Art & Culture: January 2022 Current Affairs - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| National War Memorial |

|
| 2. Sahitya Akademi Awards |

|
| 3. World Hindi Day |

|
| 4. Padma Awards |

|
| 5. Subhas Chandra Bose |

|
| 6. Durga Puja in Unesco’s Intangible Cultural Heritage |

|
National War Memorial
The eternal flame of Amar Jawan Jyoti underneath India Gate was recently put out and merged with another eternal flame at the National War Memorial.
Amar Jawan Jyoti
- The eternal flame at the Amar Jawan Jyoti was an iconic symbol of the nation’s tributes to the soldiers who have died for the country in various wars and conflicts since Independence.
- It was established in 1972, to mark India’s victory over Pakistan in 1971 War, which resulted in the creation of Bangladesh. It had been burning continuously since then.
India Gate
- The India Gate, All India War Memorial, as it was known earlier, was built by the British in 1931. It was erected as a memorial to around 90,000 Indian soldiers of the British Indian Army, who had died in several wars and campaigns between 1914-1921.
- Names of more than 13,000 dead soldiers are mentioned on the memorial commemorating them.
- As it was a memorial for the Indian soldiers killed in wars, the Amar Jawan Jyoti was established underneath it.
National War Memorial
- The National War Memorial, which is around 400 meters from India Gate was inaugurated in 2019.
- It was built to commemorate all the soldiers who have laid down their lives in the various battles, wars, operations and conflicts of Independent India.
- Eg. Sino-Indian war in 1962, Indo-Pak wars in 1947, 1965 and 1971, Indian Peace Keeping Force Operations in Sri Lanka, Kargil Conflict in 1999, United Nations peace-keeping missions, Humanitarian Assistance Disaster Relief (HADR) operations, counterinsurgency operations and Low-Intensity Conflict Operations (LICO).
- There are many independent memorials for such soldiers, but no memorial existed commemorating them all at the national level.
- The architecture of the memorial is based on four concentric circles:

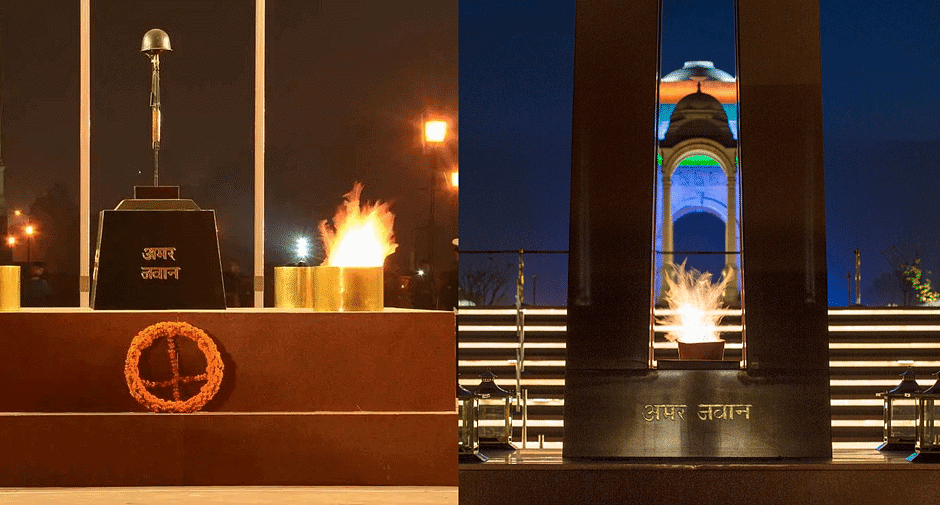 Amar Jawan Jyoti and National War Memorial
Amar Jawan Jyoti and National War Memorial
2. Sahitya Akademi Awards
- The Sahitya Akademi Awards for literary works in 2021 were announced recently.
- The award is a literary honour in India, conferred by the Sahitya Akademi. It is conferred annually on writers of the most outstanding books of literary merit published in any of the 24 major Indian languages.
- Besides the 22 languages enumerated in the Constitution of India, the Sahitya Akademi has recognised English and Rajasthani Sahitya Akademi.
- Inaugurated in 1954, Sahitya Akademi - India’s National Academy of Letters, is the central institution for literary dialogue, publication and promotion in the country.
- Functioning as an autonomous organization, it also gives special awards called Bhasha Samman to significant contribution to the languages not formally recognized by the Akademi and for contribution to classical and medieval literature.
 Sahitya Academy Awards
Sahitya Academy Awards
3. World Hindi Day
- Recently on the occasion of World Hindi Day (10th January), UNESCO's World Heritage Centre has agreed to publish Hindi descriptions of India's world heritage sites on WHC website.
- World Hindi Day is celebrated to mark the anniversary of first World Hindi Conference which was held in 1975 by then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. The day was first observed on January 10, 2006.
- National Hindi Diwas is celebrated every year on September 14. On that day in 1949, the constituent assembly adopted Hindi, written in Devanagari script, as the official language of the Union, while the focus of the World Hindi Day is to promote the language at the global stage.
- Facts About Hindi Language The word Hindi originated from the Persian word Hind, which means the land of the Indus River.
- In linguistic terms, Hindi belongs to the Indo-Iranian sub-family of the Indo-European family of language.
- Hindi has been influenced and enriched by Turkish, Arabic, Persian, English and Dravidian (ancient South India) languages.
- The earliest form of Hindi was called 'Apabhramsa', which was an offspring of Sanskrit. In 400 AD, poet Kalidas wrote Vikramorvashiyam in Apabhramsa.
 World Hindi Day
World Hindi Day
4. Padma Awards
- The Padma Awards 2022 were announced recently. 128 Padma Awards were approved this year.
- Instituted in 1954, the Padma Awards are one of the highest civilian honours of India announced annually on the eve of Republic Day and are conferred by the President later.
- The Awards are given in three categories: The Padma Vibhushan is the second-highest civilian award of the Republic of India, second only to the Bharat Ratna.
- The Padma award seeks to recognize achievements in all fields of activities or disciplines where an element of public service is involved viz. literature and education, arts, science and engineering, trade and industry, civil services, public affairs, sports, medicine etc.
- The awards are given on the recommendations made by the Padma Awards Committee, which is constituted by the Prime Minister every year. The nomination process is open to the public. Even selfnomination can be made.
- All persons without distinction of race, occupation, position or sex are eligible for these awards. However, government servants including those working with PSUs, except doctors and scientists, are not eligible for these Awards
- The awards can also be conferred on foreigners/Non-Resident Indian (NRI)/Person of Indian Origin (PIO)/Overseas Citizen of India (OCI).
- The award does not amount to a title and cannot be used as a suffix or prefix to the awardees’ name.
 Padma Awards
Padma Awards
5. Subhas Chandra Bose
- In order to commemorate the 125th birth anniversary of freedom fighter Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose, the government has decided to install his statue at India Gate.
- Born in 1897 in Cuttack, Bose was an Indian nationalist in the era of British colonialism.
- After completing his education in India, Bose left for London to prepare for the Indian Civil Services exam and cleared it.
- He had mixed feelings about working under the British, and eventually resigned in 1921 as a symbol of boycotting the British after the incident of the Jallianwala Bagh massacre.
- Role in Freedom Struggle After returning to India, Bose joined the Indian National Congress (INC) under the influence of Mahatma Gandhi and started the newspaper “Swaraj”.
- In the year 1923, he became the President of the All India Youth Congress and became the editor of the newspaper “Forward” started by C.R. Das.
- In 1928, Motilal Nehru Committee demanded Dominion Status in India but Bose along with Jawaharlal Nehru demanded complete independence of India from the British.
- He was sent to jail in 1930 during Civil Disobedience movement and was released along with other prominent leaders in the year 1931 when the Gandhi-Irwin pact was signed.
- In 1938, he was elected as President at the Haripura session of the INC. After re-elected as President in 1939, differences arose between him and Gandhi.
- The senior leadership in the Congress supported Gandhi, and Bose resigned as president and formed another group called the Forward Bloc.
- He started a mass movement against using Indian men in the wars of foreign countries which received immense support and which led him to be put under house arrest in Calcutta but he left the house in disguise in January 1941 and reached Germany.
- His attempts to get rid of the British with the help of the Nazi party and Imperial Japan during the time of the second world war left him a troubled legacy.
- In July 1943, he arrived in Singapore and took over the reins of the Indian Independence Movement started by Rash Behari Bose and organized the Azad Hind Fauj also known as the Indian National Army (INA).
- The INA liberated the Andaman and Nicobar islands but when it reached Burma, bad weather conditions, as well as the defeat of Japan and Germany in the Second World War, forced him to retreat.
- He died in a plane crash in Taipei, Taiwan in 1945.
- In honour of his contribution to the freedom struggle his birthday anniversary is celebrated as Parakram Diwas. Parakram means Courage.
 125TH Birth Anniversary of Subhash Chandra Bose
125TH Birth Anniversary of Subhash Chandra Bose
6. Durga Puja in Unesco’s Intangible Cultural Heritage
UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Committee for the Safeguarding of the Intangible Cultural Heritage has put “Durga Puja in Kolkata” on the Representative List of the Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
About Durga Puja
- Durga Puja is celebrated during the autumn. It is the most important socio-cultural and religious event in the Bengali festival calendar.
- Area of influence: West Bengal, Bihar (Biharis), Odisha (Oriyas) and Assam (Ahomiyas) as well as in other states of India where Bengali community reside. This festival is also celebrated by Bengali Diaspora outside India.
- Objective: To propitiate the Goddess Durga for her blessings as also celebrate her victory over the demon Mahishasur.
- Durga Puja is a ten-day festival, usually in October, which starts from Mahalaya, the inaugural day of the event. Mahalaya is celebrated by Agomoni or songs of welcome.
- On the tenth day, or Bijoya Dashami, the Goddess is borne away to the sounds of the dhak, or traditional drum for immersion in nearby rivers or water bodies.
- The makeshift structures, as well as the image of the Goddess are adorned with meticulous artwork and stylistic themes made with local craft materials such as shola or pith, coloured jute, woven brocades, imitation jewellery, clay and terracotta ornamentation.
- Durga Puja is seen as the best instance of the public performance of religion and art, and as a thriving ground for collaborative artists and designers.
About Intangible Cultural Heritage
- According to UNESCO, “cultural heritage does not end at monuments and collections of objects”, but “also includes traditions or living expressions inherited from our ancestors and passed on to our descendants, such as oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe or the knowledge and skills to produce traditional crafts”.
- Intangible cultural heritage, according to UNESCO, is “traditional, contemporary and living at the same time”, “inclusive”, “representative”, and “community based”. It is “an important factor in maintaining cultural diversity in the face of growing globalisation” — and “an understanding of the intangible cultural heritage of different communities helps with intercultural dialogue and encourages mutual respect for other ways of life”.
Importance of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- The term ‘cultural heritage’ has changed content considerably in recent decades, partially owing to the instruments developed by UNESCO.
- Cultural heritage does not end at monuments and collections of objects and includes traditions or living expressions inherited from our ancestors and passed on to our descendants, such as oral traditions, performing arts, social practices, rituals, festive events, knowledge and practices concerning nature and the universe or the knowledge and skills to produce traditional crafts.
- While fragile, intangible cultural heritage is an important factor in maintaining cultural diversity in the face of growing globalization. An understanding of the intangible cultural heritage of different communities helps with inter-cultural dialogue and encourages mutual respect for other ways of life.
- The importance of intangible cultural heritage lies in the wealth of knowledge and skills that is transmitted across generations.
- The social and economic value of this transmission of knowledge is relevant for minority groups and for mainstream social groups within a State and is as important for developing States as for developed ones.
Salient Features of Intangible Cultural Heritage
- Traditional, contemporary and living at the same time: intangible cultural heritage does not only represent inherited traditions from the past but also contemporary rural and urban practices in which diverse cultural groups take part.
- Inclusive, Social Cohesion & Identity: Intangible Cultural Heritage have been passed from one generation to another, have evolved in response to their environments and contribute to giving us a sense of identity and continuity, providing a link from our past, through the present, and into our future. It contributes to social cohesion, encouraging a sense of identity and responsibility which helps individuals to feel part of one or different communities within the society.
- Representative: intangible cultural heritage is not merely valued as a cultural good, on a comparative basis, for its exclusivity or its exceptional value. It thrives on its basis in communities and depends on those whose knowledge of traditions, skills and customs are passed on to the rest of the community, from generation to generation, or to other communities.
- Community-based: intangible cultural heritage can only be heritage when it is recognized as such by the communities, groups or individuals that create, maintain and transmit it. Without their recognition, nobody else can decide for them that a given expression or practice is their heritage.
Cultural Elements from India Included in UNESCO’s Intangible Heritage List
- Kutiyattam, Sanskrit theatre
- The tradition of Vedic chanting
- Ramlila, the traditional performance of the Ramayana
- Ramman, religious festival and ritual theatre of the Garhwal Himalayas, India
- Chhau dance
- Kalbelia folk songs and dances of Rajasthan
- Mudiyettu, ritual theatre and dance drama of Kerala
- Durga Puja in Kolkata
- Buddhist chanting of Ladakh: recitation of sacred Buddhist texts in the trans-Himalayan Ladakh region, Jammu and Kashmir, India
- Sankirtana, ritual singing, drumming and dancing of Manipur 11. Traditional brass and copper craft of utensil making among the Thatheras of Jandiala Guru, Punjab, India
- Nowroz
- Yoga
- Kumbh Mela
- Durga Puja
FAQs on Art & Culture: January 2022 Current Affairs - UPSC
| 1. What is the National War Memorial? |  |
| 2. What are Sahitya Akademi Awards? |  |
| 3. What is World Hindi Day? |  |
| 4. What are Padma Awards? |  |
| 5. Who is Subhas Chandra Bose? |  |



















