NCERT Solution- Resource Mobilization- 1 | Entrepreneurship Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Section A - Finance
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What do you understand by finance?
‘Finance’ refers to funds or monetary resources needed by individuals, business houses and the government.
Question 2. Give the significance of finance in an enterprise.
The significance of finance in enterprise is elucidated like a lubricant to the process of production.
Question 3. Name the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
Finance is the most important prerequisite to start an enterprise.
Question 4. State the most important factors for the survival of any business enterprise.
Financing, ‘production’, ‘marketing’ are deemed to be the most important factors for any business survival. Financing is considered to be the first because nothing can be done without money.
Question 5. State how sources can broadly be classified into two major categories.
We know that these sources could broadly be classified into two major categories:
- Internal sources
- External sources
Question 6. What do you understand by internal sources of finance?
Internal sources of finance is referred to as owner’s own money. It is also known as owner’s equity. Particularly in the case of small entrepreneurs the owner’s money is very small.
Question 7. How will you differentiate between financial market with other market? Give one difference.
Financial market is a market in which people and entities can trade financial securities (stocks and bonds), commodities (including precious metals or agricultural goods), and others like crude oil etc. at prices that reflect supply and demand. Market refers to the aggregate of possible buyers and sellers of a certain good or service and the transactions between them.
Question 8. ‘Production’, ‘Marketing’, and Financing’ – deemed as the most important factors for any business’s survival rates. Among these name the most critical element and why?
Production, marketing, and financing, deemed to be the most important factors for any business survival. ‘ Financing’ is considered to be the first because no entrepreneur can start and run the business without money. Among this the most critical element for success in business is ‘Finance’. Before doing anything, an entrepreneur should clearly answer the following three questions:
- How much money is required?
- Where will money come from?
- When does the money need to be available?
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Which sources provide the supply for long-term funds?
Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers:
Lenders supply the funds.
Investors demand funds.
The supply of long-term funds comes from the following sources:
- Household savings
- Foreign capital
- Institutional investors
- Corporate savings
- The government
Question 2. Name the sources of demand for capital comes from.
Capital market consists of lenders and borrowers:
- Lenders supply the funds
- Investors demand the funds The demand for capital comes from:
- Industrial Sector – It comes from the private sector into manufacturing or other economic activities.
- Government
Question 3. Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes, what are they?
Entrepreneur can use the capital raised for a variety of purposes including:
- Growth and expansion
- Retiring existing debt
- Corporate marketing and development
- Acquisition capital.
Question 4. How can an entrepreneur, raises funds by selling the issue mainly to the institutional investors?
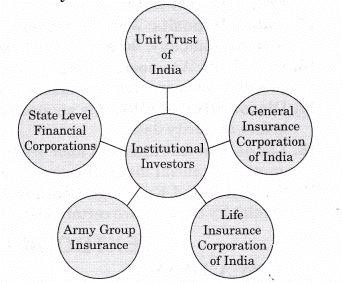
Private Placement: Any entrepreneur can directly sale of its securities of a company to a limited number of sophisticated investors. Entrepreneurs can raise funds by selling the securities mainly to the institutional investors like:
Entrepreneurs both from public limited and private limited sectors, banks heavily upon raising funds through the issues of varied financial instruments under this segment as at times they do not wish to disclose information to the open market.
Question 5. How stock options lead to enable employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company?
Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Explain some important sources of raising finance in business.
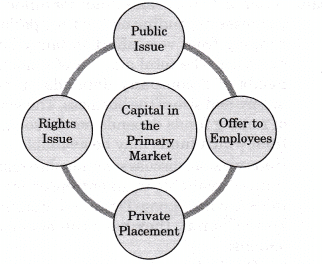
A) Methods of flotation of new issues: An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market by the following methods:
- Public issue
- Rights issue
- Private placement
- Offer to the employees
- Public issue: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. An enterprise organizing itself as a public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by preparing a prospectus.
When an entrepreneur offers shares to the public for subscription he/she is required to comply with all the restrictions and formalities pertaining to the initial issues, prospectus drafting and launch.
One of the most difficult problems in the new venture creation process is obtaining finance when an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company.- Rights issue: Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
Normally, through a circular, rights issues are proposed to the existing shareholders and in case they are not willing to subscribe, they can renounce the same in favour of another person. This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.- Private placement: Private placement means the direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors. Entrepreneurs, herein, raise funds by selling the issues mainly to the institutional investors like:
- Unit Trust of India
- Life Insurance Corporation of India
- General Insurance Corporation of India
- Army Group Insurance
- State Level Financial Corporations, etc.
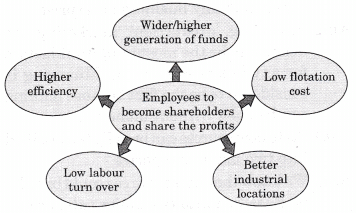
Entrepreneurs both from public limited and private limited sectors bank heavily upon raising funds through the issue of varied financial instruments under this segment as at times they do not wish to disclose information to the open market.- Offer to employees: Stock options or offering shares to the employees has gained much popularity in many countries of the world. This method enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company leading to:
- Higher efficiency
- Low labour turnover
- Better industrial locations
- Low floatation cost
- Wider/higher generation of funds.
B) Angle investors: Business angle or informal investor or an angle investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high-return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity. Venture capital is a type of private equity capital provided as seed funding to early-stage, high potential, high risk, grown up companies/entrepreneurs who lack the necessary experience and funds to give shape to their ideas.
- It is basically equity finance in relatively new companies.
- It is long-term investment in growth- oriented small or medium firms.
- Venture capitalists not only provide capital but also business skills to investee firms.
- It involves high risk-return spectrum. Funding: Obtaining venture capital is substantially different from raising debt or a loan from a lender. Lenders have a legal right to interest on a loan and repayment of the capital, irrespective of the success or failure of a business.
SFIs were established to meet the long-term financial requirement of such enterprises on economic and social ground. These Specialized Financial Institutions in India are not only committed to financial services but are also devoted towards playing a role of a promotional “mentor” and technical advisor to a wide range of the upcoming and existing entrepreneurs. Thus, these Specialized Financial Institutions (SFIs) make an important source of medium and long-term financing amongst all the financial institutions in India, to the industry.
- At national level/All India development banks
- Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
- Small Industries Development-Bank of India (SIDBI)
- Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)
- Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI)
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD)
- Industrial Investment Bank of India Ltd. (IIBI)
- At state level
- State Financial Corporation (SFCs)
- Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
- State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC)
Section B - Financial Markets
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. Define capital market.
A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs.
Question 2. Name the two players in the capital market.
Capital Market
- Primary Market
- Secondary Market
Question 3. Identify the reward IPO investors seek as an appreciation of their investment.
The only reward the IPO investors seek is an appreciation of their investment and possibly dividends.
Question 4. Identify the method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis.
Question 5. What do you understand by pro-rata allotment of securities?
It is used to describe a proportionate allocation. It is a method of assigning shareholders a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
Question 6. What is Right Issue?
Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
Question 7. When the right issue are proposed to the existing shareholders and if they are not ready to subscribe what is the next step taken by an entrepreneur?
When rights issues are proposed to the existing shareholders and in case they are not willing to subscribe, they can renounce the same in favour of another person
Question 8. Why right issue method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive?
The right issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as no intermediaries are required like any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.
Question 9. What do you understand by private placement?
Private placement means the direct sale by a company of its securities to a limited number of sophisticated investors.
Question 10. What is meant by stock options or offering shares to the employees?
A stock option is granted to specified employees of a company. ESOs carry the right, but not the obligation, to buy a certain amount of shares in the company at a predetermined price.
Question 11. Name the method which enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company.
Stock options or offering shares to the employees is the method that enables employees to become shareholders and share the profits of the company.
Question 12. What is a secondary market?
It refers to the market for the purchase and some of existing securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market.
Question 13. What is the need of secondary market?
The secondary capital market, which is also known as old securities market or stock exchange deals with buying and selling of old securities i.e. the market securities issued earlier are sold by existing investors in this market, thus paving way for the entrepreneurs that if they offer high returns to market, investors will remain inclined to invest therein. The secondary market enhances the marketability of securities and thereby provides liquidity to investments.
Question 14. In what forms company can raise capital through primary market?
An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market by the following methods:
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. For what purpose is finance required right from the very beginning i.e. conceiving an idea?
Question 2. What is the need of finance?
- Finance is one of the important prerequisites to start an enterprise.
- It helps an entrepreneur to arrange all other required resources together like, personnel, machines, materials, methods, land, etc. to start up the business systematically.
- It helps an entrepreneur to start and run his business activities smoothly and convert a dream into reality.
Question 3. An entrepreneur is a person who bears the risks, unites various factors of production and carries out a creative innovation, and for doing all these, what is the basic requirement to be reached to this extent.
Finance.
Question 4.State some mushrooming sources of raising finance in the business.
A company may raise funds for different purposes depending on the time periods ranging from very short to fairly long duration. The total amount of financial needs of a company depends on the nature and size of the business. The scope of raising funds depends on the sources from which funds may be available. Here, we shall discuss some mushrooming sources available to an entrepreneur to raise finance; Long-Term and Medium- Term Capital, they have the following options:
- Capital markets:
- Issue of Shares
Equity shares: The rate of dividend on these shares depends on the profits available and the discretion of directors. Hence, there is no fixed burden on the company. Each share carries one vote.- Preference shares: Dividend is payable on these shares at a fixed rate and is payable only if there are profits. Hence, there is no compulsory burden on the company’s finances. Such shares do not give voting rights.
- Issue of Debentures.
- Angle investors: Business angle or an angle investor, is an affluent individual who provides capital for a business start-up and early stage companies having a high-risk, high- return matrix usually in exchange for convertible debt or ownership equity.
- Venture capital: Venture capital is an equity based investment in a growth-oriented small to medium business to enable the investors to accomplish objectives, in return for minority shareholding in the business. It is a way in which investors support entrepreneurial talent with finance and business skills to exploit market opportunities and obtain long-term capital gains.
- Specialized financial institutions Specialized Financial Institutions (SFIs) make an important source of medium and long term financing amongst all the financial institutions in India, to the industry.
- At national level/All India development banks
(i) Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI)
(ii) Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)
(iii) Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI)- At state level
(i) State Financial Corporation (SFC)
(ii) Tourism Finance Corporation of India (TFCI)
(iii) State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDC).
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. State the nature of money market. Who are the major participants in the money market?
Money market refers to transactions involving lending and borrowing of money for short periods like a day a week a month or 3 to 6 months. It meets the short term requirements.
The major participants in the market are:
- Reserve Bank of India
- Commercial Banks, Cooperative Banks
- Non-Banking Finance Companies
- State Government
- Large Corporate Houses and Mutual Funds
- LIC, GIC, UTI, etc.
Question 2. Explain how capital markets are the most important source of raising finance for an entrepreneur.
Capital markets are the most important source of raising finance for the entrepreneurs. This market:
- Mobilises the financial resources on a nation-wide scale.
- Secures the much required foreign capital and know-how to promote economic growth at a faster rate.
- Ensures the most effective allocation of the mobilized financial resources by directing the same either to such projects which are capable of the highest yield or to the under developed priority areas where there is an urgent need to promote balanced and diversified industrialization. The needs of entrepreneurs who actually use the savings for productive purposes are varied. The capital market satisfies the tastes of savers and the needs of investors through its financial instruments and institutions.
Question 3. What do you understand by capital market? How can the capital market in India be broadly classified into different categories?
A capital market may be defined as an organized mechanism meant for effective and smooth transfer of money capital or financial resources from the investors to the entrepreneurs. The capital market in India may be broadly classified into:
Question 4. Write down the sectors of organized and unorganized market.
The capital market in India may be broadly classified into:
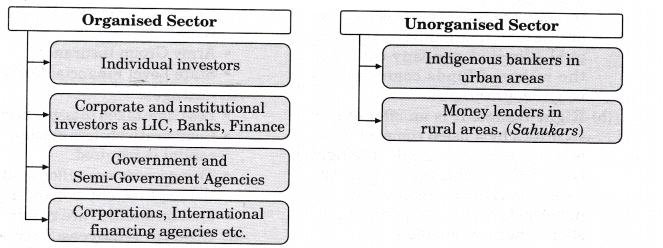
- Organized Markets: This segment comprises of
- Corporate enterprises
- Government and semi-government institutions requiring funds for various development activities
- Individual investors
- Corporate and institutional investors, as LIC, Banks, Finance Corporations, International financing agencies, etc.
- Unorganized Sector: The unorganized sector consists of
- The indigenous bankers in urban areas.
- The money lenders in rural areas.
Question 5. What is meant by primary market? Briefly explain the concept of ‘Right Issue for existing companies’.
Primary market is basically meant to facilitate transfer of resources from the savers to the entrepreneurs seeking funds for:
- Setting new enterprises,
- Expanding,
- Diversifying.
- Rights issue is a method of raising additional finance from existing shareholders by offering securities to them on pro-rata basis i.e. giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.
- It is proposed through a circular to all the existing shareholders only.
- It is not mandatory to purchase these shares if any shareholders are not willing to subscribe, they can reject or disclaim and others can subscribe for it.
Very Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1. “An entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market.” Explain the various methods of raising the funds in the primary market by an entrepreneur.
Yes, an entrepreneur can raise the required capital in the primary market. The various methods of raising the funds in the primary market by an entrepreneur are as follows:
- Public Issue
- Rights Issue
- Private Placement
- Offer to the employees
- Public Issue/Going Public: Public issue is the most popular method of raising capital these days by the entrepreneurs. This involves raising of funds directly from the public through the issue of prospectus. An entrepreneur organizing itself as public limited company can raise the required funds commonly by adopting prospectus.
- Right Issues: It is an offer of new securities by a listed company to its existing shareholders only. The right issues are done always on the pro-rata basis (giving them a right to a certain number of shares in proportion to the shares they are holding.)
- The companies send the letter of offer (circular) to all those existing shareholders whose names are recorded in the books on a particular date to issue rights.
- The time given to accept the right offer should not be less than 15 days.
- The circular/notice issued to the shareholder must state the right of the shareholder to renounce the offer in favour of others.
- After the expiry of the time mentioned in the notice, the Board of Directors has the right to dispose the unsubscribed shares in any manner as per the benefit of the company.
The existing shareholders whose names are there in the list has four options:- They can exercise the rights.
- They can renounce the rights and sell them the same in the open market in favour of another person.
- They can renounce part of the rights and exercise the other part.
- Doing nothing.
This method of issuing securities is considered to be inexpensive as it does not require any brokers, agents, underwriters, prospectus or enlistment, etc.- Private Placement: It refers to the direct sale of newly issued securities by the company to a small number of institutional investors through merchant bankers. They are generally selected clients.
- Unit Trust of India
- Life Insurance Corporation of India
- General Insurance Corporation of India
- Army Group Insurance
- State Level Financial Corporations
Advantages:- Less time taken to issue these shares.
- Comparatively less amount of cost of capital is required.
- These issues are tailor-made to suit the requirement of both the parties.
- Less formalities are required.
- Offer to employees: Stock options to the employees refers to the offer given by the company to the employees to become shareholders. This method facilitates the employees to become shareholder and can earn a part of the share of profits.
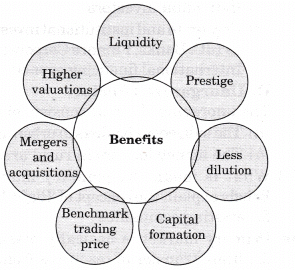
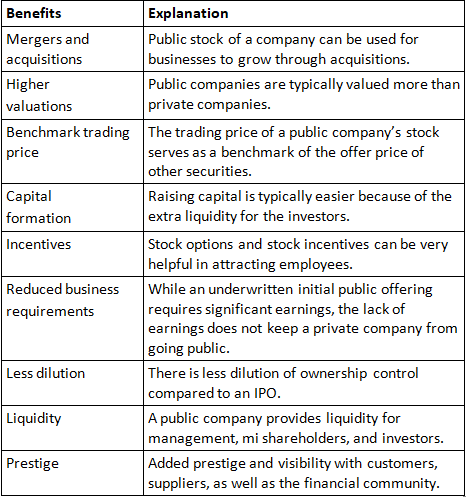
Question 2. When an entrepreneur decides to go public and become a public company, he/ she tends to be in advantageous position and get many benefits out of it. Explain the benefits.
Question 3. While there are benefits to going public, at the same time additional obligations and reporting requirements on the companies and its directors means disadvantages too. What are they? Explain.
While there are benefits to going public, it also means additional obligations and reporting requirements such as:
- Increasing accountability to public shareholders
- Need to maintain dividend and profit growth trends
- Becoming more vulnerable to an unwelcome takeover
- Need to observe and adhere strictly to the rules and regulations by governing bodies
- Increasing costs in complying with higher level of reporting requirements
- Relinquishing some control of the company following the public offering
- Suffering a loss of privacy as a result of media interest
Discussions with lawyers, independent accountants and other professional advisors will also provide better considerations.
Overall, going public is a complex decision that requires careful consideration and planning.
Entrepreneurs should examine their current and future capital needs, and be aware of how an IPO will affect the availability of future financing.
High Order Thinking Skill
Question 1. Why primary market is also known as new issue market? Give one reason.
When an entrepreneur decides to issues securities like shares, debentures to the public for the first time for the purpose of obtaining capital funds such issues of securities are even referred as “new money issues”. Primary market is known as new issue market.
|
19 videos|103 docs|12 tests
|