Surface Tension, Viscosity & Applications | Physical Chemistry PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Viscosity and Surface Tension |

|
| What is Surface Tension? |

|
| What is Viscosity? |

|
| Viscosity Measurement |

|
Viscosity and Surface Tension
Viscosity and surface tension, are dependent on molecular interactions.
- However, viscosity results due to collaboration among molecules of the identical molecules located in the same material (in case of fluids).
- Whereas surface tension is determined by the difference of interactions between the molecules of the material (fluid) with the molecules of the material in contact.
What is Surface Tension?
Surface tension is the amount of energy required to increase the surface of the liquid by unit area.
- In other words, it is also the property of the liquid surface that resists force. Intuitively, it keeps a barrier between foreign materials and liquid as well as this is the force that holds the liquid molecules bind together.

For example, if we add soap to the water, it is surface tension decreases, thereby the liquid with soap easily mixes with dirt on hand and thus cleans it. It is also the property of the liquid surface that resists force.
- Intuitively, it keeps a barrier between foreign materials and the liquid. This is the force that holds the liquid molecules bonded together.
- If we add soap to the water, it is surface tension decreases, thereby the liquid with soap easily mixes with dirt on hand and thus cleans it.
- Surface tension is sometimes seen in terms of energy. That is more is the surface tension, more is the energy, and thus to minimize energy the fluids assume the shape with the smallest surface area.
- This is the reason behind the water droplets being spherical. A sphere has a minimal surface area, for a given volume.
What is Viscosity?
An important rheological measurement that is closely related to the resistance to flow is called viscosity.
Viscosity is the resistance of a fluid to flow.
- For example, oil has a high viscosity, but when we put it in the car and heat it up, it becomes less viscous and thus flows smoothly through an engine and other parts of the car. Higher the viscosity, slow will be the liquid flow. Viscosity decreases with increase in temperature, with some exceptions.
- Viscosity is sometimes also understood as frictional forces that act in between fluid and the surface of contact. The surface can either be a solid surface like a pipe and water can be the fluid. Now the resistance provided by the pipe to the water flow is viscosity. However, viscosity can also arise in between two fluids flowing at different velocities.
The above phenomenon of viscosity is very much particular to liquid, to be precise Newtonian fluids. However, in the case of non-Newtonian fluids, the interactions are quite bizarre and are always hard to model and understand.
Viscosity Measurement
The viscosity is calculated in terms of the coefficient of viscosity.
It is constant for a liquid and depends on its liquid’s nature. The Poiseuille’s method is formally used to estimate the coefficient of viscosity, in which the liquid flows through a tube at the different level of pressures.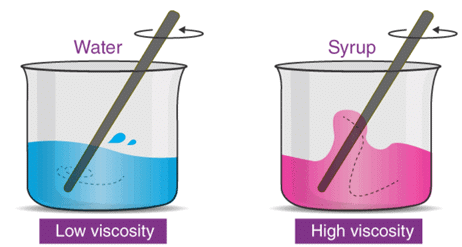
- The coefficient of viscosity of fluids will be decreased as the temperature increases, while it is inverse in the case of gases. While the coefficient of viscosity of gases will increase with the increase in temperature.
- The increase in temperature for the fluid deliberate the bonds between molecules. These bonds are directly associated with the viscosity and finally, the coefficient is decreased.
- An important question most people do not ask is, why even measure Viscosity? The main reason behind this being, that viscosity data on a material gives manufacturers a chance to predict how the material will react and behave when consumers interact with it.
- The most simplistic formula for measuring viscosity is:
Viscosity = shear stress/shear rate
The Coefficient of Viscosity Formula
The force of friction between two layers of fluid having the area in square centimeter and separated by distance will have a velocity is given by: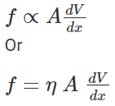
Here,
η is coefficient of viscosity
dV/dx is velocity gradient
Viscosity Examples
If dx is 1cm, A is 1cm2 and dv is 1cm/s
Then, f = η
- The coefficient of viscosity is defined as the force of friction that is required to maintain a difference of velocity of 1cm/s between parallel layers of fluid. The unit is usually expressed in poise or centipoise.
- As we all know that viscosity is nothing but the measure of a substance’s resistance to the motion under an applied force The resulting unit is measured in centipoise which is the equivalent of 1 mPa (MilliPascal second)
- The major industries where Viscosity measurements are used are in the food industry to improve the overall cost-effectiveness and maximizing production efficiency. Besides, the food industry Viscosity is also primarily used in other industries such as Adhesives, Petroleum, Concrete, and Cosmetics industry.
|
90 videos|144 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Surface Tension, Viscosity & Applications - Physical Chemistry
| 1. What is surface tension? |  |
| 2. What factors affect surface tension? |  |
| 3. How is surface tension measured? |  |
| 4. What is viscosity? |  |
| 5. How is viscosity measured? |  |




















