Climatic Regions | Geography Optional for UPSC PDF Download
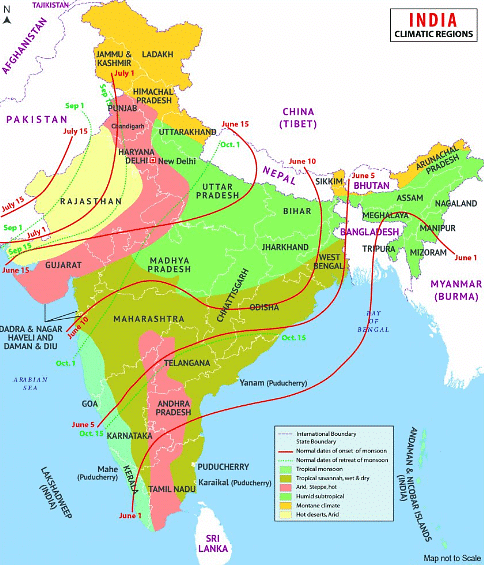 Climatic Regions of India
Climatic Regions of India
Trewartha’s Classification of Climate
According to Trewartha’s scheme, the main climatic regions of India include:
- Tropical Rainforest Climate (Am): The Tropical Rainforest Climate, characterized by high temperatures and heavy precipitation, is found primarily along the western coastal plain and Sahyadris, as well as parts of Assam and Meghalaya. Temperatures in this region are typically above 18.2°C, with rainfall exceeding 200 cm. The vegetation in this area consists mainly of dense evergreen forests.
- Tropical Savannah Climate (Aw): The Tropical Savannah Climate has a mean annual temperature of around 27°C and a mean annual rainfall of less than 100 cm. This climate type is marked by a distinct dry season and covers most of Peninsular India, excluding the coastal plains and the western slopes of the Western Ghats.
- Tropical Steppe Climate (BS): The Tropical Steppe Climate has a mean annual temperature of about 27°C and is found in peninsular India, east of the Western Ghats. This climate type covers the rain-shadow areas of the Western Ghats, including parts of Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- Sub-tropical Steppe Climate (BSh): The Sub-tropical Steppe Climate is a semi-arid climate found in parts of Gujarat, eastern Rajasthan, Mahanadi, Andhra Pradesh, and southern Haryana. This region experiences a mean annual temperature of over 27°C, with the mean monthly January temperature around 15°C. The annual range of temperature is significantly high, and the mean annual rainfall varies between 60 – 75 cm.
- Tropical Arid Climate (BWh): The Tropical Arid Climate is prevalent in the Thar Desert, west of the Aravallis. The mean maximum temperature during May and June may exceed 48°C. This region experiences the lowest annual rainfall in the country, with less than 25 cm of precipitation. Consequently, the natural vegetation consists of thorny bushes.
- Humid Subtropical Climate (Caw): The Humid Subtropical Climate covers the majority of the Great Plains of India, from Punjab to Assam. The mean January temperature is less than 18°C, while the mean maximum temperature in the summer may exceed 45°C. The average annual rainfall ranges from 250 cm in the east to about 65 cm in the west.
- Mountain Climate (H): The Mountain Climate is found in the hilly regions of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, and other hilly parts of north-east India. The average summer temperature is around 17°C, while the average January temperature is generally around 8°C. The average temperature varies according to topographical features and slope. Rainfall generally decreases from east to west, with the Western Himalayas receiving some winter precipitation from western disturbances.
Koeppen’s Classification of Climatic Regions of India
- Koeppen’s Classification of Climatic Regions of India is an empirical classification based on mean annual and mean monthly temperature and precipitation data.
- Koeppen identified a close relationship between the distribution of vegetation and climate.
- He selected certain values of temperature and precipitation and related them to the distribution of vegetation and used these values for classifying the climates.
- Koeppen recognized five major climatic groups, four of them are based on temperature and one on precipitation.
- The capital letters:
- A, C, D and E delineate humid climates and
- B dry climates.
- The climatic groups are subdivided into types, designated by small letters, based on seasonality of precipitation and temperature characteristics.
- The seasons of dryness are indicated by the small letters : f, m, w and s, where
- f – no dry season,
- m – monsoon climate,
- w – winter dry season and
- s – summer dry season.
- The above mentioned major climatic types are further subdivided depending upon the seasonal distribution of rainfall or degree of dryness or cold.
- a: hot summer, average temperature of the warmest month over 22°C
- c: cool summer, average temperature of the warmest month under 22°C
- f: no dry season
- w: dry season in winter
- s: dry season in summer
- g: Ganges type of annual march of temperature; hottest month comes before the solstice and the summer rainy season.
- h: average annual temperature under 18°C
- m (monsoon): short dry season.
- The capital letters S and W are employed to designate the two subdivisions of dry climate:
- semi-arid or Steppe (S) and
- arid or desert (W).
- Capital letters T and F are similarly used to designate the two subdivisions of polar climate
- tundra (T) and
- icecap (F).
Climatic Groups According to Koeppen
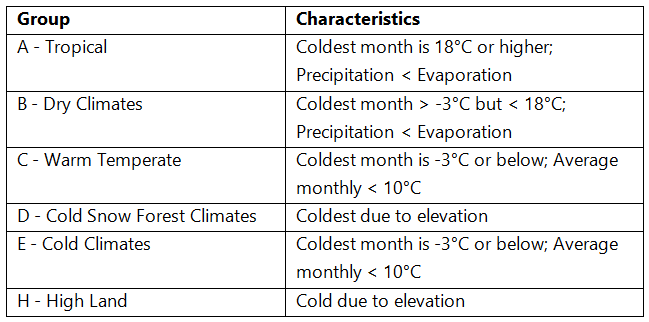
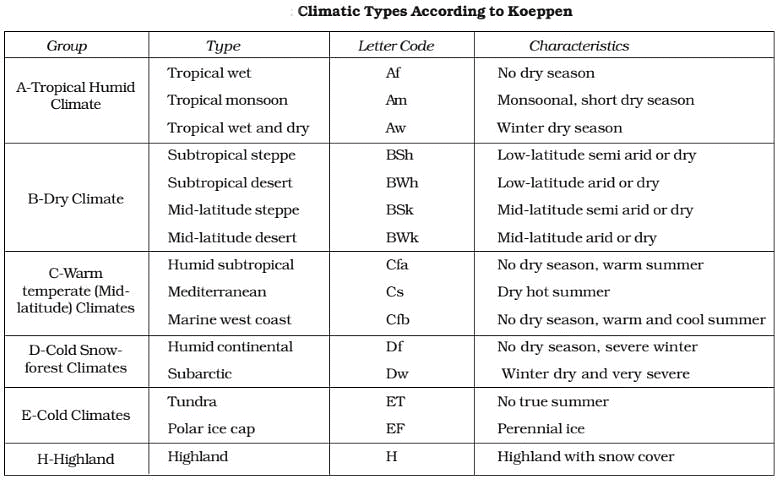
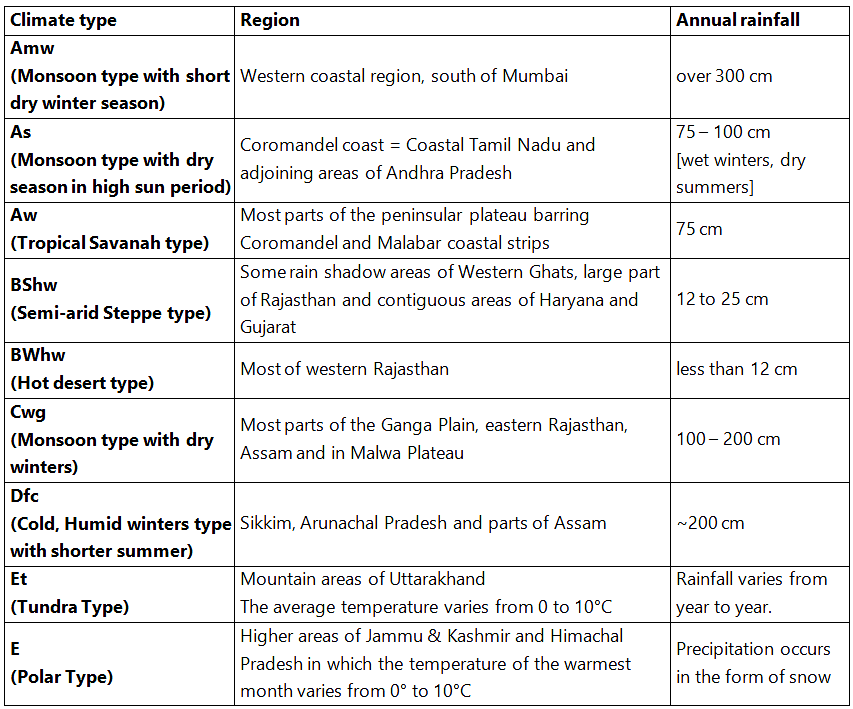
Koeppen divided India into nine climatic regions making use of the above scheme.
Koeppen’s Scheme Climatic Regions of India
Conclusion
In conclusion, India's diverse climate can be classified into various types according to Trewartha's scheme. These include the Tropical Rainforest, Tropical Savannah, Tropical Steppe, Sub-tropical Steppe, Tropical Arid, Humid Subtropical, and Mountain climates, which are determined by factors such as temperature, rainfall, and topography. These distinct climatic regions contribute to the country's rich biodiversity, resulting in varied vegetation and ecosystems across the nation.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Climatic Regions
What are the key climatic regions of India according to Trewartha's classification?
Trewartha's classification identifies the following key climatic regions in India: Tropical Rainforest Climate (Am), Tropical Savannah Climate (Aw), Tropical Steppe Climate (BS), Sub-tropical Steppe Climate (BSh), Tropical Arid Climate (BWh), Humid Subtropical Climate (Caw), and Mountain Climate (H).
Which region in India experiences the lowest annual rainfall and what kind of vegetation is found there?
The Tropical Arid Climate (BWh) region, prevalent in the Thar Desert west of the Aravallis, experiences the lowest annual rainfall in the country, with less than 25 cm of precipitation. The natural vegetation in this area consists of thorny bushes due to the arid conditions.
How does the Mountain Climate in India vary according to topographical features and slope?
The Mountain Climate, found in the hilly regions of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, and other hilly parts of north-east India, exhibits variations in average temperature and rainfall depending on topographical features and slope. For instance, the average temperature may range from around 8°C in January to around 17°C in the summer, while rainfall generally decreases from east to west, with the Western Himalayas receiving some winter precipitation due to western disturbances.
|
303 videos|636 docs|252 tests
|
FAQs on Climatic Regions - Geography Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are climatic regions? |  |
| 2. How are climatic regions classified? |  |
| 3. What are the major climatic regions on Earth? |  |
| 4. How do climatic regions impact agriculture? |  |
| 5. How do climatic regions affect human settlements? |  |
















