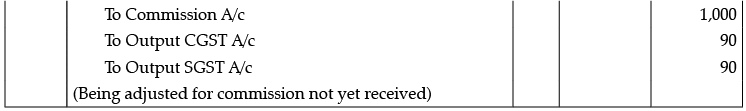Class 11 Accountancy: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 1 | Sample Papers for Class 11 Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class Xl Accountancy |

|
| Time: 2 Hours |

|
| Max. Marks: 40 |

|
| Part-A (Accounting Process) |

|
| Part-B (Financial Accounting and Computer in Accounts) |

|
Class Xl Accountancy
Time: 2 Hours
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions :
- The Question Paper consists of two Parts – A and B. There are total 12 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Part – A consists of Accounting Process.
- Part – B consists of Financial Accounting and Computers in Accounts.
- Question Nos. 1 to 2 and 5 to 6 are short answer type questions – I carrying 2 Marks each.
- Question Nos. 3 and 7 to 9 are short answer type questions – II carrying 3 Marks each.
- Questions Nos. 4 and 10 to 12 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 3 questions of three marks and 1 question of five marks.
Part-A (Accounting Process)
1. Calculate the due dates of the following bills:
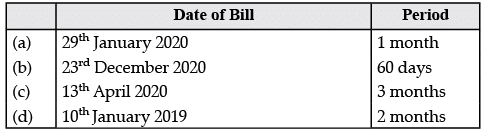
(a) 29th Jan + 1 months + 3 days = 3rd March 2020
(b) 23rd Dec + 60 days + 3 days = 21st February 2021
(c) 13th April + 3 months + 3 days = 16th August 2020
(d) 10th Jan + 2 months + 3 days = 13th March 2019
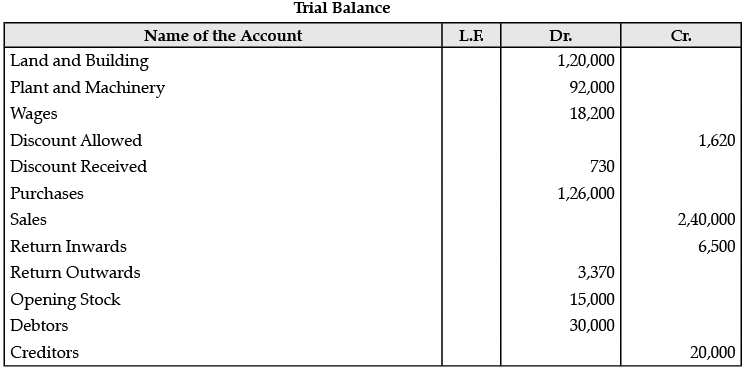
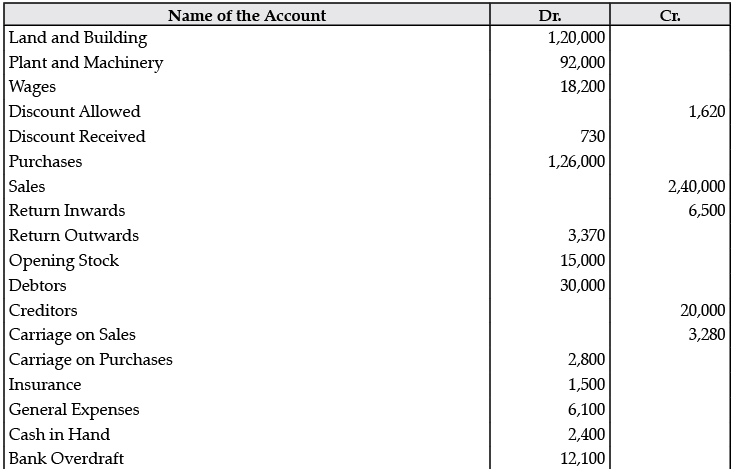
Q.2. The following Trial Balance has been prepared by an inexperienced accountant. Redraft it in a correct form:

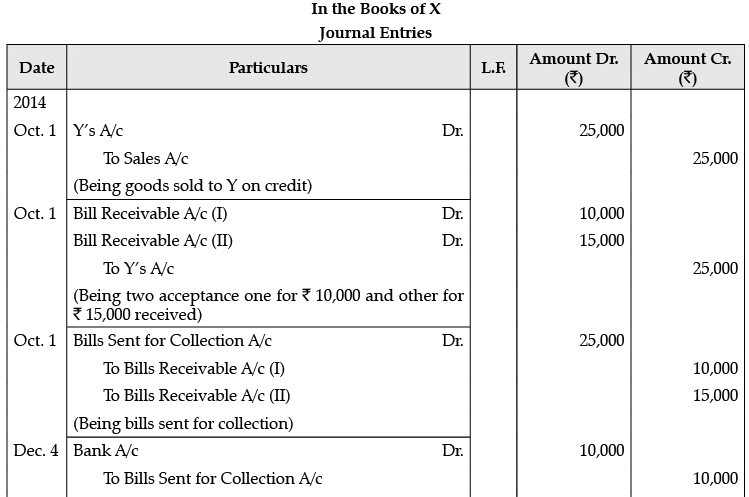
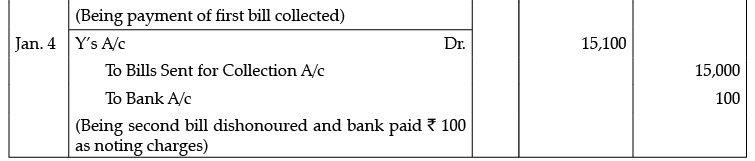
Q.3. On 1st October, 2014, X sells goods to Y for Rs. 25,000 and draws two bills of exchange on him: the first for Rs. 10,000 for two months and second for Rs. 15,000 for 3 months. Y accepts and returns these bills to X. Both the bills are sent to the bank for collection. In due course, X receives the information from the bank that the bill for Rs. 10,000 has been duly met and the other bill for Rs. 15,000 has been dishonoured. Noting charges paid on the dishonour of the second bill are Rs. 100.
Pass Journal entries in the books of X.
OR
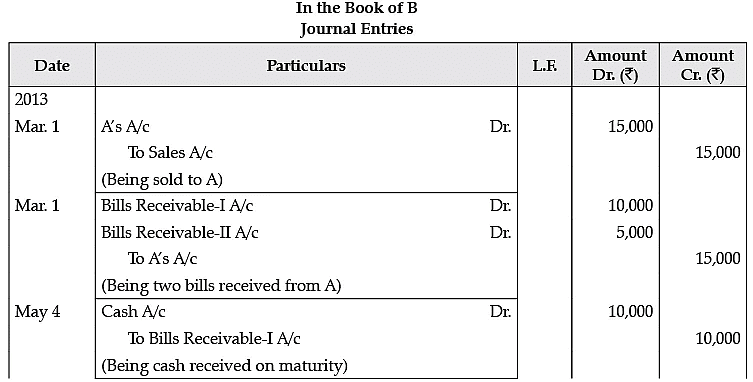
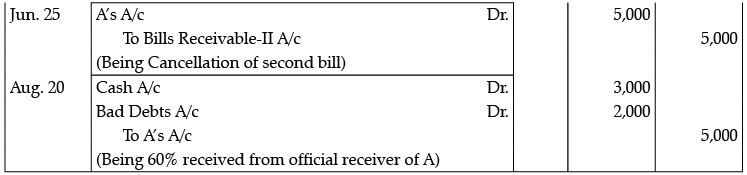
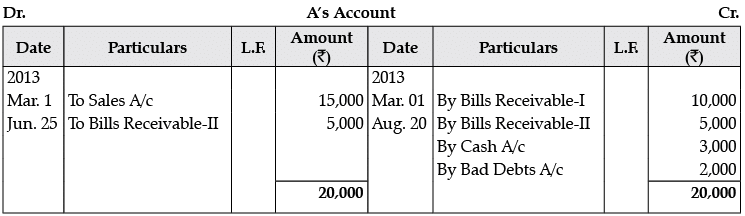
A purchased goods for Rs. 15,000 from B on 1st March. 2013 and gives him two Bills. One for ` 10,000 at two months and other for Rs. 5000 at four months. A meet the first bill at maturity but on 25th June, 2013 he was declared insolvent and 60 paise in a rupee amount was received from him on August 20, 2013. Journalise in the books of B and prepare A’s A/c.
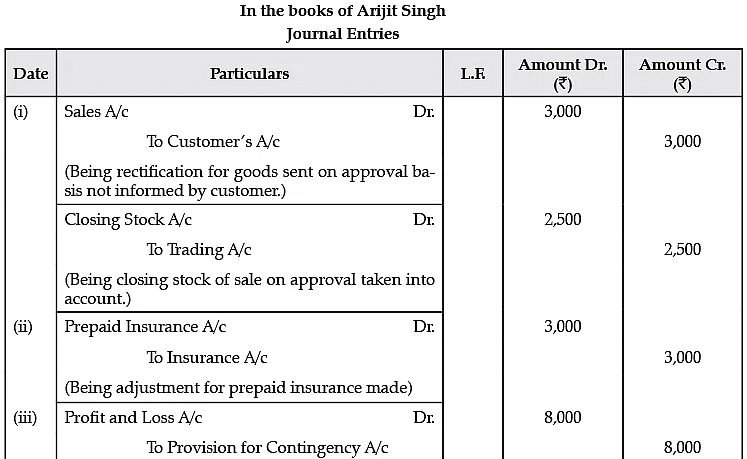
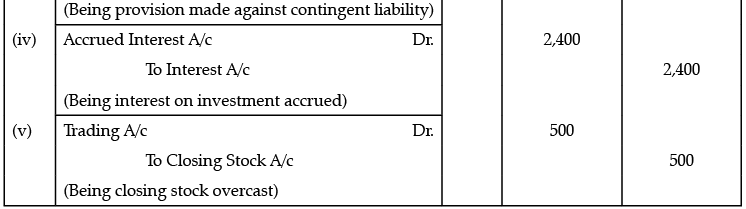
Q.4. On 31st March 2018, Arijit Singh finds that he has committed following errors:
(i) Goods costing Rs. 2,500 were sent to customer on sale on approval basis for ` 3,000. The entry was made in Sales Book, but the customer has not informed regarding their acceptance by 31st March 2018.
(ii) Unexpired insurance of Rs. 3,000 has not been considered while preparing Profit & Loss A/c.
(iii) An amount of Rs. 17,000 on account of claim against the customer was in dispute and it was estimated that Rs. 8,000 would probably have to be paid on this account.
(iv) Interest accrued on Investment was Rs. 2,400.
(v) Closing Stock was overcast by Rs. 500.
Give necessary journal entries.
Part-B (Financial Accounting and Computer in Accounts)
Q.5. Operating profit earned by M/s Arora and Sachdeva in 2013-14 was Rs. 17,00,000. Its non-operating incomes were Rs. 1,50,000 and non-operating expenses were Rs. 3,75,000. Calculate the amount of net profit earned by the firm.
Net Profit = Operating Profit + Non- operating Income – Non-operating Expenses = Rs. 17,00,000 + Rs. 1,50,000 – Rs. 3,75,000
= Rs. 14,75,000
Net profit earned by M/S Arora and Sachdeva in 2005–06 was ` 14,75,000.
Q.6. From the following information, calculate capital at the beginning:

Calculation for capital at the beginning:
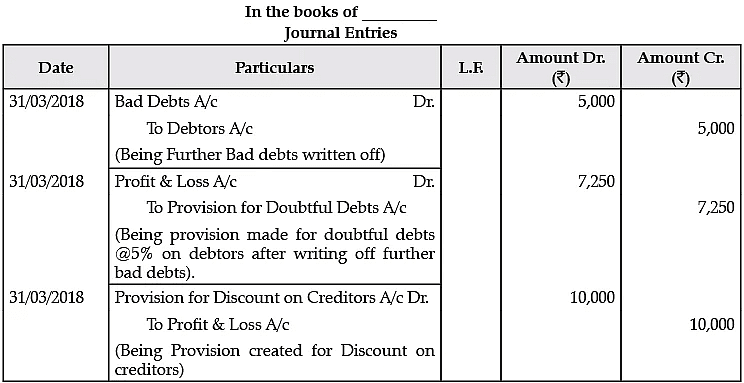
Q.7. From the following pass the necessary journal entries:
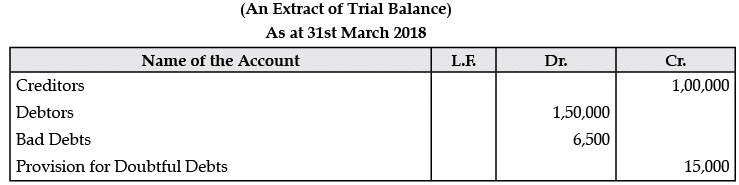
Adjustments:
(1) Write off further Bad debts of Rs. 5,000.
(2) Provision for Doubtful Debts is to be kept at 5% of Debtors.
(3) Provision for discount on Creditors is to be maintained at 10%.
Q.8. Briefly explain the various components of a Computer Hardware.
Computer Hardware is a physical part of a computer. It has following components:
(i) Mother-Board: Mother-Board is a main board of a computer. It is also called logic board. It allows communication between many crucial electronic components of a system.
(ii) Keyboard: Keyboard is an input device. It is used to input text into the computer. All the keys in keyboard are arranged in specific order.
(iii) Speaker: Speaker produces electrical signal produced with the help of amplifier and turn these into sound waves.
(iv) Monitor: It is a computer screen. The Operator can see the result. Now-a-days, LCD Monitors are used instead of CRT monitors which were used in old days.
OR
Explain the importance or application of computers in accounting.
The importance of computers in accounting can be understood by the following:
(i) Accuracy: Accounting through computers is more accurate as there is less possibility of errors. In built controls in the computer reduce the possibility of making errors.
(ii) Time Saving: Accounting in computers saves time. A journal entry is required to be passed in accounts whereas the ledgers, trial balance, profit and loss account are automatically prepared.
(iii) Analysis: Accounting data in computers make analysis of the performance easier. Programs can be written-to generate important performance indicators such as ratios, graphs, etc.
(iv) Audit Trail: The information in computers have audit trails therefore, the entry flow of transaction can be easily determined at one click.
(v) Prevention of Fraud: Information in computers can be prevented from deletion. Moreover, the person who passes the entry is also recorded. Hence, it provides a better control against fraud.
(vi) Data Storage: Accounting through books and registers are cumbersome and also prone to damage. Computer information can be easily stored as well as backup can also be taken.
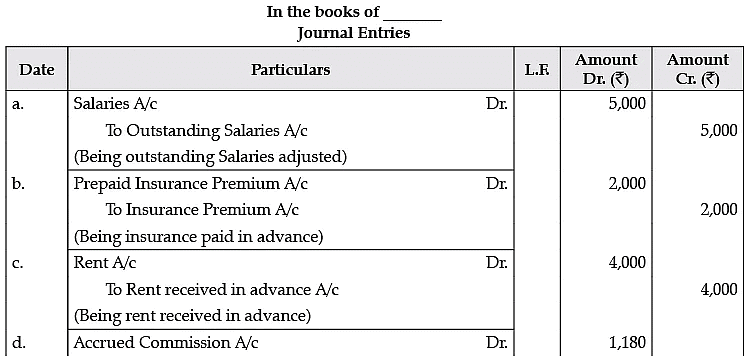
Q.9. Give Journal Entries for the following Adjustments in final accounts assuming CGST and SGST @9% each:
(A) Salaries Rs. 5,000 are outstanding.
(B) Insurance amounting to Rs. 2,000 is paid in advance
(C) Rs. 4,000 for rent have been received in advance.
(D) Commission earned but not yet received Rs. 1,000.
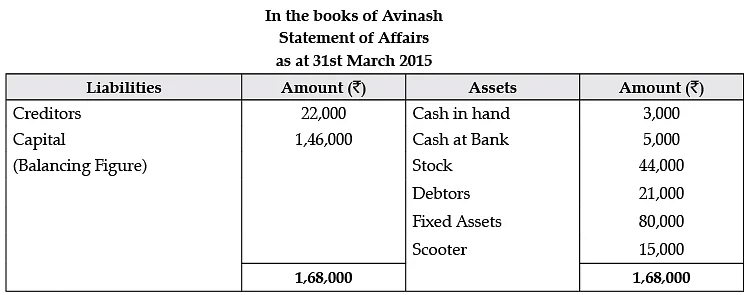
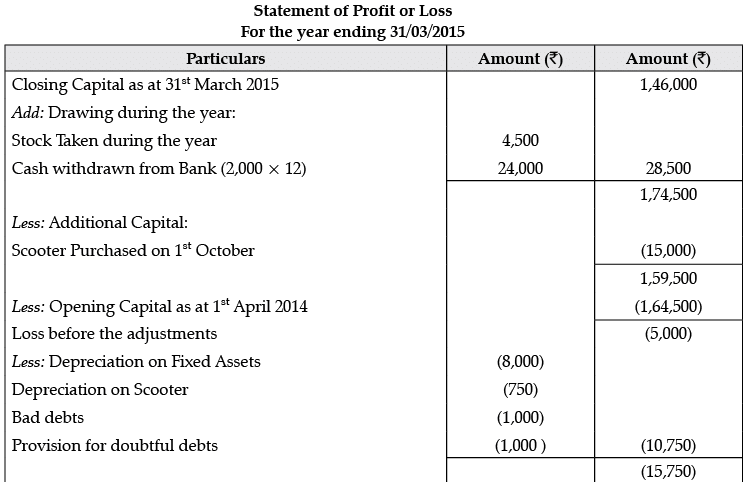
Q.10. The following is the statement of affairs of Avinash as on 1st April 2014:
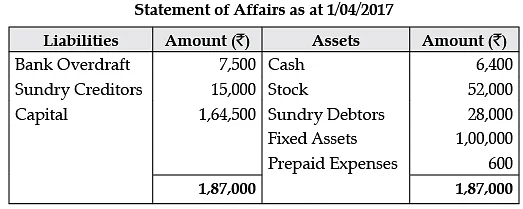
His position on 31st March 2015 are: Cash in Hand Rs. 3,000; Cash at Bank Rs. 5,000; Stock Rs. 44,000; Debtors Rs. 21,000; Fixed Assets Rs. 80,000; Creditors Rs. 22,000.
You are informed that Avinash has taken stocks worth Rs. 4,500 for his private use and that he has been regularly transferring Rs. 2,000 per month from his business banking account by way of drawings. Out of his drawings, he spent Rs. 15,000 for purchasing a scooter for the business on 1st October 2017.
You are requested to find out his profit or loss and also prepare the Statement of Affairs after considering the following:
(a) Depreciate Fixed Assets and Scooter by 10% p.a.
(b) Write Bad-debts Rs. 1,000 and provide 5% for doubtful debts on Sundry Debtors.
(c) Commission earned but not received by him was Rs. 2,500.
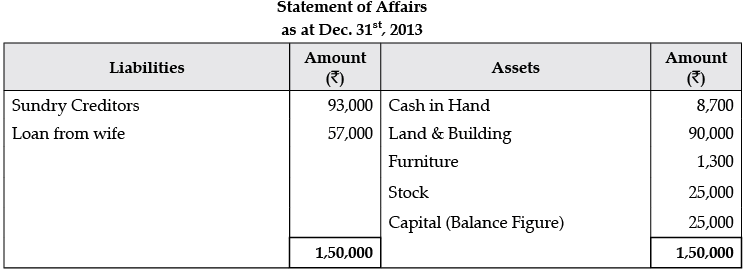
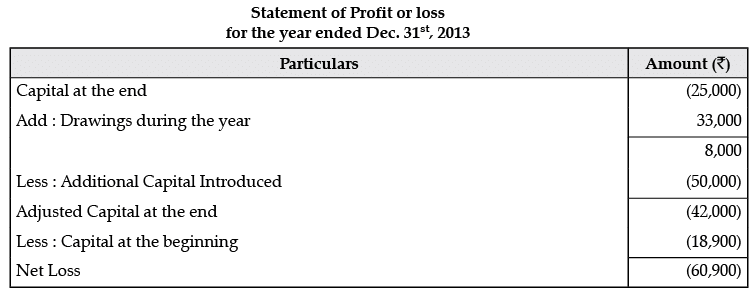
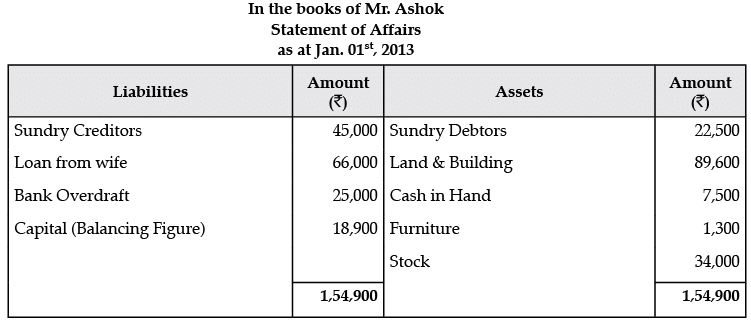
Q.11. Mr. Ashok does not keep his books properly. Following information is available from his books:

During the year Mr. Ashok sold his private car for Rs. 50,000 and invested this amount into the business. He withdraw from the business Rs. 1,500 per month upto July 31, 2013 and thereafter Rs. 4,500 per month as drawings. You are required to prepare the statement of profit or loss and statement of affairs as on December 31st, 2013.
Working Note:
Q.12. (a) Define Accounting Information System.
(a) An Accounting Information System is a system of collecting, processing, summarizing and reporting information about a business organization in monetary terms.
(b) State any three purpose of Accounting Information System.
(b) The purpose of Accounting Information System is as follows:
(i) Sales order Processing: The customer’s orders are processed, and invoices are made. This also facilitates the inventory control and sales analysis.
(ii) Inventory Control: Inventory at various levels of manufacturing process can be easily controlled and monitored with the frequent changes happening in the stock.
(iii) Accounts Receivable: The track of all the debtor of the company and the amount owed by them can be easily traced and calculated.
(iv) Accounts Payable: The record of the amount paid and owed to the creditors can be easily tracked.
(v) Payroll: The computerised recording of the employee time card and the payment to be made accordingly can be easily calculated. It also enables in producing pay checks and efficiency analysis report of individual employee.
(vi) General Ledger: The consolidation of all the accounting information is done easily from the data received.
FAQs on Class 11 Accountancy: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 1 - Sample Papers for Class 11 Commerce
| 1. What are the topics covered in the Class Xl Accountancy exam? |  |
| 2. What is the duration of the Class Xl Accountancy exam? |  |
| 3. How many marks are allotted for the Class Xl Accountancy exam? |  |
| 4. Can you provide more details about Part-A (Accounting Process) in the Class Xl Accountancy exam? |  |
| 5. What are the topics covered in Part-B (Financial Accounting and Computer in Accounts) of the Class Xl Accountancy exam? |  |