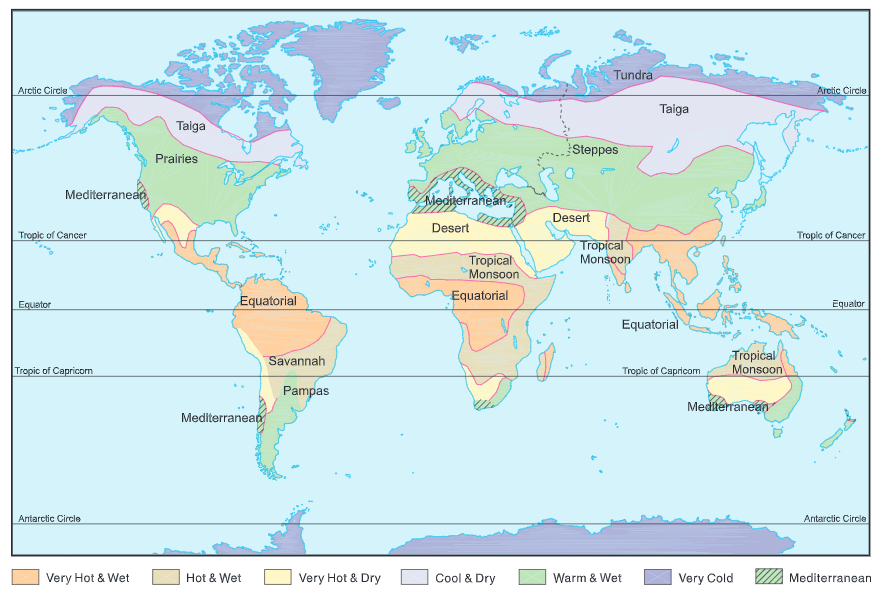 The seven major climatic regions of the world
The seven major climatic regions of the world
Factors That Determine The Climate of a Place
Many factors influence the distribution of heat on Earth, thereby affecting the climate. Let us read about them.
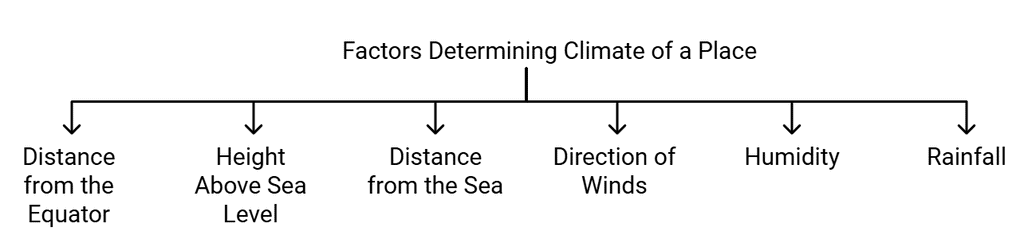 Factors determining climate of a place
Factors determining climate of a place
1. Distance from the Equator
- The sun’s rays fall directly over the regions that are nearest to the equator. They cover a small area.
- As such, regions near the equator are hotter. The position is different at places near the poles.
- The rays of the sun are spread over a much larger area. Here they strike in a slanting fashion. So places near the poles are relatively colder.
- The areas between the poles and the Arctic and Antarctic circles are very cold.
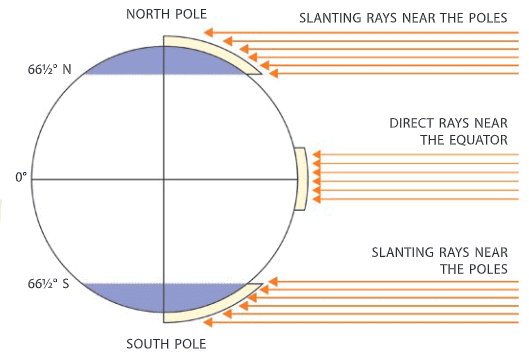 How the sun's rays fall on the earth.
How the sun's rays fall on the earth.
Climatic Zones
Regions of the world having similar climatic conditions are grouped together in different heat zones.The world is divided into three climatic zones:
(a) Torrid zone
(b) Temperate zone
(c) Frigid zone
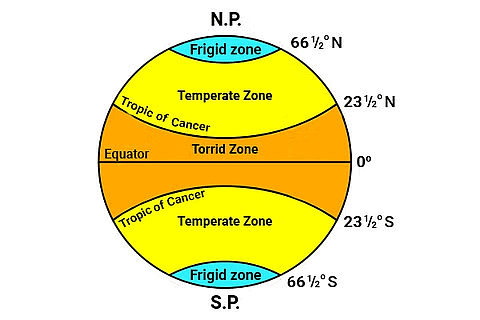 Climatic Zones
Climatic Zones
(a) Torrid Zone
- The Torrid zone lies in the area between the Tropic of Cancer and the Tropic of Capricorn.
- This zone receives direct rays of the Sun and is very hot and humid.
- Some areas in this receive high rainfall.
(b) Temperate Zone
- The region between the Tropic of Cancer to the Arctic Circle in the Northern Hemisphere and the tropic of Capricorn to the Antarctic Circle in the Southern Hemisphere falls in a Temperate Zone.
- This zone receives slanting rays of the sun and is neither very hot nor very cold.
(c) Frigid Zone
- The region extending from the Arctic Circle to the North Pole in the Northern Hemisphere and the Antarctic Circle to the South Pole in the Southern Hemisphere fall in this zone.
- This region is extremely cold and remains covered with snow throughout the year. The climate varies in different parts of the world.
- Some regions in the world remain hot throughout the year, whereas other regions experience heavy snow and ice. Desert regions are hot and dry while some experience rainfall
2. Height Above Sea Level
- The height of a place above sea level is called the altitude of a place. The higher we
go, the cooler it gets.
Bengaluru is cooler than Chennai. The two places are nearly equidistant from the equator. The difference lies in their height above sea level–Altitude. Chennai is situated at sea level, while Bengaluru is about 550 meters above sea level.
- The air above the surface of the earth works like layers of blankets. The more the layers, the hotter it would be at a particular place.
- If a place is situated at a higher altitude, there are fewer layers and hence the place is cooler. It is very cold at the high mountain peaks.
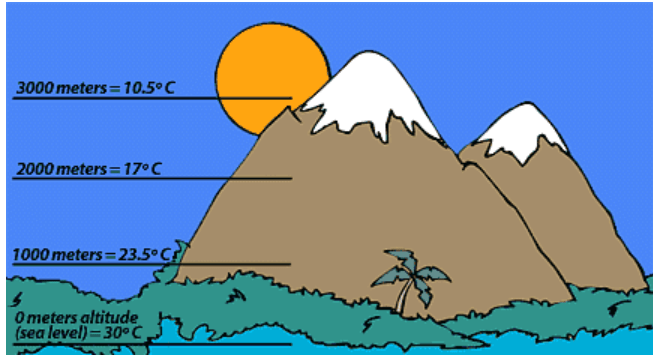 As height increases temperature decreases.
As height increases temperature decreases.
- The rivers of ice (glaciers) slowly move down the mountain slopes. As ice comes down to lower heights, where temperatures are higher, it melts forming rivers.
- River Ganga originates from the glacier Gangotri. When it is summertime in the plains, people move to hill stations to escape the heat.
- Ferozpur (Punjab) and Shimla (Himachal Pradesh) may have nearly the same latitude. Shimla (2000–2430 m above sea level) rarely has temperatures exceeding 25°C.
- Ferozpur, on the other hand, is very hot during the summer season. For every 165 meters above sea level, the temperature drops by 1°C. Now we have Rule II. The climate varies with altitude or the height above sea level.
3. Distance from the Sea
- Patna in Bihar is farther from the Equator as compared to Kolkata in West Bengal and yet Patna is hotter than Kolkata. The difference arises because Kolkata is situated near the sea. During the day time, the land gets heated more quickly than water. The air over the land surface becomes lighter and rises up creating a low-pressure zone.
- Breezes from the neighbouring sea blow to fill up the low-pressure zone on the coast. The moist sea breezes moderate the heat over the land surface.
Sea Breeze (Daytime)
- Land gets hot, air rises.
- Cool air comes from the sea to the land.
- Day → Sea to Land
Land Breeze (Nighttime)
- Sea is warmer, air rises.
- Cool air comes from the land to the sea.
- Night → Land to Sea
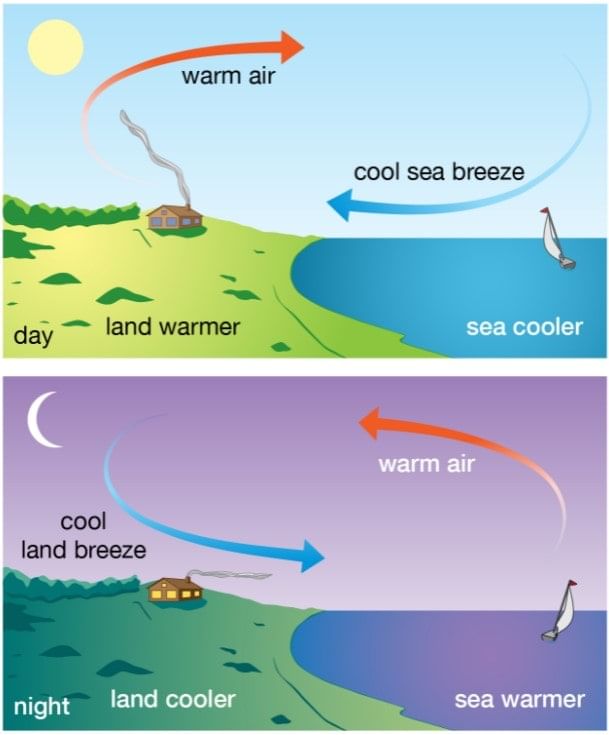 The sea has a moderating influence on the region close to it.
The sea has a moderating influence on the region close to it.
- The reverse happens at night. The movement of breezes from the sea during the day and from land to sea during night makes the climate moderate on the seashores. Places far off from the sea have extreme climates.
- For that reason, Patna is very hot during summers and cold during winters. The seaports are neither very hot during summers nor very cold during the winters. Rule III tells us that: distance from the Sea makes climate moderate or extreme.
4. The direction of the winds
- The climate of a location is affected by the direction of the wind and where it comes from.
- Winds that blow from the sea to the land carry a lot of moisture and cause rainfall.
- Most of the rain falls during summer, specifically in July and August, when winds come from the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
- In contrast, winter is typically dry because, during this season, winds move from the land to the sea.
- Winds that originate from cold areas lower the temperature, while winds from hot areas raise it.
- For instance, in northern India, there is a hot and dry wind called Loo that occurs in May and June.
- In extremely cold places, icy winds can blow, making the climate very cold.
5. Humidity
- Humidity is related to the amount of moisture in the air. It depends on the distance of the place from any large water body such as a lake, a river or a sea. It also depends on the wind direction.
- A place close to any large water body will have more moisture in the air hence the climate will be humid.
 Places that are humid receive a lot of rainfall.
Places that are humid receive a lot of rainfall.
- Winds carrying more moisture for any reason will make the place humid. Places getting rain in the Monsoon season are humid in that season.
6. Rainfall
- How much a place receives rainfall also affects its climate. Some places get rainfall almost all around the year and others may not get any rainfall at all. In both cases, climates are going to be different.

- The climate of a place is determined by some of the reasons stated above, working together to decide its climate.
- It is always interesting to look for the reasons which have determined the climate of a particular place or region.
|
33 videos|264 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Weather and Climate Class 5 Notes SST
| 1. What is the difference between weather and climate? |  |
| 2. How does the distance from the Equator affect the climate of a place? |  |
| 3. Why does height above sea level impact climate? |  |
| 4. How does being near the sea influence the climate of a location? |  |
| 5. What role does humidity play in determining climate? |  |

















