Best Study Material for NEET Exam
NEET Exam > NEET Notes > Wave Optics
Wave Optics - NEET PDF Download
FAQs on Wave Optics - NEET
| 1. What is wave optics? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between wave optics and geometric optics? |  |
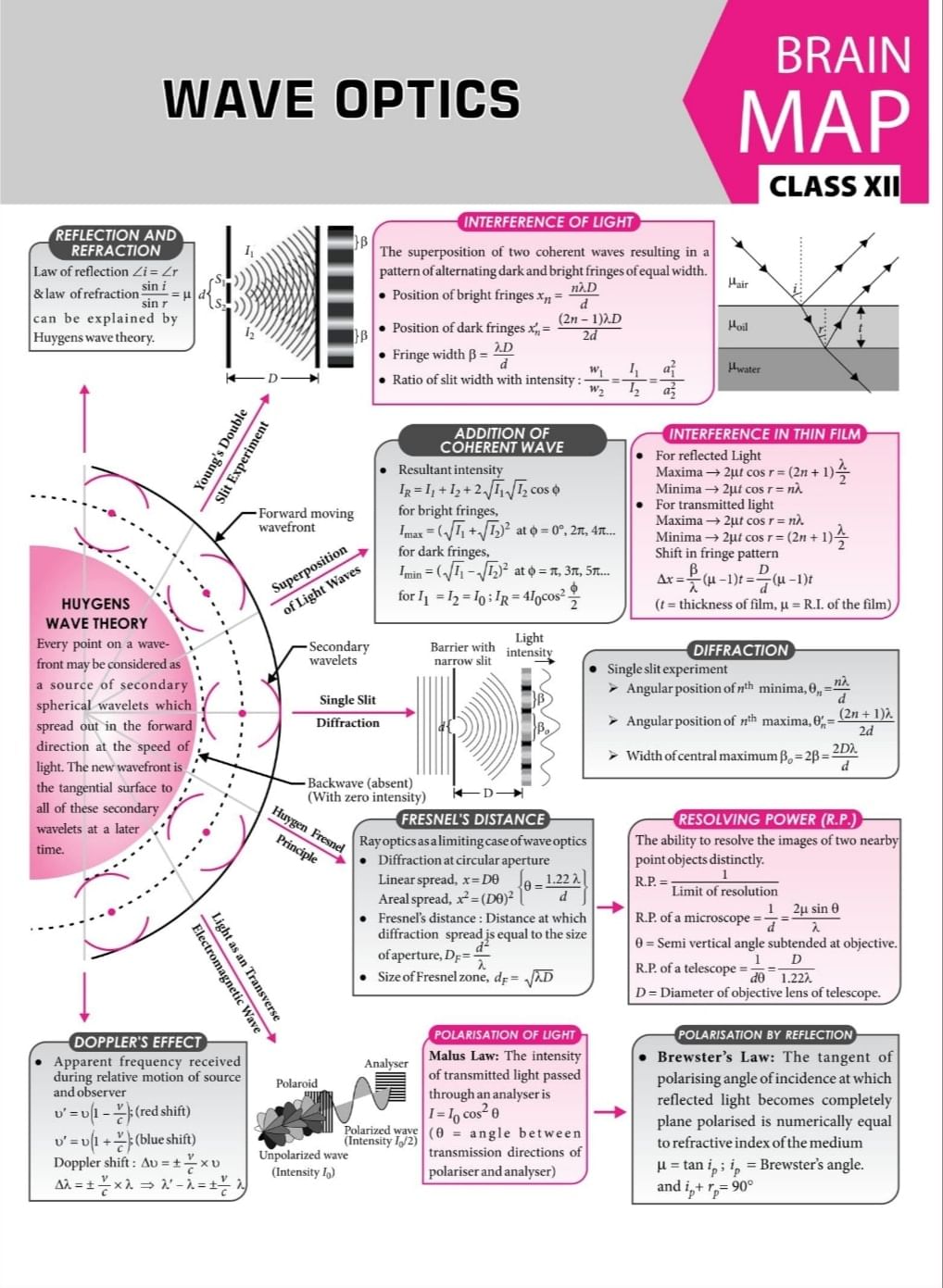
Ans. Wave optics and geometric optics are two different approaches to understanding the behavior of light. Geometric optics focuses on the path of light rays and uses the laws of reflection and refraction to determine how light interacts with surfaces and lenses. On the other hand, wave optics treats light as a wave and explains its behavior through concepts such as diffraction and interference.
| 3. How does diffraction occur in wave optics? |  |
Ans. Diffraction is a phenomenon that occurs when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit that is comparable in size to its wavelength. In wave optics, diffraction is explained as the bending or spreading out of light waves as they pass through small openings or around obstacles. This bending of waves leads to the characteristic patterns of bright and dark regions, known as diffraction patterns.
| 4. What is interference in wave optics? |  |
Ans. Interference is the phenomenon that occurs when two or more light waves superpose or combine with each other. In wave optics, interference is explained as the constructive or destructive interference of light waves. Constructive interference occurs when the peaks of two waves align, resulting in a brighter region. Destructive interference occurs when the peaks of one wave align with the troughs of another wave, resulting in a darker region.
| 5. How is polarization explained in wave optics? |  |
Ans. Polarization refers to the orientation of the electric field vector of a light wave. In wave optics, polarization is explained as the alignment of the electric field vectors of individual light waves. Light waves can be linearly polarized, where the electric field oscillates in a single plane, or they can be circularly polarized, where the electric field vector rotates in a circular motion. Polarization plays a crucial role in various optical phenomena and applications such as 3D movie technology and polarized sunglasses.
Download as PDF
Related Searches