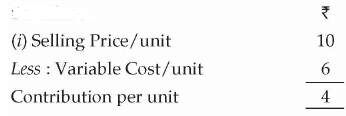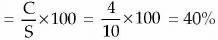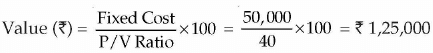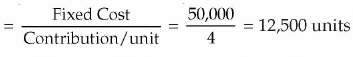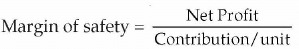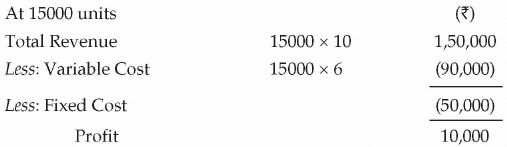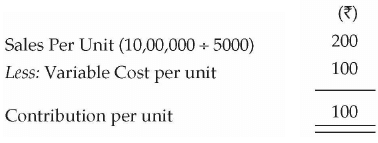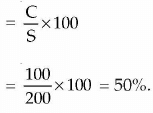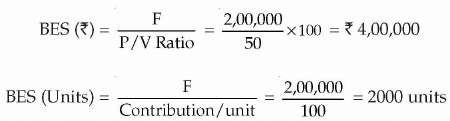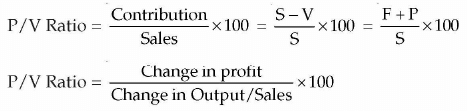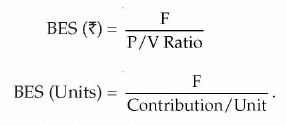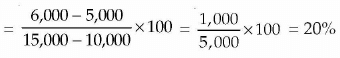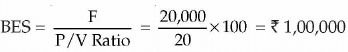Business Arithmetic: Notes | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Importance of Business Arithmetic
Business Arithmetic will help the entrepreneur to do a careful analysis of various options available to him or her for business strategy.
- In the previous chapters, we studied various topics like a business plan, growth strategy, marketing, etc.
- All these analysis require some mathematical tools and formulae to be used.
- In this chapter, some of the concepts to understand their application are discussed.
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis (CVP) Analysis
Managerial accounting methods provide techniques for evaluating the viability and ability to grow or "scale" a business. These techniques are called cost-volume-profit analysis (CVP).
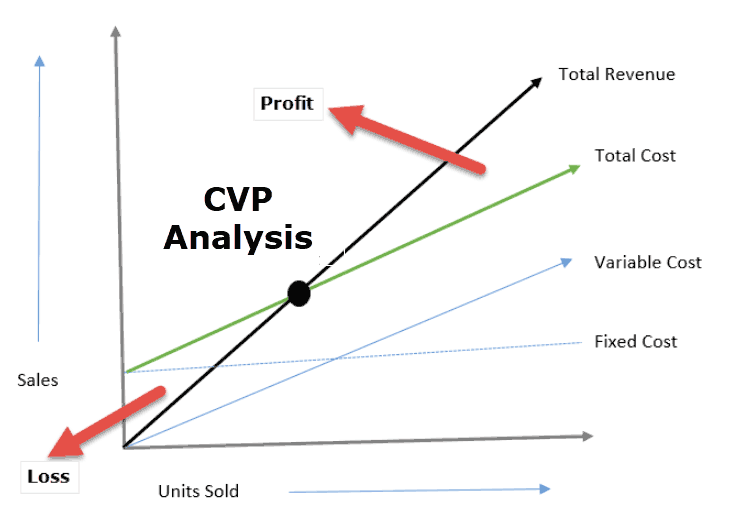
- An entrepreneur should be aware of certain concepts of cost and revenue to analyze the number of products to be produced to ensure that the desirable profitability is achieved.
- This is part of managerial accounting which helps in taking effective decisions.
- CVP means developing an understanding of the nature and behavior of an entity's costs.
- In order to understand how a business is going to perform over time and with shifts in volume, it is imperative to first consider the cost structure of the business.
- This requires a detailed study of specific types of costs that are to be incurred and trying to understand their unique characteristics. Break-even analysis is one of the tools of CVP analysis.
Break-Even Analysis
In today's complex business world, bringing a balance amongst variables like revenue, cost, profit, etc. is a tedious task. Managerial economists use various tools to analyze these variables.
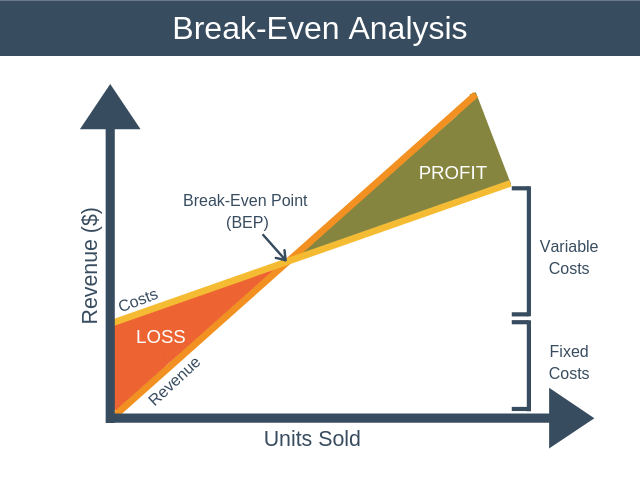
- Break-Even Analysis is one of the most efficient tools to analyze revenue, cost, and profit variables and bring a balance between them.
- Break-Even Analysis seeks to analyze Break-Even Point (BEP) which is the point of equality between sales and cost. In other words, BEP indicates no profit no loss situation for a firm.
- The importance of the break-even point lies in the fact that it sets up bottom-line sales for managers below which the firm would be incurring losses. It is an efficient technique of managing sales and costs.
- Break-even analysis may be defined as the analysis of cost elements like fixed cost and variable cost and their impact on a firm's sales and profits. It is also termed as cost volume profit (CVP) analysis.
- Under break-even point analysis, the total cost is segregated between fixed and variable costs.
- Fixed Cost
It is the cost element that is not affected by changes in the level of production like Rent, Salary of employees, etc. - Variable Cost
It is the cost element that changes with the change in the level of production like raw material, labour, etc. - Sales
Sales = Total Cost + Profit
Sales = Fixed Cost + Variable Cost + Profit
Sales - Variable Cost = Fixed Cost + Profit
i.e. S - V = F + P
Total Contribution = S - V = F + P. - Total contribution indicates the excess of sales over variable cost or the sum total of fixed cost and profit.
- Contribution Ratio, C/S Ratio, or P/V Ratio
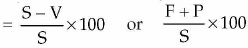
Break-Even Point
Total Cost = Total Sales
⇒ E + V = S ⇒ S - V = F
⇒ (S - V)/S = F/S [Dividing b y sales i.e., " S " l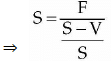

Break-Even sales in value or Rupees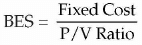
Break-Even Sales in units
The margin of safety in value (₹) = Actual Sales (₹) - BES (₹))
Margin of safety in units = Actual Sales (units) - BES (units)
- The margin of safety indicates an excess of actual sales over break-even sales.
- It helps managers to analyze how safe the business is positioned from incurring losses.
- A higher margin of safety indicates a strong business position in terms of sales and cost. On the other hand, a lower margin of safety indicates a weak business position in terms of cost and sales.
Some Solved Examples
Example 1: The following information is extracted from the records of ABC Ltd.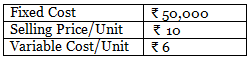
You are required to determine
(i) P/V Ratio
(ii) Break-Even Point in terms of value (₹)
(iii) Break-Even Point in terms of units
(iv) Margin of safety when Actual Sales are 15,000 units.
(v) Prepare a Break-Even Chart.
Contribution Ratio or P / V Ratio
(ii) Break even Point in terms of(iii) Break Even Point in terms of units
(iv) Margin of safety
= Actual Sales - Break Even Sales
= 15000 - 12,500 = ₹ 2,500 units
or
(v) Break Even ChartIn the above diagram, fixed cost is indicated by horizontal line FC parallel to x-axis. Total Revenue curve is shown by 45° line from the origin. Total cost curve is drawn by Joining Total Revenue at 12,500 units (point L) and point P at Y-axis.
Example 2: From the following information of ABC Plastics Ltd., calculate Break-Even Sales terms of value and volume.
Contribution Ratio or P / V Ratio
Formulae to Remember for Break Even Analysis
- Contribution = Sales - Variable Cost
Contribution = Fixed Cost + Profit- Margin of Safety = Actual Sales - BES
Example 3: Calculate P/V Ratio, BES, and Margin of Safety from the following information: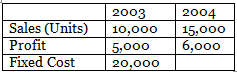
Assumptions: Underlying Break-Even Analysis
(i) The analysis is applicable to short-term decision-making.
(ii) In the short run the costs can be classified into fixed and variable,
(iii) There is no change in sales per unit and variable cost per unit.
(iv) All the goods produced are sold.
Importance or Use of Cash Flow Projections
Cash flow projection indicates the cash inflow and outflow estimates for a particular period.
- An entrepreneur should always have visibility for the cash position of the business venture. It enables a better working capital planning of the business.
- If a business runs out of cash and is not able to obtain new finance, it will become insolvent. It is no excuse for management to claim that they didn't see a cash flow crisis coming.
- So in business, "cash is king". Cash flow is the life-blood of all businesses - particularly start-ups and small enterprises.
- As a result, it is essential that management forecast (predict) what is going to happen to cash flow to make sure the business has enough to survive.
The following are the importance of cash flow projection:
- Cash flow projection helps in identifying potential shortfalls in cash balances in advance. It acts as an "early warning system". This is a very important reason to have a cash flow projection.
- It ensures that the entrepreneur can afford to pay suppliers and employees. Suppliers who don't get paid will soon stop supplying the business; it is even worse if employees are not paid on time.
- It helps to spot problems with customer payments. It also encourages the business to look at how quickly customers are paying their debts.
- External stakeholders such as banks may require a regular forecast. Certainly if the business has a bank loan, the bank will want to look at cash flow forecasts at regular intervals.
Budgeting and Managing the Finances
Another important exercise for an entrepreneur is to prepare a budget for future years and managing the company finances accordingly.
The process of preparing budgets is as follows:
- Revenue Projection: Revenue projection will be based on the projected quantity to be sold and the price of the product in the next years. The estimated revenue is derived by multiplying the quantity sold with a price.
- Expense Projection: Expense estimate will be based on the future operational plan of the business and the resources required for the period. Each department should estimate its expense and get it approved before it is compiled in the final budget.
- Compilation of Income Statement: Once a future estimate of the revenue and expense is finalized then it is compiled in the income statement to show the estimated profitability of the business. Profitability will be determined by deducting expenses from the revenue.
- Compilation of Balance Sheet and Cash Flow: The balance sheet is prepared on the basis of capital expenditure projected for the future years and debtors and creditors projection. Similarly, a cash flow statement is prepared for estimating the cash requirements.
Budgeting involves the preparation of a budget and analysis of variances with the actual performance of the business. An entrepreneur should also arrange the funds for the future period to ensure that the finances are available when the requirement arises. We can see the format of the budget as below: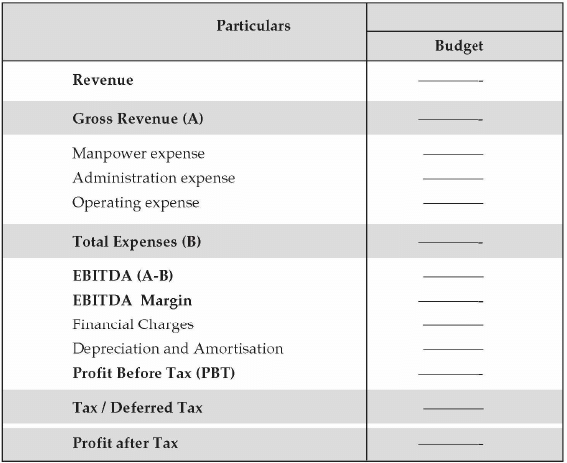
Computation of Working Capital
Working capital is the difference between current assets and current liabilities. It measures the liquidity or cash availability for day to day business operations.
- Current assets refer to cash or the assets which can be converted into cash in the next 12 months like debtors, bills receivable, short-term investment, inventory, prepaid expense, etc.
- Similarly, current liabilities refer to the obligations for payment to vendors or other parties in the next 12 months like creditors, bills payable.
Inventory Control and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
Inventory control is an important aspect of the production planning process. The key decision to inventory control is how much stock one should hold to bring a balance between the demand and investment cost in such stock levels. In other words, inventory control is concerned with minimizing the total cost of inventory. There are three factors that affect the inventory control decision:
- The cost of holding the stock: The interest cost of the money invested in holding stock.
- The cost of placing an order: This involves postage cost, tendering cost etc.
- The cost of shortage: looking for alternative arrangements if there is shortage of stock in the factory.
There are different levels of stock that can be maintained depending on the size of the business and the level of demand of the product in the market. Broadly there are three levels of inventory.
Reorder Level
The reorder level is the inventory level at which an entity should issue a purchase order to replenish the quantity on hand. When calculated correctly, the reorder level should result in replenishment inventory arriving just as the existing inventory quantity has declined to zero.
The formula for reorder level is Maximum Consumption x Maximum Reorder Period For example, maximum consumption 1,000 units per week, Delivery time 8-10 weeks.
Reorder level = 1,000 x 10 = 10,000 units.
Minimum Level
- The minimum level of inventory is that level that is needful for continuing of production without any disturbance.
- With simple mathematical formula, we can calculate this level. Always this stock should be in the store or factory.
- When the inventory will go to the minimum level, the production or store department should send the notice of inventory requirement to the purchase department.
- Minimum Level = Reorder Level - (Normal Consumption x Normal Reorder Period)
For example, maximum consumption 1,000 units per week, normal consumption 750 units per week, minimum consumption 500 units per week. Delivery time 8-10 weeks. Reorder level 10,000 units. - Minimum Level = 10,000 - (750 x 9) = 3250 Units
- We have a minimum level of 3,250 units which means, when there are only 3,250 units in our stock, we should issue the purchase order or manage for getting stock at the earliest, otherwise production will stop and our machine and labor and other invested capital will be free.
- So, our fixed cost will increase.
Maximum Level
- The maximum level of inventory is the maximum quantity of material which have to keep in store.
- We should not keep the stock more than the maximum level because if we keep more stock than the maximum level it will increase the cost of capital because we do not need the stock more than maximum level.
- Excess stock than maximum level will increase the cost of storing.
Maximum Level = Reorder Level + Economic Order Quantity - (Minimum rate of usage x Minimum lead time) - For example, maximum consumption 1,000 units per week, normal consumption 750 units per week, minimum consumption 500 units per week.
- Delivery time 8-10 weeks. Reorder level 10,000 units, Economic Order Quantity 7,500 Units.
Maximum Level = 10,000 + 7,500 - (500 x 8) 13,500 Units
Economic Order Quantity
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) is a simple inventory management model to determine the point at which the combination of inventory order costs and inventory carrying costs are the least. In other words, EOQ represents the balance between the inventory ordering cost and inventory carrying cost. It indicates the most cost-effective quantity to order. EOQ is beneficial when you have repetitive purchasing of an item.
The formula for EOQ is as Follows:
Where U stands for annual consumption
P stands for cost of placing an order
C S stands for the cost of storing one unit for one year.
- Annual Usage: This is expressed in units and based on prior-year unit sales or forecasted unit sales or a combination of both.
- Order Cost: This is the sum of the costs that are incurred each time an item is ordered. These costs are associated with
(i) Physical activities are required to process the order as well as the costs charged to ship and receive the stock.
(ii) Cost to enter the purchase order, cost to communicate with the vendor, the cost to process the receipt, incoming inspection, invoice processing and vendor payment, inbound freight, and insurance associated with the shipment. - Carrying Cost: Carrying costs are the variable costs per unit of holding an item in inventory. Below are the primary components of carrying cost.
(a) Interest: If an inventory is built upon the basis of borrowed money then the interest accumulated on that borrowed money will form part of the carrying cost.
(b) Insurance: Insurance costs are directly related to the total value of the inventory. Hence, it should be included as part of the carrying cost.
(c) Storage Costs: Storage costs should only include costs that are variable based upon inventory levels.
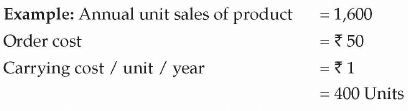
This means that if the sales do not fluctuate then one should order 400 units every quarter to keep the ordering and carrying cost at a minimum level.
Return On Investment (ROI) and Return One Quity (ROE)
- Return on investment and return on equity are two important measures of the profitability performance of the firm.
- An entrepreneur should calculate and analyze these two ratios to assess the profitability of the business.
- Return on Investment (ROI) is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency of an investment or to compare the efficiency of a number of different investments.
- Return on Equity (ROE) is the amount of net income returned as a percentage of shareholder's equity.
- Return on equity measures a corporation's profitability by revealing how much profit a company generates with the money shareholders have invested.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What is a budgeting process?
- Budgeting is a collective process for preparing and estimating budgets.
- The operating units estimate their budgets as per the projected sales, costs and expenses.
- The budget of each operating unit is provided to the upper management for reviewing
- Keeping in mind the overall goals, upper management makes necessary changes in the budgets
- Finally, the approved budget is the road map for the following year or for specific time
- After the implementation of budget, the performance is measured and then compared with actual standards to find out deviations and take corrective action, if necessary.
Q.2. What is a budget? What are the essentials of a budget?
- A budget is a financial and/or quantitative statements, prepared prior to a defined period of time of the policy to be pursued during the period for the purpose of attaining a given objective.
- It is prepared in advance and is future based. Information is expressed in monetary terms and it also states the physical units.
- Essential of budget are:
To know and control the resources of the enterprise.
To communicate plans to various stakeholders
Give the managers a target to achieve
Evaluate the performance of the company and managers and fix responsibility and accountability of people
Q.3. What is financial management? What is the main objective of financial management?
- Financial management is concerned with optimal procurement as well as the usage of finance.
- Financial Management involves the following activities:
Identification of sources of finance
Comparison of the sources vis-à-vis cost & associated risks
Investment of the finance procured in most profitable avenues- Objectives of financial management:
The primary objective of Financial Management is Maximisation of Shareholder’s Wealth
This can be done by keeping a regular and adequate supply of funds to the concerned.- Assuring adequate returns to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Optimum utilization of funds.
- Forming a capital structure to maintain debt and equity.
Q.4. There is a Budget to suit every business and its need. Elucidate.
There are the following types of budget:
a. Sales budget: It provides an estimate of sales in the future. It reflects both units and rupees and is used to create target sales to be achieved during a specific period.
b. Production budget: It gives a projection of the number of units that should be manufactured for the target sales. This also estimates different costs involved in the manufacturing of these units.
c. Capital budget: It evaluates whether a long-term investment in the new machinery, research and development projects, and other long-term assets are worth or not.
d. Cash budget: It estimates cash receipts and expenditures for a particular time period and analyses whether income will be sufficient to cover expenses. it also determines the quantum of finance that will be required from other sources.
e. Marketing budget: It provides an estimate of the funds required for promotion, advertisement, and public relations for increasing the market share
f. Project budget: It is the task-wise budget of a project that incorporates the costs related to and accruing to a specific project. Different task budgets are consolidated to prepare the project budget.
g. Operational budget: It is a budget that is used to forecast annual revenues and expenses for a business.
|
19 videos|70 docs|12 tests
|
FAQs on Business Arithmetic: Notes - Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the importance of business arithmetic? |  |
| 2. How does cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis help businesses? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of cash flow projections in financial management? |  |
| 4. How does budgeting help in managing finances? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of inventory control and economic order quantity (EOQ) in business operations? |  |