Class 4 Science - Food Our Basic Need - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs).
(i) Which of these are energy-giving nutrients?
 (a) Vitamins and minerals
(a) Vitamins and minerals
(b) Carbohydrates and fats
(c) Proteins and fats
(d) Vitamins and carbohydrates
Ans: (b)
The nutrients that provide energy are commonly referred to as macronutrients (carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins). Carbohydrates and proteins provide a similar amount of energy per gram of food.
(ii) Which of these nutrients is very important but required only in very small quantities?
(a) Proteins
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) Water
(d) Fats
Ans: (d)
Fats are essential for health but are needed in smaller amounts compared to carbohydrates and proteins.
(iii) Which of the following is not good for our body?
(a) Junk food
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) Proteins
(d) Balanced diet
Ans: (a)
Junk food is unhealthy and can lead to various health issues.
(iv) Which nutrient helps your body make new cells for growth?
(a) Proteins
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) Vitamins
(d) Fats
Ans: (a)
Proteins give your body amino acids — the building blocks that help your body's cells do all of their everyday activities. Proteins help your body build new cells, repair old cells, create hormones and enzymes, and keep your immune system healthy.
(v) Which of these are known as protective foods? (a) Vitamins
(a) Vitamins
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) Proteins
(d) Fats
Ans: (a)
Foods that are rich in minerals and vitamins are referred to as protective foods. Foods such as leafy or yellow vegetables, meat, citrus fruits, egg, milk, which contain sufficient quantities of vitamins, minerals and high-quality proteins that protect against the occurrence of a disease of deficiency.
(vi) Which of the following in a way to preserve food?
(a) Canning
(b) Frying
(c) Pickling
(d) Baking
Ans: (a)
Among the oldest methods of preservation are drying, refrigeration, and fermentation. Modern methods include canning, pasteurization, freezing, irradiation, and the addition of chemicals. Advances in packaging materials have played an important role in modern food preservation.
Q2: True or False.
(i) The fibre or roughage in our diet is not digested and does not provide nourishment.
Ans: True
Fiber, also known as roughage or bulk, is the part of plant foods that our bodies do not break down during digestion. Since fiber isn't digested, it doesn't provide calories, although it may be present in foods with other carbohydrates.
(ii) Water is essential for all bodily functions and for life.
Ans: True
Water plays vital roles in the body, including regulating body temperature, moistening tissues, protecting organs, and transporting nutrients and oxygen to cells.
(iii) Vitamin D is essential to build strong bones and teeth.
Ans: True
Vitamin D is crucial for strong bones and muscles because it aids in the absorption of calcium, which is vital for bone health. A deficiency can lead to conditions such as rickets in children.
(iv) Water also helps in digestion, and the elimination of waste.
Ans: True
Water is essential for dissolving waste products generated from food breakdown and metabolism, allowing them to be excreted from the body through urine and sweat.
(v) Food in submerged in oil in boiling.
Ans: False
Food is typically submerged in boiling water, not oil, during cooking processes such as boiling.

Q3: Fill in the blanks.
(i) The food that keeps the body warm ______
Ans: Fats also provide energy for the body. They act as reserve of energy when carbohydrates are not available. It helps to keep body warm. Food rich in fats include oil, butter, nuts, coconut, ghee, cheese, cream etc.
(ii) This makes up more than half of our body weight ______
Ans: Water constitutes a significant portion of the human body, contributing to various physiological functions.
(iii) Component of food that helps to get rid of undigested food ______
Ans: Dietary fibres are also known as roughage, and roughage is mainly provided by plant products. It does not provide nutrients, but it is an essential component of our food and adds to its bulk. It also helps our body get rid of undigested food.
(iv) Food adversely affects kidney, liver and other vital organs. ______
Ans: A kidney-friendly diet limits those foods that contain large amounts of saturated fat, protein and certain minerals, including sodium, potassium and phosphorus.
(v) Diet that has all the necessary nutrients ______
Ans: A balanced diet is a diet that contains differing kinds of foods in certain quantities and proportions so that the requirement for calories, proteins, minerals, vitamins and alternative nutrients is adequate and a small provision is reserved for additional nutrients to endure the short length of leanness.
Q4: Match the following.
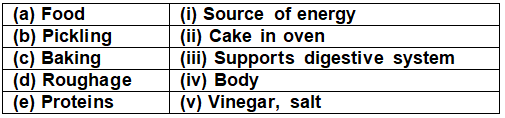
Ans: (a) Food - source of energy
(b) Pickling - Salt, vinegar
(c) Baking - Cake in oven
(d) Roughage - supports digestive system
(e) Proteins - Body building food
Q5: Which nutrient am I?
(i) I help you to grow and repair damaged parts of your body.
Ans: Proteins
Protein is the major structural component of cells and is responsible for the building and repair of body tissues. Protein is broken down into amino acids, which are building blocks of protein.
(ii) I keep you warm.
Ans: Fats
Fats also provide energy for the body. They act as reserve of energy when carbohydrates are not available. It helps to keep body warm. Food rich in fats include oil, butter, nuts, coconut, ghee, cheese, cream etc.
(iii) I help in the smooth excretion of waste from the body.
Ans: Fibre
Since we do not digest it, the fiber in food passes into the intestine and absorbs water. The undigested fiber creates "bulk" so the muscles in the intestine can push waste out of the body.
(iv) If you need quick energy, I am the one you need.
Ans: Carbohydrates
Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains, are a great source of sustained energy.
(v) My name starts with V and cure some diseases.
Ans: Vitamins
Vitamins help in curing some diseases.
(vi) I am not a nutrient but I make up more than half of your body weight.
Ans: Water
Water makes up more than half of your body weight.
Q6: Answer the following questions in brief.
(i) Why do we need food?
Ans: Food is essential for our body to develop, replace and repair itself. Food provides us energy to work and play. It protects us from diseases and help to recover fast from illness.
(ii) How does it help to include sufficient roughage in the diet?
Ans: Roughage has numerous health benefits. It helps improve digestion and promotes gut health. It may also improve certain risk factors for heart disease and help you manage your weight and blood sugar.
(iii) How is freezing different than the drying in preserving food?
Ans: Freezing delays spoilage and keeps foods safe by preventing microorganisms from growing and by slowing down the enzyme activity that causes food to spoil. As the water in the food freezes into ice crystals, it becomes unavailable to those microorganisms that need it for growth.
(iv) What is the difference between energy provided by carbohydrates and fats?
Ans: The body uses three main nutrients to function— carbohydrate, protein, and fat. These nutrients are digested into simpler compounds. Carbohydrates are used for energy (glucose). Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids.
(v) What makes a balanced diet?
Ans: A balanced diet is made up of foods from the five food groups: starchy carbohydrates, fruits and vegetables, protein, dairy and healthy fats. Each provides the range of vitamins and minerals our bodies need to function efficiently.
Q7: Answer the following questions in detail.
(i) What are the precautions we should take while cooking food?
Ans: We must take certain precautions while cooking food to prevent the growth of bacteria. The way we cook our food is as important as the way we prepare and store it. To avoid food poisoning, it is essential to prevent cross-contamination from raw to cooked foods, which can occur through hands or utensils.
(ii) What are the different nutrients we get from food? Mention their functions and sources.
Ans: Nutrients are substances found in food that drive biological activity and are essential for the human body. They are categorised into several groups, including proteins, fats, carbohydrates (which include sugars and dietary fibre), vitamins, and minerals. Each type of nutrient performs vital functions:
- Building all parts of the body, such as muscles, bones, teeth, and blood.
- Producing energy for power and heat.
- Maintaining the body in good working order.
|
49 videos|156 docs|34 tests
|
FAQs on Class 4 Science - Food Our Basic Need - CBSE Worksheets Solutions - 1
| 1. What are the main nutrients that our body needs from food? |  |
| 2. How does our body utilize the energy obtained from food? |  |
| 3. What are the consequences of not having a balanced diet? |  |
| 4. How can we ensure that we are consuming a balanced diet? |  |
| 5. Is it necessary to drink a certain amount of water every day? |  |





















