Our Rights and Duties Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is a Constitution? |

|
| Equality and Secularism |

|
| Fundamental Rights |

|
| Directive Principles |

|
Introduction
On August 15, 1947, India became independent from British rule after years of struggle. This day is celebrated as Independence Day every year. However, when India became free, it was divided into two countries:
- India and Pakistan.
- Pakistan was made from parts of India in the northwest and east.

Challenges after Independence
- Migration
- Many Hindus who lived in parts of what became Pakistan had to leave their homes and move to India. This is called migration.
- They had left behind their houses, lands, and belongings. The Indian government had the difficult task of helping them find new homes and jobs in India.
- New Rules for Free India
- After gaining freedom, India needed its own set of rules or laws. These laws would guide how the country should be run.
- The responsibility of writing these rules was given to the Constituent Assembly, a group of elected people.
Creating the Constitution of India
The Constituent Assembly worked for about three years to write the rules for the new country. The person in charge of writing these rules was Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, who was the Chairman of the Drafting Committee.
The Constitution (the set of rules) was ready and approved on November 26, 1949. It was put into action from January 26, 1950, and that’s why we celebrate Republic Day on this date every year.
 Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
What is a Constitution?
Every country has a set of rules that guides how the government runs the country. This set of rules is called a Constitution.
India also has its own Constitution, which is the longest-written Constitution in the world. It became active on 26 January 1950, and since then, India became a republic. That's why we celebrate Republic Day on this date every year.
What is a Democratic Government?
- Democracy means that the people of the country choose their leaders through voting.
- In India, all citizens above 18 years old have the right to vote and elect representatives. These representatives make the laws and rules for the country.

No Kings or Queens in India
- India is a Democratic country, which means there are no kings or queens ruling the country. In the past, some countries had kings and queens, and the title would pass from parent to child.
- In India, people have the power to choose who will govern the country. The government is made by the people and works for the welfare of everyone.
Equality and Secularism
India is a secular country, meaning people from all religions are treated equally.
The government does not favor any one religion and works for the welfare of all citizens, no matter their faith.
In some countries, like Pakistan, only a Muslim can become the President. This is not the case in India, where people of all religions have the same rights.
Three Important Features of India
India is described as:
- Democratic – The people of India choose their government.
- Socialist – The government works to reduce the gap between the rich and poor.
- Secular – People of all religions have equal rights and the government does not favor any one religion.
Directive Principles of State Policy
The Constitution gives future governments certain guidelines, called Directive Principles, to follow. These include:- Laws should be made to improve the living conditions of people.
- Education should be available to all children up to 14 years of age, and it should be free and compulsory.
- Special help should be given to Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, and weaker sections of society.
- Men and women should be paid equally for the same work.
Fundamental Rights
Our Constitution provides every citizen with some basic rights. These are called Fundamental Rights. They are important for the well-being of all citizens.
If any of these rights are taken away, a person can go to court to protect their rights. There are six Fundamental Rights that every citizen of India has:
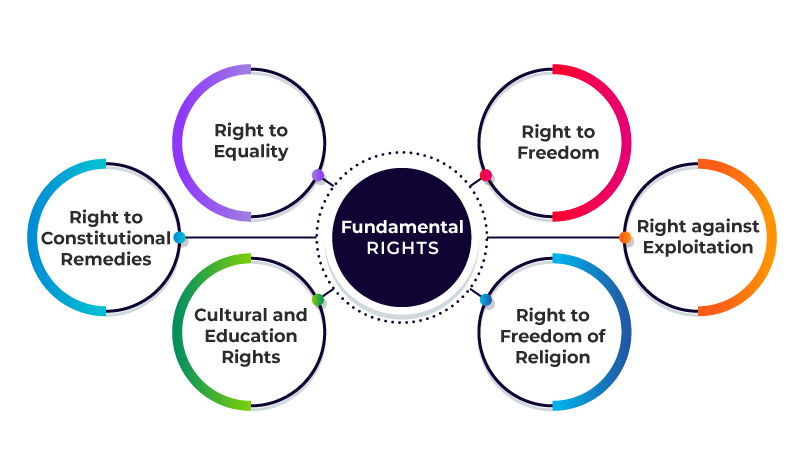
1. Right to Equality
- This means that everyone is equal before the law.
- No matter a person’s religion, caste, race, gender, or place of birth, everyone is treated equally.
2. Right to Freedom
This gives people several freedoms:- Freedom to speak freely.
- Freedom to choose any occupation (job).
- Freedom to live and travel anywhere in India.
3. Right Against Exploitation
- Exploitation means taking unfair advantage of someone to benefit from them.
- This right ensures that poor people are not forced to work without pay.
- It also does not allow children below 14 years to be employed.
4. Right to Freedom of Religion
- This right means that every person is free to follow any religion they choose.
5. Cultural and Educational Rights
- Some groups of people, called minorities, are fewer in number than others.
- This right allows these minorities to protect and preserve their culture and get an education in their own language or culture.
6. Right to Constitutional Remedies
- This right allows every person to go to court if any of their Fundamental Rights are denied.
7. Fundamental Duties
- Just like rights, we also have duties. These duties are things we must do for our country. These are called Fundamental Duties.
Some of the important Fundamental Duties are:
- We must respect the Constitution of India.
- We must show respect to the national flag and national anthem.
- We must take care of the environment and keep it clean.
- We should protect public property (things owned by the government, like parks and schools).
- We must preserve our cultural heritage, meaning we should value and protect the traditions and cultures of our country.
- Parents or guardians must send their children to school to ensure they get an education.
Directive Principles
Our Constitution also provides some guidelines for the government. These are called Directive Principles. These principles guide the government to work for the welfare of the people. Some important Directive Principles are:
- The government should make sure that people have proper living conditions, like enough food, water, and shelter.
- Every child should be able to go to school and get an education.
- Every person should receive proper treatment when they are sick, so that everyone stays healthy.
|
49 videos|177 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Our Rights and Duties Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What is the purpose of a Constitution? |  |
| 2. How does equality manifest in a Constitution? |  |
| 3. What are Fundamental Rights? |  |
| 4. What are Directive Principles of State Policy? |  |
| 5. How do rights and duties relate to each other in the Constitution? |  |















