Satellite Frequency Bands | Science & Technology for UPSC CSE PDF Download
In this article, You will read about Satellite Frequency Bands: L, S, C, X, Ku, Ka-band for UPSC IAS.
Satellite technology is developing fast, and the applications for satellite technology are increasing all the time. Not only can satellites be used for radio communications, but they are also used for astronomy, weather forecasting, broadcasting, mapping, and many more applications.
With the variety of satellite frequency bands that can be used, designations have been developed so that they can be referred to easily.
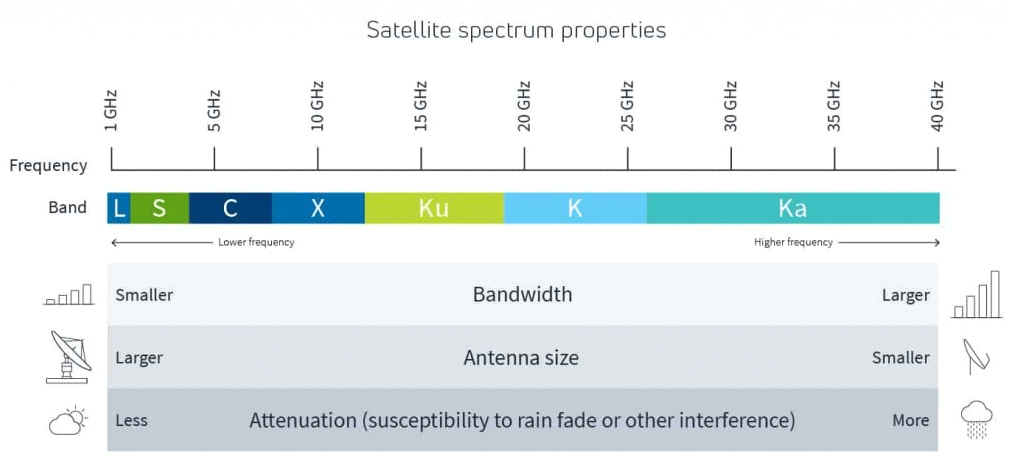
The higher frequency bands typically give access to wider bandwidths but are also more susceptible to signal degradation due to ‘rain fade’ (the absorption of radio signals by atmospheric rain, snow, or ice).
Because of satellite’s increased use, number and size, congestion has become a serious issue in the lower frequency bands. New technologies are being investigated so that higher bands can be used.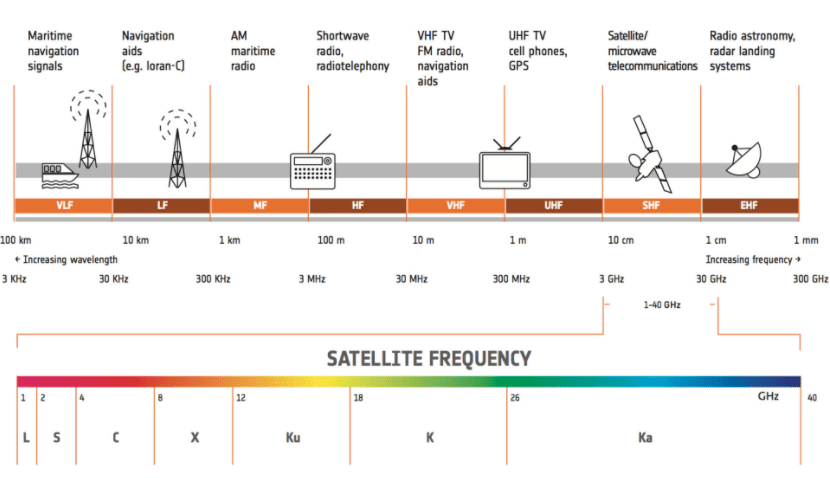 Frequency Bands
Frequency Bands
Satellite Frequency Bands
- L-band (1–2 GHz)
- S-band (2–4 GHz)
- C-band (4–8 GHz)
- X-band (8–12 GHz)
- Ku-band (12–18 GHz)
- Ka-band (26–40 GHz)
1. L-band (1–2 GHz)
Global Positioning System (GPS) carriers and also satellite mobile phones, such as Iridium; Inmarsat providing communications at sea, land, and air; WorldSpace satellite radio.
2. S-band (2–4 GHz)
Weather radar, surface ship radar, and some communications satellites, especially those of NASA for communication with ISS and Space Shuttle. In May 2009, Inmarsat and Solaris mobile (a joint venture between Eutelsat and Astra) was awarded each a 2×15 MHz portion of the S-band by the European Commission.
3. C-band (4–8 GHz)
Primarily used for satellite communications, for full-time satellite TV networks or raw satellite feeds. Commonly used in areas that are subject to tropical rainfall, since it is less susceptible to rain fade than Ku band (the original Telstar satellite had a transponder operating in this band, used to relay the first live transatlantic TV signal in 1962).
4. X-band (8–12 GHz)
Primarily used by the military. Used in radar applications including continuous-wave, pulsed, single-polarisation, dual- polarisation, synthetic aperture radar, and phased arrays. X-band radar frequency sub-bands are used in civil, military and government institutions for weather monitoring, air traffic control, maritime vessel traffic control, defense tracking, and vehicle speed detection for law enforcement.
5. Ku-band (12–18 GHz)
Used for satellite communications. In Europe, the Ku-band downlink is used from 10.7 GHz to 12.75 GHz for direct broadcast satellite services, such as Astra.
6. Ka-band (26–40 GHz)
Communications satellites for close up high resolutions applications, uplink in either the 27.5 GHz and 31 GHz bands, close-range targeting radars on military aircraft.
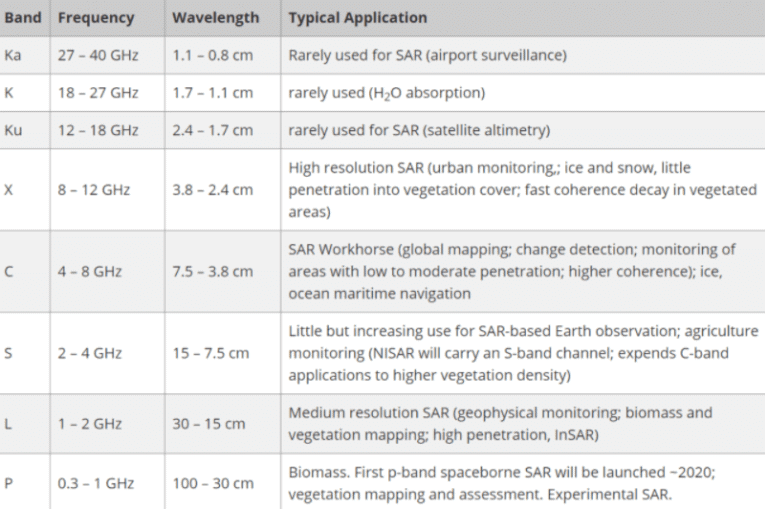 Table on Bands
Table on Bands
India has recently launched its GSAT-6 from Sriharikota in S-Band to enable multimedia applications for solely strategic military purposes and societal uses in case of emergencies.
|
90 videos|488 docs|209 tests
|
FAQs on Satellite Frequency Bands - Science & Technology for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are satellite frequency bands? |  |
| 2. How many satellite frequency bands are there? |  |
| 3. What is the advantage of using different satellite frequency bands? |  |
| 4. Can satellite frequency bands be reused for different purposes? |  |
| 5. How are satellite frequency bands regulated? |  |





















