Class 4 Maths - Introduction to Numbers - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
 Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) What is the place value of 5 in 1536?
(a) 5
(b) 50
(c) 500
(d) 5000
Ans: (c) 500
The place value of 5 is 500. (Hundred) Here are the values of each number:
Here are the values of each number: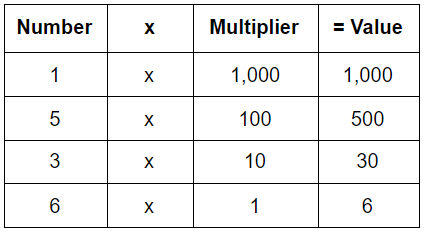
(ii) Which number comes first in ascending order?
7308, 7038, 7348, 7304
(a) 7308
(b) 7038
(c) 7348
(d) 7304 
Ans: (b) 7038
(iii) What is the short form of 8,00,000 + 2,000 + 30 + 6?
(a) 80,236
(b) 8,20,036
(c) 8,02,036
(d) 8,20,306
Ans: (c) 8,02,036
8,00,000 + 2,000 + 30 + 6 = 8,02,036
We start by adding the place values together:
- 8,00,000 (Lakhs place)
- 2,000 (Thousands place)
- 30 (Tens place)
- 6 (Ones place)
- When we put these values together in one number, we get 8,02,036.
(iv) Which is the largest number in this group? 7,20,163; 7,20,136; 7,02,163; 7,02,613
(a) 7,20,136
(b) 7,02,613
(c) 7,02,163
(d) 7,20,163
Ans: (d) 7,20,163
(v) Which is the smallest 4-digit number amongst the following?
(a) 1303
(b) 1234
(c) 0132
(d) 0142
Ans: (b) 1234
Q2: True or False
(i) The place value of 4 in 3,49,026 is 4,000.
Ans: False
(ii) In the number 8036, 3 is in the hundreds place.
Ans: False
(iii) The number 1,25,471 is smaller than 61,832.
Ans: False
(iv) The smallest whole number is 0.
Ans: True
(v) 7,36,000 is the predecessor of 7,35,999.
Ans: False
Q3: Fill in the Blanks
(i) In 1042, 2 is at the _____ place.
Ans: Ones
(ii) The place value of 6 in 6,00,087 is _____.
Ans: 6,00,000 (Lakhs)
(iii) The first six multiples of 4 are ____, ____, ____, ____, ____, and ____.
Ans: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24
(iv) Arrange the numbers 62,917; 1,00,008; 45,132; 36,472 in descending order:
Ans: 1,00,008; 62,917; 45,132; 36,472
(v) The predecessor of the smallest 6-digit number is ____.
Ans: 99,999
Q4: Answer the Following Questions
(i) Write the place value of 2 in 7,52,693.
Ans: 2,000 (Thousands)
(ii) Which is greater: 3,69,501 or 3,69,510?
Ans: 3,69,510
(iii) Write the short form of: 9,00,000 + 4,000 + 200.
Ans: 9,04,200
(iv) Arrange the numbers 4526, 4256, 4569, 4325 in ascending order.
Ans: 4256, 4325, 4526, 4569
(v) Write the number name for 4,65,009.
Ans: Four lakh sixty-five thousand and nine
Q5: Find the place-value of 6 in each of the following numbers:
(a) 19,356
Ans: The place value of 6 is 6 (ones)
(b) 6,00,087
Ans: The place value of 6 is 600000 (lakhs)
Q6: Write the number names for each of the following numbers:
(a) 2,50,006
Ans: Two lakh fifty thousand and six.
(b) 4,65,009
Ans: Four lakh sixty five thousand and nine.
|
33 videos|168 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Class 4 Maths - Introduction to Numbers - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
| 1. What is numeration and why is it important in mathematics? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of numeration systems used in mathematics? |  |
| 3. How do you convert numbers from one numeration system to another? |  |
| 4. What are place values and how do they work in different numeration systems? |  |
| 5. How can I practice and improve my numeration skills effectively? |  |






















