Cultural Region of the World | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction to Cultural Region of the World
- Culture is a fluid and evolving concept that undergoes subtle changes over time. It can be enriched and enhanced through the exchange and interaction of diverse cultural elements. Culture is a reflection of various aspects of society, including socio-religious and economic conditions, standards of living, technological advancements, and people's perception of their environment.
- Although it is challenging to capture the essence of culture through words, it can be characterized by elements such as language, religion, ethnicity, lifestyle, and various rituals, customs, traditions, and tools. Culture is an abstract concept, yet it can be understood through these different components.
- India, for example, is a rich tapestry of diverse cultures found in various regions, such as North India, South India, and the Himalayan region. This mosaic of cultures highlights the vast array of unique cultural expressions and elements found throughout the country.
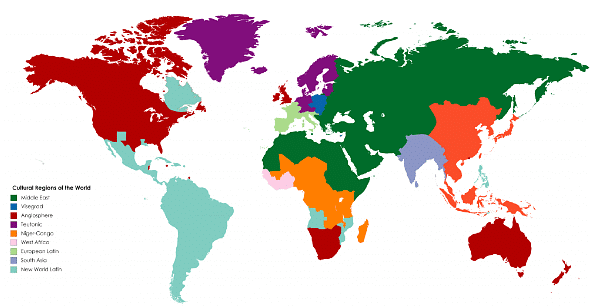
Defining Cultural Regions/Realm
- A cultural realm is a geographic region where cultural traits are homogenous and maintained across the area. These cultural traits are often influenced by the regional geographical conditions, making regional geography the foundation for determining cultural realms around the world. The concept of a cultural landscape, introduced by Ratzel, encouraged geographers to focus on cultural regionalization.
- In addition to geographers like Blache and Spencer, historians, anthropologists, and sociologists have also attempted to divide the world into distinct cultural realms. Cultural variables include economic organization, social customs, traditional values, dietary habits, dress patterns, and language.
- Cultural hearths are considered source areas from which ideas, innovations, and ideologies spread and transformed the world. While cultural hearths are an ancient concept and no longer exist, they were once found in places such as the Hwang Ho and Mesopotamia regions. There are seven well-known cultural hearths:
- The Nile river valley
- The Indus river valley
- The Wei-Huang river valley
- The Ganga river valley
- Mesopotamia
- Mesoamerica
- West Africa
- As cultural hearths expanded, they developed into cores, a concept from medieval times. For example, India has three core areas: Rigvedic culture in Punjab, Later Vedic culture in Bihar, and Dravidian culture in the south (around Thanjavur).
- Regions, a modern concept, do not necessarily have geographical continuity and are often defined by geopolitical boundaries. In contrast, a realm is the largest area of cultural influence, encompassing overlaps and transitional areas, and can be discontinuous. For example, the Islamic realm is a cultural realm that spans across various regions.
Classification of Cultural Regions of World
Several attempts have been made by various experts, such as geographers, anthropologists, and historians, to divide the world into cultural regions. However, this task is not easy, and the advent of communication and the concept of a global village (cultural intermingling) have made it even more difficult. Nevertheless, some environmental factors are bound to create cultural differences, and factors such as language and social aspects also create divisions.- Renowned political geographer Moodie stated that "land is a great divide line of the peoples of the world." The emergence of the European state serves as an example of this. Toynbee has divided the world into three cultural regions: Living Realm, Arrested Realm, and Abortive Realm.
- Broek and Webb attempted to establish the dominance of a particular phenomenon over the evolution of the cultural landscape. They found that religious values have a tremendous impact on the entire cultural system. A cultural-religious investigation reveals that the culture of a particular region becomes ineffective once the religious impact is withdrawn.
Broek and Webb used eight variables for their cultural regionalization of the world:
- Race
- Religion
- Language
- Economic Unionism
- Folk
- Habit or Diet
- Dresses
- Beliefs (orthodox/scientific)
According to Broek, the emergence of these variables is based on the environmental factors or geographical realities of the regions. For example, people living in polar areas would not opt for cotton clothing. Broek further wrote that of all these eight variables, religion has the most significant influence on society. Religion compels people to adopt certain types of economies, clothing, food habits, and beliefs. It also encourages learning certain languages and provides some restrictions during cultural mingling.
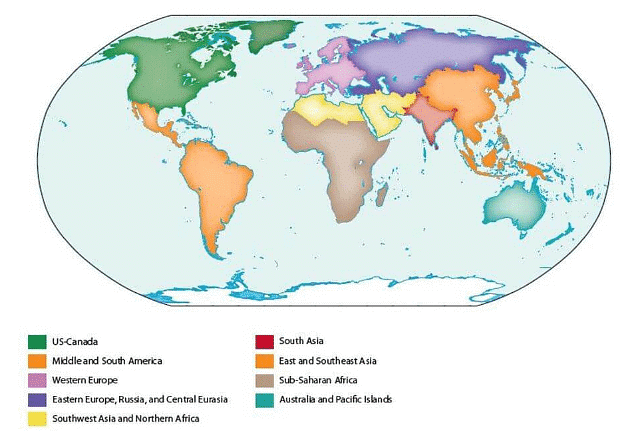
- All other variables are directly or indirectly controlled by religion. However, giving due emphasis to all these factors, Broek and Webb divided the world into major, meso, and micro cultural realms. They divided the world into four major cultural realms and two meso realms.
The major cultural realms are:
- Occidental Realm
- Islamic Realm
- Indian Realm
- East Indian Realm
The minor cultural realms are:
- Southeast Asian Realm
- Meso-African or Negro-African Realm
These realms are further subdivided into micro-realms.
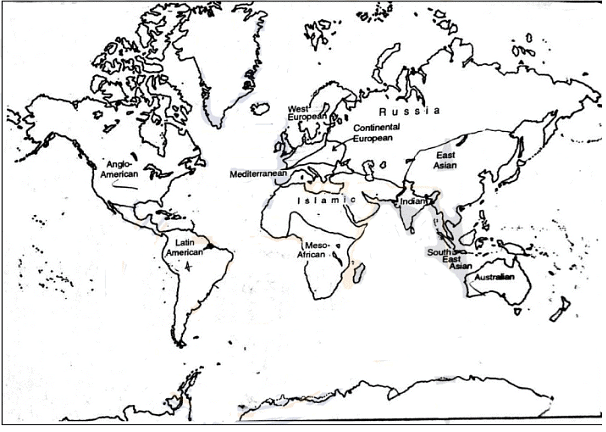
Major Cultural Realms
Occidental Realm
The Occidental cultural realm refers to the culture of European society, which is heavily influenced by Christianity. However, due to factors such as industrialization, political and economic ideologies, colonization, commercialization, urbanization, and the development of transportation and social, political, and economic institutions, there are regional variations within this cultural realm. In many parts of the Occidental culture, the impact of non-religious factors, especially modernization, has overshadowed religious values. Post-industrial Europe is quickly becoming a society where traditional values are being left behind. The Occidental cultural realm is extensive and can be further divided into six sub-regions based on regional environmental influences.
- Western Europe represents the most industrialized and urbanized culture within the Occidental realm.
- Continental European culture is shaped by various political and economic ideologies, with Christianity remaining a significant influence.
- Mediterranean Europe encompasses countries south of the Alps, where Christianity is dominant. Some geographers believe that the deeply ingrained traditional social systems in countries like Spain, Portugal, and southern Italy have limited their economic development compared to Northern and Western European countries that have adapted their social systems.
- The Anglo-American and Australian cultural realms are essentially offshoots of Western European culture, with only minor regional differences. Both regions are populated by migrants from Western Europe.
- Latin American culture closely resembles Mediterranean culture. It is the only region within the Occidental realm that is located in the tropics and remains underdeveloped. Latin America became part of the Occidental culture due to the conversion of tribes to Christianity. Colonial languages, such as Spanish and Portuguese, have become the official languages of the region. Latin American architecture has been influenced by Spanish and Portuguese styles, and most countries maintain economic, cultural, and social ties with Mediterranean countries.
Islamic Cultural Realm
The Islamic Cultural Realm is a vast region characterized by its desert and semi-desert landscapes, stretching from Morocco in the west to Pakistan in the east. The culture within this realm is heavily influenced by Islamic values, and the population is sparsely distributed due to the harsh environmental conditions. Areas with more favorable conditions, such as coastlines, river basins, and oases, have served as the birthplaces of Arabian culture. This region is often referred to as the Middle East by the British and as a part of the oriental culture by the Germans.
- This cultural realm lies between traditional Indian culture to the east and modern European culture to the west. Islamic culture in this region is known for its orthodoxy and adherence to traditional beliefs, which is reflected in high female illiteracy rates. Despite their high per capita incomes, countries in the Islamic Cultural Realm have low levels of modernization.
- Israel stands out as a distinct culture within this region due to its differing religious context. The Central Asian Republics, on the other hand, represent a transitional cultural type. For many years, these countries were part of the Eastern European cultural sphere due to economic unionism, but they have since moved closer to Islamic culture following the policies of Glasnost and Perestroika.
- Historically, the Islamic Cultural Realm has been dominated by nomadism, food-collecting, wandering, and caravan routes. The scarcity of food and water has been a major influence on the development of the region's culture. Islam has also played a significant role in shaping the culture, with its teachings encouraging the establishment of permanent settlements and cultural continuity.
- In recent times, the influx of 'petro-dollars' has led to increased urbanization and modernization, with immigrants creating a more pluralistic urban culture. However, the social systems in these countries have not undergone significant changes or modernization, which is why they have not yet achieved the status of developed countries despite their high incomes.
Indian Cultural Realm
The Indian Cultural Realm, also known as the Monsoonal Culture, encompasses the diverse and rich culture of the Indian subcontinent. This region is well-defined by its geographical boundaries, with the Himalayas to the north, the Indian Ocean to the south, and the Hindukush Mountains to the west. Notably, this is the only cultural realm where religion does not act as a binding factor in cultural development. Instead, it is a region marked by racial and religious tolerance, where various groups of people have migrated, settled, and enriched the local culture.
- Some scholars, like Baker, have referred to this as a subcontinental culture, while others like D. Stamp have called it a paddy culture. This realm is characterized by aspects such as the joint family system, village communities, caste system, semi-feudal land relations, subsistence agriculture, paddy farming, seasonal climate changes, and the synchronization of the agricultural season throughout the region.
- The cultural values of this realm are heavily influenced by the Vedic traditions, which have subtly impacted the social systems of the various communities inhabiting the region. Despite being home to a diverse range of religious groups, including Hindus, Muslims, Sikhs, Jains, and a smaller Christian population, there is a significant blending of religious customs among these groups.
In summary, the Indian Cultural Realm represents a culturally rich and diverse region marked by racial and religious tolerance. It is characterized by features such as the joint family system, village communities, and subsistence agriculture. The influence of Vedic values is evident in the social systems, and a unique aspect of this realm is the blending of religious customs among different groups.
East Asian Culture
East Asian culture is a diverse region mainly inhabited by Mongoloid people, and is primarily influenced by Buddhism with regional adaptations. True Buddhist culture can be observed in countries like South Korea and Japan, although their cultural practices have been impacted by industrialization, urbanization, and modernization. Mainland China, on the other hand, has incorporated its own modifications to the Buddhist system.
- This cultural adaptation took place after World War II, with East Asian people originally inheriting traditions such as horse-riding, pastoralism, and nomadic lifestyles. However, when they settled in the plains of China and the islands of Japan, they began to establish permanent dwellings. While Buddhism is still practiced in the region, its impact is not as strong as other factors like geographical location or socio-cultural philosophies.
- East Asian culture can be further divided into Chinese culture and Japanese culture, which can be described as Continental culture and Marine Culture, respectively. Continental or Chinese culture is influenced by socialist traditions, and despite some reforms, the commune system remains at its core. This culture is characterized by a village cooperative system that spans from Mongolia to Hainan Island and is also known for its paddy agriculture.
- On the other hand, Maritime culture is prevalent in Japan, Taiwan, and South Korea. These countries have a stronger connection to Buddhism compared to their Chinese counterparts, but they have also adopted democratic values, social and economic progress, as well as industrial and commercial development. Japan, in particular, is often referred to as the "Britain of the East" due to its similar culture to that of the United Kingdom, with the exception of race and language. In these countries, religion does not play a significant role in their cultural practices.
Minor Cultural Realms
South-East Asian RealmThe South-East Asian Realm is an area characterized by its cultural diversity and tolerance. This region serves as a melting pot of various cultures, as people from all over the world have settled here. Due to its location, there is no single indigenous culture that dominates the South-East Asian Realm.
- This region is a unique blend of different cultural influences, such as Buddhism, which is the dominant religion in Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam. The South-East Asian Realm is home to a variety of races, including Mongoloids, Negroids, Caucasoids, Indics, and Islamics, all of whom have contributed to the rich tapestry of cultures in the area.
- Christianity is prevalent in the Philippines, while the islands of Indonesia have a strong Indie cultural influence. Islamic traditions can be seen in Malaysia and the Indonesian islands, showcasing the variety of religious influences present in the realm. The island of Bali is predominantly Hindu, further adding to the cultural diversity of the region.
- Singapore is an example of a pluralistic society within the South-East Asian Realm, where multiple cultures and religions coexist harmoniously. This region has been referred to as both the "Museum of Culture" and the "Storehouse of Culture," reflecting its unique and vibrant blend of traditions and customs from around the world.
Meso-African Culture
- Meso-African culture, also known as Negro culture, encompasses the diverse traditions of various African tribes. Due to the numerous tribes with distinct cultures, the development of a unified Meso-African culture has been challenging. In fact, there are about 220 distinct cultural pockets within Africa.
- The majority of these tribes practice animism, a belief system that emphasizes the importance of nature and natural elements rather than a specific deity. As such, these tribes often live in harmony with their natural surroundings, such as residing in tree habitats. Although modern values have slowly begun to influence these tribes, the interaction with modernization remains limited.
- The Meso-African culture is primarily found in tropical Africa, but similar cultural systems can also be observed among the indigenous peoples of the Americas, such as the American Red Indians and Latin American tribes, as well as Australian aboriginals and several tribes in the Asia-Pacific region. Historian Toynbee referred to these traditional cultural units as "marginalized culture," highlighting their relative isolation from mainstream society. Some geographers even include Eskimos in this cultural realm, emphasizing the widespread distribution of marginalized and relatively isolated communities across the globe.
Criticisms
- The classification gives more emphasis on religion
- There is a neglect of the influence of physiographic aspects
Conclusion
In conclusion, the world can be divided into various cultural realms, each with its unique characteristics and influences. These realms include the Occidental Realm, the Islamic Realm, the Indian Realm, the East Asian Realm, the Southeast Asian Realm, and the Meso-African Realm. Each of these cultural regions is shaped by factors such as religion, language, ethnicity, lifestyle, and geography, creating a rich tapestry of diverse cultural expressions. The study of these realms helps us understand the complex and dynamic nature of human culture and the importance of preserving and appreciating our global cultural heritage.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Cultural Region of the World
What is a cultural realm?
A cultural realm is a geographic region where cultural traits are homogeneous and maintained across the area. These cultural traits are often influenced by regional geographical conditions, making regional geography the foundation for determining cultural realms around the world.
What are the major cultural realms of the world?
The major cultural realms include the Occidental Realm, Islamic Realm, Indian Realm, and East Asian Realm. There are also minor cultural realms, such as the Southeast Asian Realm and the Meso-African or Negro-African Realm.
How are cultural realms classified?
Cultural realms are classified based on various factors, such as race, religion, language, economic organization, social customs, traditional values, dietary habits, dress patterns, and beliefs. These factors are often influenced by geographical conditions and environmental factors.
What is the significance of religion in shaping cultural realms?
Religion plays a significant role in shaping the culture of a region, as it often influences people's lifestyles, beliefs, social customs, and values. However, the impact of religion varies across different cultural realms, with some regions being heavily influenced by religious values, while others are influenced more by other factors such as industrialization, urbanization, and modernization.
Can cultural realms change over time?
Yes, cultural realms can change over time due to factors such as globalization, migration, and the spread of new ideas and technology. As cultures interact and influence each other, the boundaries of cultural realms may shift, and new cultural regions may emerge. However, some cultural traits remain deeply ingrained and resistant to change, allowing cultural realms to maintain their unique identities despite external influences.
|
303 videos|635 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Cultural Region of the World - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is a cultural region? |  |
| 2. How are cultural regions classified? |  |
| 3. What are some major cultural realms in the world? |  |
| 4. How do cultural regions impact global interactions? |  |
| 5. How do cultural regions change over time? |  |
















