NCERT Notes: Animal Kingdom | NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - NEET PDF Download
Basis of Classification
- In spite of differences in structure and form of different animals, there are fundamental features common to various individuals in relation to the arrangement of cells, body symmetry, nature of coelom, patterns of digestive, circulatory or reproductive systems.
- These features are used as the basis of animal classification and some of them are discussed here.
(a) Levels of Organisation
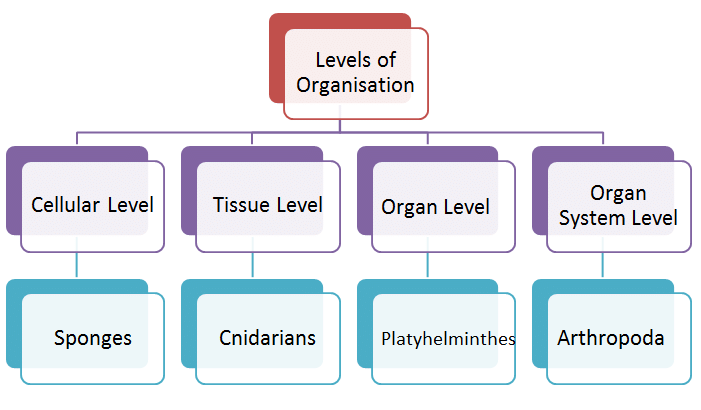 Arrangement of Cells
Arrangement of Cells
 Body Symmetry
Body Symmetry
- Incomplete digestive system has one opening but complete digestive system has two opening:
(i) Mouth
(ii) Anus - Open Circulatory System: Blood is pumped out of heart and cells and tissue are directly bathed in it.
- Closed Circulatory System: Blood is circulated through arteries, veins and capillaries.
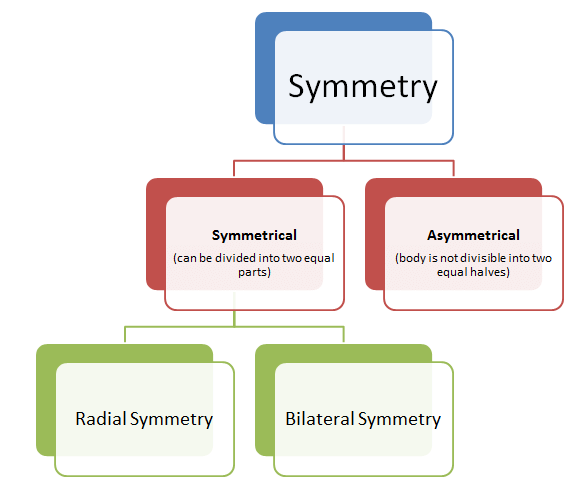
(b) Symmetry
- When an organism can be divided into two identical halves by a plane passing through its central axis, it is said to have radial symmetry. Animals like coelenterates, ctenophores, and echinoderms exhibit this type of body plan.
- On the other hand, animals such as annelids and arthropods display bilateral symmetry, where the body can be divided into identical left and right halves, but only in one plane.
(c) Diploblastic and Triploblastic Organisation
- The animals in which cells are arranged in two embryonic layer, external ectoderm and internal endoderm are called diploblastic. Eg. Coelenterates.
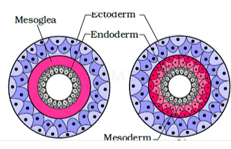
- The animals in which developing embryo has a third germinal layer, mesoderm besides ectoderm and endoderm are called triploblastic. Eg. Platyhelminthes to Chordates.
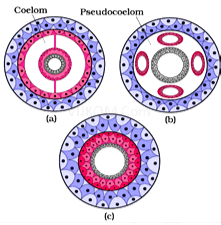
(d) Coelom
- The body cavity which is lined by mesoderm is called coelom. Animals possessing coelom are called coelomate (Annelida, Chordates, Mollusca). In some animals cavity is not lined by mesoderm but scattered as pouches in between ectoderm and endoderm, are called pseudocoelomates. (Aschelminthes). The animals in which body cavity is absent are called acoelomate (Platyhelminthes).
(e) Segmentation
- In some animals, body is externally and internally divided into segments with serial repetition as in earthworm, called metamericsegmentation.
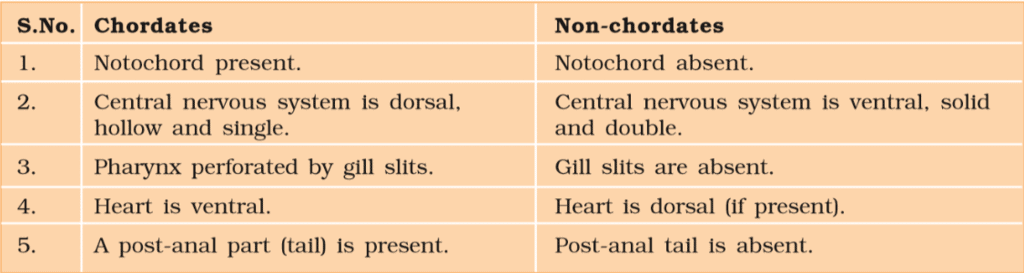
(f) Notochord
- Notochord is a mesodermally derived rod-like structure formed on the dorsal side during embryonic development in some animals.
- Animals with notochord are called chordates and those animals which do not form this structure are called non-chordates, e.g., porifera to echinoderms.
.
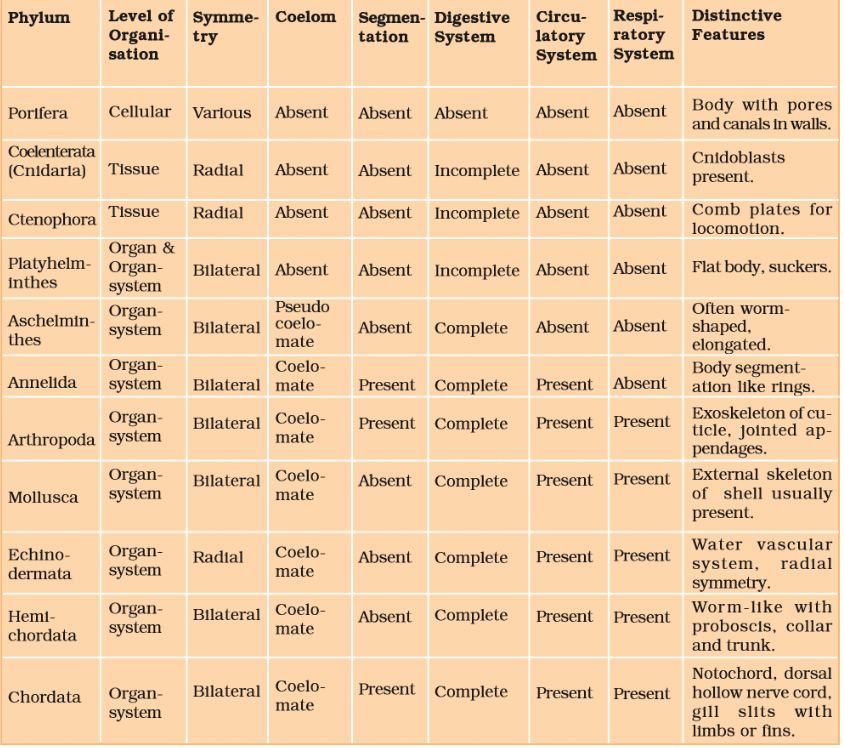
Classification of Animals
(i) Phylum Porifera
- Members of this phylum are commonly known as sponges.
- They are generally marine and mostly asymmetrical animals.
- These are primitive multicellular animals and have cellular level of organisation.
- Sponges have a water transport or canal system.
- Water enters through minute pores (ostia) in the body wall into a central cavity, spongocoel, from where it goes out through the osculum.
- This pathway of water transport is helpful in food gathering, respiratory exchange and removal of waste.
- Choanocytes or collar cells line the spongocoel and the canals.
- Digestion is intracellular.
- The body is supported by a skeleton made up of spicules or spongin fibres.
- Sexes are not separate (hermaphrodite), i.e., eggs and sperms are produced by the same individual.
- Sponges reproduce asexually by fragmentation and sexually by formation of gametes.
- Fertilisation is internal and development is indirect having a larval stage which is morphologically distinct from the adult.
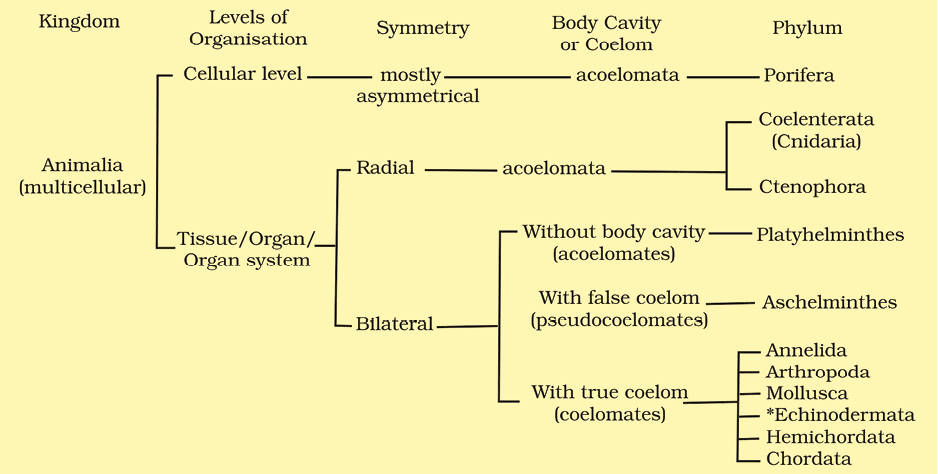
- Examples: Sycon (Scypha), Spongilla (Fresh water sponge) and Euspongia (Bath sponge).
 (a) Sycon (b) Euspongia (c) Spongilla
(a) Sycon (b) Euspongia (c) Spongilla
(ii) Phylum Cnidaria (Coelenterate)
- cnidoblasts or cnidocytes (which contain the stinging capsules or nematocysts) present on the tentacles and the body.
- Cnidoblasts are used for anchorage, defense and for the capture of prey.
- Cnidarians exhibit tissue level of organisation and are diploblastic.
- They have a central gastro-vascular cavity with a single opening, mouth on hypostome.
- Digestion is extracellular and intracellular.
- Some of the cnidarians, e.g., corals have a skeleton composed of calcium carbonate.
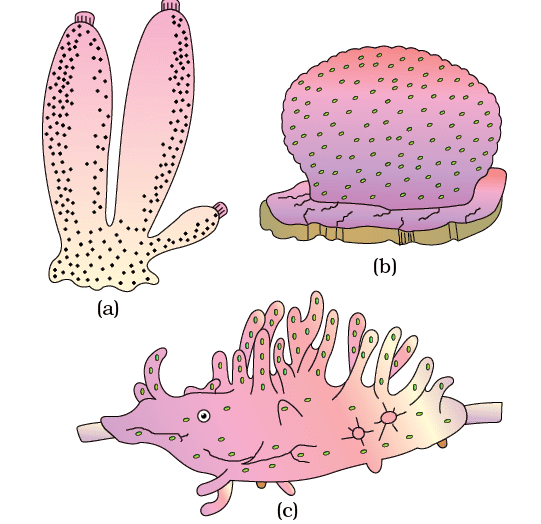
- Cnidarians exhibit two basic body forms called polyp and medusa.
- The former is a sessile and cylindrical form like Hydra, Adamsia, etc. whereas, the latter is umbrella-shaped and free-swimming like Aurelia or jelly fish.
- Those cnidarians which exist in both forms exhibit alternation of generation (Metagenesis), i.e., polyps produce medusae asexually and medusae form the polyps sexually (e.g., Obelia).
- Examples: Physalia (Portuguese man-of-war), Adamsia (Sea anemone), Pennatula (Sea-pen), Gorgonia (Sea-fan) and Meandrina (Brain coral).
 (a) Aurelia (Medusa) (b)Adamsia (Polyp)
(a) Aurelia (Medusa) (b)Adamsia (Polyp)
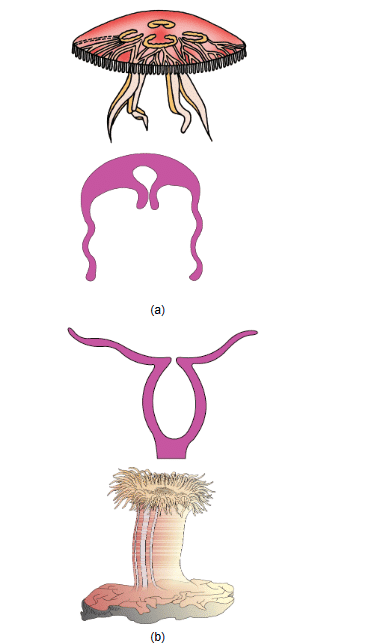
(iii) Phylum Ctenophora
- Commonly known as the Comb Jellies or Sea Walnuts.
- Exclusively marine, diploblastic, radially symmetrical, with tissue level of organization.
- Body bears eight ciliated comb plates which help in locomotion.
- Bioluminescence (to emit light) is present in Ctenophores.
- Are Hermaphrodite, fertilisation is external, development indirect.
Example- Ctenoplana, Pleurobranchia.
 Pleurobrachia
Pleurobrachia
(iv) Phylum Platyhelminthes (The Flat worms)
- Dorso-ventrally flattened body, bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, acoelomate with organs levels of organization.
- Hooks and sucker are present in parasitic forms. Flame cells help in osmoregulation and excretion.
- Fertilisation is internal, development is indirect. They are hermaphrodite.
Example- Taenia, Planaria, Fasciola.
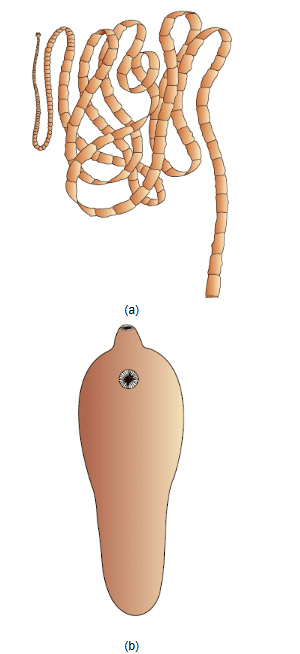 (a) Tape worm (b) Liver fluke
(a) Tape worm (b) Liver fluke
(v) Phylum Aschelminthes (The Round Worm)
- They may be free-living, aquatic, terrestrial or parasitic in plants or animals.
- Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, pseudo coelomate.
- Alimentary canal is complete with well-developed muscular pharynx.
- They are Dioecious. Females are longer than male.
Example- Ascaris (round worm), Wucheriria(filarial worm), Ancyclostoma.
 Ascaris ( Round worm
Ascaris ( Round worm
(vi) Phylum Annelida
- Aquatic or terrestrial, bilaterally symmetrical, segmented with organ system level of organization.
- Aquatic Annelids like Nereis possesses lateral appendages parapodia, for swimming. Nephridia help in osmoregulation and excretion.
- Neural system consists of paired ganglia connected by lateral nerves to a double ventral nerve cord.
- Dioecious (Nereis) or monoecious (earthworm, leech)
Example- Pheretima (earthworm), Hirunidaria (Blood sucking leech).
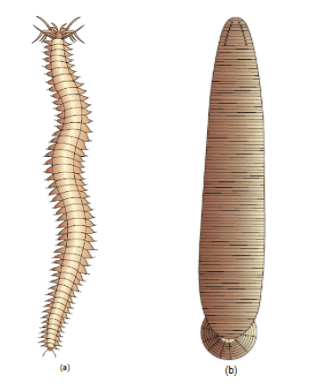 (a) Nereis (b) Hirudinaria
(a) Nereis (b) Hirudinaria
(vii) Phylum Arthropoda
- Largest phylum of animals which includes insects. They have organ system of organization. They are triploblastic, coelomate, bilaterally symmetrical with chitinous exoskeleton.
- Body consists of head, thorax and abdomen, jointed appendages (jointed feet). Respiratory organs are gills, book lungs or tracheal system with open circulatory system.
- Excretion through malpighian tubules, sense organs antenna or eyes. Fertilisation internal, mostly oviparous.
Example:
Economically important – Apis (honey bee), Bombyx (silk worm).
Vectors – Anopheles, Ades, Culex (mosquito).
Living fossils – Limulus (king crab)
 (a) Locust (b) Butterfly (c) Scorpion (d) Prawn
(a) Locust (b) Butterfly (c) Scorpion (d) Prawn
(viii) Phylum Mollusca
- Terrestrial or aquatic, organ level of organization, bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate.
- Body divided into head, muscular foot and visceral hump. Unsegmented and covered with calcareous shell.
- Feather like gills are present between hump and mantle.
- Mouth contains file like rasping organ for feeding called radula.
Example- Pila, Octopus.
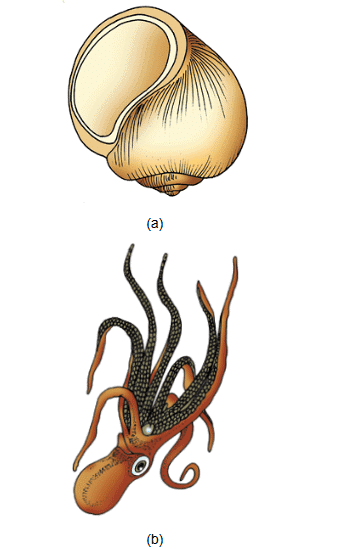 (a) Pila (b) Octopus
(a) Pila (b) Octopus
(ix) Phylum Echinodermata (The Spiny Skinned Animals)
- Endoskeleton of calcareous ossicles, marine with organ system of organization.
- Triploblastic, coelomate, presence of water vascular system help in locomotion, capture of food and respiration.
- Sexes are separate, fertilisation is external and development is indirect.
Example- Asterias (Star fish), Cucumaria (Sea cucumber), Antedon (Sea lily).
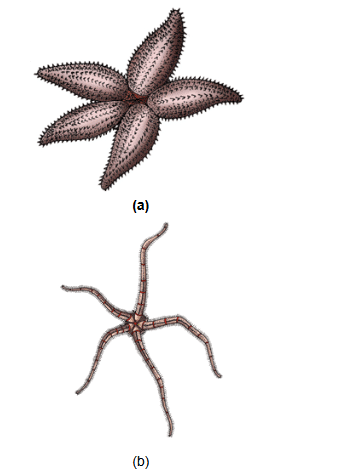 (a) Asterias (b) Ophiura
(a) Asterias (b) Ophiura
(x) Phylum Hemichordata
- Worm-like marine animals with organ system of organization, bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and coelomate animals.
- Body is cylindrical, composed of anterior proboscis, a collar and a long trunk.
- Open circulatory system, respiration by gills, excretory organ is proboscis glands.
- Sexes are separate, fertilisation external, indirect development.
Example- Balanoglossus, Saccoglossus.
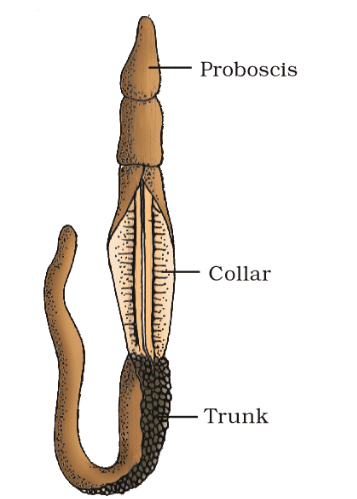 Balanoglossus
Balanoglossus
(xi) Phylum Chordates
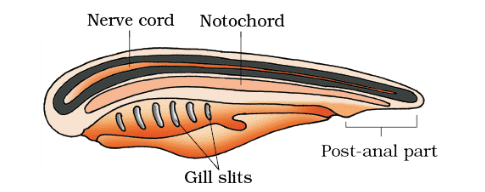
- Presence of notochord, have dorsal hollow nerve chord and paired pharyngeal gill slits.
- Bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic, coelomate with organs system levels of organization.
- Closed circulatory system, ventral heart, post-anal tail is present.
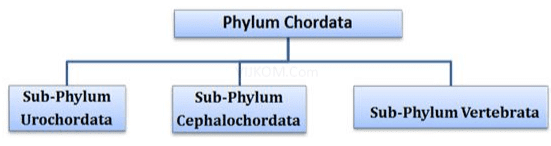
- In Urochordata, notochord is present only in larval tail. In Cephalochordate it extends from head to tail and persists throughout the life.
- Vertebrata possesses notochord in embryonic period which is replaced by vertebral column in the adults.
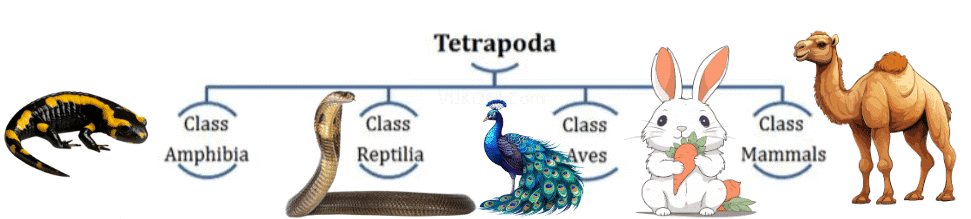
- Subphylum Vertebrata is further divided into two division Agnatha(lacks jaw) and Gnathostomata (bears jaw).
- Gnathostomata is further divided into two super class- Pisces(bears fins) and Tetrapoda (bears limbs).
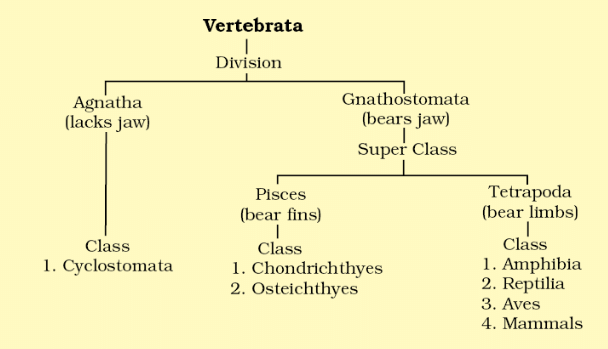
(a) Class Cyclostomata (Circular mouthed fishes)
- They are ectoparasites on some fishes. They have sucking and circular mouth without jaws.
- Body devoid of scales, gill slits for respiration, cranium and vertebral column is cartilaginous.
- Circulation is closed type. They are marine but migrate to fresh water for spawning and die after few days. Larva return to seas after metamorphosis.
Example– Petromyzon (Lamprey), Maxine (Hag fish).
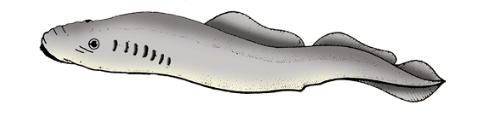 Petromyzon (Lamprey)
Petromyzon (Lamprey)
(b) Class Chondrichthyes (The Cartilaginous Fish)
- They are marine, streamlined body, have cartilaginous endoskeleton, cold blooded, tough skin with minute placoid scales.
- Gill slits are separate without operculum.
- They have powerful jaw and are predators.
- Air bladder is absent, hence to avoid sinking swims constantly. Heart is two chambered, cold blooded (Poikilothermous).
- Sexes separate. Males have pelvic fins which bear claspers. Internal fertilisation, many are viviparous.
- Electric organ is present in Torpedo and Poison sting in Trygon
Example- Scoliodon (Dog fish), Carcharodron (great white shark).
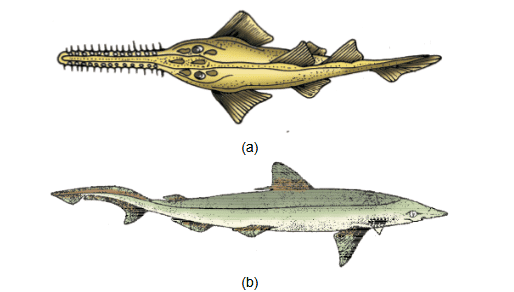 (a) Scoliodon (b) Pristis
(a) Scoliodon (b) Pristis
(c) Class Osteichthyes (The body fish)
- Marine and fresh water both have bony endoskeleton. Streamlined body with four pair of gills covered by operculum.
- Skin is covered with scales, air bladder is present, and heart is two chambered, cold blooded.
- Sexes are separate, fertilisation external, oviparous and development direct.
Example:
Marine - Hippocampus (Sea horse), Exocoetus (Flying fish).
Fresh water- Labeo (Rohu), Catla ,Clarias (Magur).
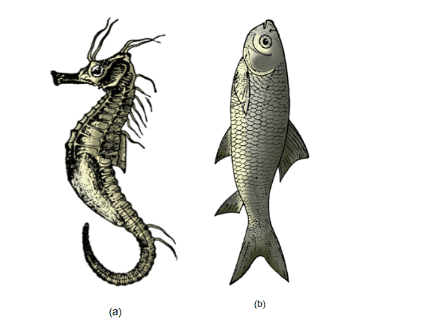 (a) Hippocampus (b) Catla
(a) Hippocampus (b) Catla

|
237 docs|243 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Notes: Animal Kingdom - NCERT Textbooks, Tests & Solutions - NEET
| 1. What is the classification of animals? |  |
| 2. How are animals classified in the animal kingdom? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of animal classification? |  |
| 4. How many phyla are there in the animal kingdom? |  |
| 5. What are the main characteristics used for animal classification? |  |
















