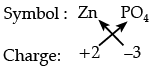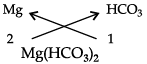Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper Term II- 1 (With Solutions) | Science Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class - IX |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class - IX
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section–A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section–B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section–C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section - A
Q.1: Sum of the total number of protons and neutrons present in the nucleus of an atom is the mass number of an atom while, total number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom is its atomic number. The table below shows the mass number and the atomic number of certain elements named C, D and E. Study the given data and answer the following questions: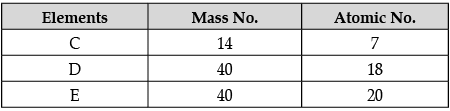
(a) Which element is a noble gas?
(b) Which two elements are isobars?
(a) The atomic number of element D is 18. So, it's electronic configuration will be 2, 8, 8. The outermost shell is complete, so, it is a noble gas.
(b) The elements having different atomic numbers but same mass numbers are called isobars. Element D and E both have same mass number i.e., 40 but different atomic number.
Q.2: Zinc ion and phosphate ion together constitute compound "A".
(a) Write the chemical formula for compound "A".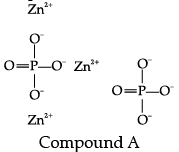
(b) Calculate the ratio by mass of atoms present in a molecule of carbon dioxide.
[Given : C = 12, O=16]
(a)
(b) Atoms of carbon = 1
Mass or carbon = 12 u
Atoms of oxygen = 2
Mass of oxygen = 2 × 16 = 32 u
Thus, the ratio by mass of constituting elements in carbon dioxide is mass of carbon to the mass of oxygen atoms: 12 : 32 3 : 8
Q.3: Ernest Rutherford was interested in knowing how the electrons are arranged within an atom. Rutherford designed an experiment for this. In this experiment, fast moving alpha (α)-particles were made to fall on a thin gold foil. State the observations in the experiment, which led Rutherford to make the following conclusions:
(a) Most of the space in an atom is empty.
(b) Whole mass of an atom is concentrated in its centre.
(a) Most of the alpha-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected.
(b) Very few particles were deflected from their path by 180°, indicating that whole mass of the atom is present at its centre.
Q.4: A person is suffering from an incurable disease. His reports say that he is infected with HIV.
(a) Identify the disease the person is suffering from.
(b) State any two ways by which this disease spreads from an infected person to a healthy person.
(a) The person is suffering from the disease called AIDS (Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome).
(b) (i) Sexual contact with infected person.
(ii) Fro m a pregnant mother to her foetus.
(iii) Blood contact with infected person.
(iv) Using needle or syringe of infected person.
Q.5: A person suffering from disease 'X' cannot fight even minor infections as it damages the immune system. It is mainly transmitted through sexual contacts with infected person. Identify the disease and state its causative agent.
OR
Study the picture and answer the following questions: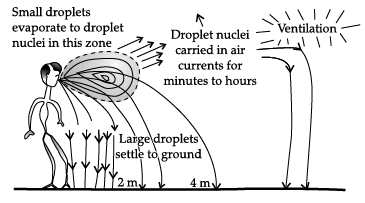 (a) Identify the mode of transmission of the disease in the above picture.
(a) Identify the mode of transmission of the disease in the above picture.
(b) Which of the following diseases could be spread by this mode of transmission: Common cold/ cholera?
Name of the disease: Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
Causative agent: Human immuno-deficiency virus (HIV).OR
(a) Mode of transmission - Air
(b) Through air - Common cold or cough may occur as these are communicable diseases which spread through air.
Q.6: Students of class IX visited a thermal power station as a part of their project. They came to know about how the conversion of energy takes place. Teacher has asked them to find the answers for conversion of energy in following cases:
(a) When coal is burnt.
(b) In a thermal power plant.
OR
The physical quantity 'X' is defined as rate of doing work.
(a) Identify the quantity. State its SI unit.
(b) An electric bulb is rated 15 watts. What does it mean?.
(a) Chemical energy is converted to heat energy.
(b) Chemical energy of fuel is converted to electrical energy.OR
(a) Power is the rate of doing work. Hence the quantity "X" is power. Its SI unit is Watt.
(b) If the power of an electric bulb is 15 W, it consumes 15 joules per second.
Q.7: An astronaut carried a pot containing soil weighing 60 N from the earth to the surface of moon. He kept it there and just before the return journey from moon to earth he weighed the soil on the surface of moon and found that it was only 10 N. Why did its weight decrease and how much was the loss in mass of the soil ? (gearth = 10 ms–2) (gmoon= gearth / 6)
OR
A stone and the Earth attract each other with an equal and opposite force. Then, why we see only the stone falling towards the earth but not the earth rising towards the stone?
Given, the weight of the soil on earth is 60 N.
gearth = 10 ms–2
Mass on the earth, m1 = 60/10 = 6 kg
Weight of the soil on the moon = 10 N
gmoon = gearth/6 = 10/6ms-2
Mass on the moon m2 = 10 x 6 / 10 = 6 kg
Because m1 = m2, hence there has been no loss in mass of the soil on the surface of moon and decrease in weight was due to difference in the gravity.OR
The mass of a stone is very small, due to which the gravitational force produces a large acceleration in it. Due to large acceleration of stone, we see stone falling towards the earth. The mass of earth is, however, very, very large. Due to the very large mass of the earth, the same gravitational force produces very, very small acceleration in the earth, that it cannot be observed. And hence we do not see the earth rising up towards the stone.
Section - B
Q.8: Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
(a) Whose container is heavier?
(b) Both containers have same number of atoms. Explain by calculations.
(c) Which term is used to refer the exact number of atoms present in 12 gm of Carbon-12?
(a) Sohan’s container is heavier.
Explanation: Mass of container containing 5 moles of C atoms = 5 × 12 = 60 g
Mass of container containing 5 moles of Na atoms = 5 x 23 = 115 g
Hence, container containing 5 moles of sodium is heavier.
(b) Yes, it is correct. Both containers have same number of atoms since they contain same number of moles of each carbon and sodium.
No. of moles of Sohan = 5 mol
No. of atoms = 5 × 6.023 × 1023
= 30.115 × 1023 atoms
No. of moles of Rohan = 5 mol
No. of atoms = 5 × 6.023 × 1023
= 30.115 × 1023 atoms.
(c) The exact number of atoms present in 12 gm of Carbon-12 is called Avogadro’s constant.
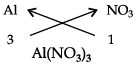
Q.9: Write the chemical formulae of the following :
(a) (i) Aluminium nitrate (ii) Magnesium hydrogen carbonate.
(b) Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(i) Quick lime
(ii) Hydrogen bromide
OR
During an experiment performed in a laboratory, 14 g of sodium bicarbonate was allowed to react with 10 gm of acetic acid. After the reaction was completed, it was found that only 16.67 g of the solution was left because a gas escaped from the container.
(a) What was the mass of the gas that escaped into the atmosphere?
(b) Name and state the law applied to find the answer.
(a) (i)
(ii)
(b) (i) Calcium and oxygen (CaO)
(ii) Hydrogen and bromide (HBr)OR
(a) Mass of the gas that escaped into the atmosphere = 24 – 16.67 = 7.33 gm
(b) The law applied was the law of conservation of mass. The law states that matter can either be created nor destroyed or mass of reactants is always equal to that of product.
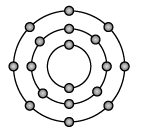
Q.10: Atomic number and mass number of an element are 18 and 40 respectively. Identify the element and write the number of electrons and neutrons present in its atom. Show the schematic atomic structure of the atom.
Name of element : Argon
Number of electrons = 18
Number of neutrons = 22
Structure : 2, 8, 8
Q.11: Composition of the nuclei of two atoms ‘X’ and ‘Y’ are given below :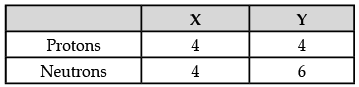 (a) Give the mass number of X and Y. Mention the relationship between the two atoms.
(a) Give the mass number of X and Y. Mention the relationship between the two atoms.
(b) Write the formula for calculating the maximum number of electrons in an orbit.
(a) (i) Mass number i.e., Atomic mass of element X = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
= 4 + 4 = 8 u
(ii) Mass number i.e., atomic mass of element Y = Number of protons + Number of neutrons
= 4 + 6 = 10 u
Relationship between X and Y: Isotope. The atomic number of both the elements is same, but their atomic masses are different.(b) The formula for calculating the maximum number of electrons in an orbit is 2n2.
Q.12: Find the momentum of a body of mass 100 g having kinetic energy 500 J.
OR
A boy is pulling a cart by supplying a constant force of 8 N on a straight path of 20 m. On a round about of 10 m diameter he forgets the path and takes 1 x 1/2 turns and then continues on the straight path for another 20 m. Find the net work done by the boy on the cart.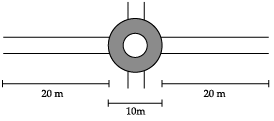
Using the formula for K.E. we get,
K.E. = 1/2mv2
m = 100 g = 0.1 kg
K.E. = 500 Jv2 = 2 x 500/0.1 = 10000
v = 100 m/s
Momentum = Mass × Velocity
= 0.1 × 100 = 10 kg m/sOR
Work done, F = 8N
W = F ×s
W1= 8 × 20 = 160 J
D = 10 m
So, radius r = D/2 = 5 m
Circumference of a circle = 2πr
= 2 × 22/7 × 5 m
= 31.43 m
Distance in 1/2 circle = πr
= 22/7 ×5 = 15.71 m
Total distance covered in 1½ circle
= 31.43 + 15.71 = 47.14 m
Therefore, work done will be,
W2 = F ×s = 8 × 47.14 = 377.12 J
Again travelling for 20 m, work done will be,
W3 = 20 × 8 = 160 J
Total work done = 160 + 377.12 + 160
= 697.12 J
Q.13: Weight is the force by which an object is attracted towards the earth. A man's weight when taken at the poles is 600 N.
(a) Will his weight remain the same when measured at the equator?
(b) Will there be an increase or decrease in his weight? Explain.
(a) No, his weight will not remain same as that at the poles.
(b) There will be a decrease in his weight at the equator. As the radius of the earth increases from the poles to the equator, the value of 'g' becomes greater at poles decreasing towards equator. Also, the force of gravity decreases from poles to the equator.
Section - C
Q.14: Read the passage and answer the following questions.
Human beings live in societies. Our social environment is an important factor in our individual health. We live in villages, towns or cities. In such places, even our physical environment is decided by our social environment. At any place, our body may feel sickness. There are many tissues in the body which make up physiological systems to carry out functions. When there is a disease some changes give rise to symptoms and signs of disease.
(a) What is a disease?
(b) What are called the symptoms of a disease?
(c) What can be various causes for a person getting diseased?
OR
Based on duration what are the two main types of diseases? Explain giving one example for each.
(a) Any condition which impairs the health, or interferes with the normal functioning of the body is called disease.
(b) A symptom is a phenomenon that is experienced by the individual affected by the disease.(c) Causes :
(i) Extrinsic factor : Water, food.
(ii) Intrinsic factor : Poor eating habits, poor nourishment.
(iii) Genetic constitution : Weak immune system.
(iv) Social reason : Poor public services
Q.15: Since, Work is done when a force acting on a body produces displacement in it.
Work done = Force × Displacement in the direction of force. If four men lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it without raising or lowering it
(a) How much work do they do in just holding it?
(b) Why do they get tired while holding it?
(c) How much work is done by the men in lifting the box?
OR
Define the work done by a constant force. Write its SI unit and define this unit.
(a) Work done will be zero because the box does not move. So, the displacement is zero that's why work done is zero.
(b) In holding the box, men are applying a force which is opposite and equal to the gravitational force acting on the box. While applying the force, muscular effort is involved. So, they feel tired.
(c) Given, Mass, m = 250 kg,
Height, h = 1 m
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 10 m/s
Work done by the man in lifting the box=Potential energy of box
W = mgh
On putting the values,
W = 250 × 1 × 10 = 2500 JOR
Work is said to be done when a force acts on an object and the object covers some distance. Its SI unit is Joule. Joule is equal to the work done by a force of one newton acting through one meter.
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper Term II- 1 (With Solutions) - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the duration of Class 9 Science Term II-1 exam? |  |
| 2. What are the different sections in the Class 9 Science Term II-1 exam? |  |
| 3. How many questions are there in each section of the Class 9 Science Term II-1 exam? |  |
| 4. What is the difficulty level of the questions in the Class 9 Science Term II-1 exam? |  |
| 5. Where can I find sample question papers with solutions for Class 9 Science Term II-1 exam? |  |