Class 12 Geography: CBSE Sample Question Papers- Term II (2021-22)- 1 | CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Humanities - Humanities/Arts PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class XlI |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
| Section - E |

|
Class XlI
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 5 sections A,B,C,D & E
- In section A question number 1 to 3 are Very Short Answer type questions.
- In section B question number 4 is Source based question.
- In section C question number 5 & 6 are Short Answer type questions.
- In section D question number 7 to 9 are Long Answer type questions.
- In section E question number 10 is a Map based question.
Section - A
Q.1. Mention any two problems of the Ruhr Industrial Region.
Problems of the Ruhr Industrial Region are:
(i) Industrial waste(ii) Pollution
(iii) Iron ore exhaustion
Q.2. Write the meaning of ‘medical tourism’.
When medical treatment is combined with international tourism activity, it is commonly known as medical tourism. Here people are travelling for gaining international medical care. It is also known as health tourism, surgical tourism or medical travel.
Q.3. What is nuclear power? Mention any two important nuclear power stations in India.
The power obtained by splitting atoms is called nuclear power. Nuclear power has emerged as a viable source in recent times. Important minerals used for the generation of nuclear energy are uranium & thorium. Tarapur in Maharashtra and Narora in Uttar Pradesh are two important nuclear power stations in India.
OR
What is ‘sectoral planning’?
The sectoral planning provides general guidelines directed towards ensuring the orderly and efficient development of facilities, land uses, transportation systems, population density and sequencing of development. Full consideration must be given to the costs and benefits of various actions upon the present and future social, economic and environmental fabric of the area.
Section - B
Q.4. Read the extract given below and answer the questions that follow:
Manufacturing means ‘to make by hand’. However, now it includes goods ’made by machines’. It is essentially a process which involves transforming raw materials into finished goods of higher value for sale in local or distant markets. Conceptually, an industry is a geographically located manufacturing unit maintaining books of accounts and records under a management system. As the term industry is comprehensive, it is also used as synonymous with ‘manufacturing’. When one uses terms like ‘steel industry’ and ‘chemical industry’, one thinks of factories and processes. But there are many secondary activities which are not carried on in factories such as what is now called the ‘entertainment industry’ and ‘Tourism industry’, etc. So for clarity, the longer expression ‘manufacturing industry’ is used.
(i) What do you understand by the term Manufacturing?
Manufacturing literally means ‘to make by hand’. However, now it includes goods ’made by machines’..
(ii) “Manufacturing involves value addition.” Explain with a suitable example.
It is essentially a process which involves transforming raw materials into finished goods of higher value. Example–Raw cotton is transformed to more valuable threads and then threads are further transformed into more valuable fabric..
(iii) Name two industries that provide services rather than production of goods.
The ‘Entertainment industry ’ and ‘Tourism industry ’.
Section - C
Q.5. Describe the three advantages of water transport in India.
Advantages of water transport in India:
(i) Waterways is an important mode of transport for both passenger and cargo traffic in India. It is the cheapest means of transport.
(ii) It is a fuel-efficient, eco-friendly mode of transport.
(iii) It is the most suitable mode of transport for carrying heavy and bulky material.
Q.6. What is noise pollution? Explain any three sources of noise pollution.
Noise pollution refers to the state of unbearable and uncomfortable noise to human beings, which is caused by noise from different sources. In recent years, noise pollution has become a serious problem. The following sources are mainly responsible for noise pollution:
(i) The main sources of noise pollution are various factories, mechanised construction and demolition works, automobiles and aircrafts, etc.
(ii) Various community activities also produces polluting noise through sirens, loudspeakers etc.
(iii) Out of all the sources, the biggest nuisance is the noise produced by traffic because of its intensity and nature depend upon factors, such as the type of aircraft, vehicle, train and the condition of road, as well as, that of vehicle.
OR
Describe any three major problems of slums in India.
The three problems faced by slum dwellers in India are:
(i) The areas in which they live (dilapidated houses) are overcrowded having narrow street pattern prone to serious hazards from fire.
(ii) Lack of basic amenities like drinking water, light and toilet facilities. Their houses have poor ventilation and poor hygienic conditions.
(iii) These slums in the nearby areas cause a lot pollution and thus, result in health hazards. Since they have no place to bathe, go to the toilet, wash their clothes, all this daily work is done in the open causing inconvenience to the residents of the areas.
Section - D
Q.7. How do Quaternary services differ from Tertiary services? Give three reasons why the service sector in developing and developed countries is growing faster than the manufacturing sector?
The activities which involve intangible outputs and are relatively attached from material products such as the services of a technician or a teacher are referred to as Tertiary activities.
The activities concerning knowledge such as education, information, research and development and more intellectual activities where the major task is to think, research and develop ideas are Quaternary activities.
(i) The rising per capita income in both, developed and developing countries has generated proportionately larger increases in the many kinds of services.
(ii) There is also demand for educational services at all levels with the increase in the demand for literacy and computer skills at the workplace.(iii) Demand for non-direct production workers is also increasing proportionally in most manufacturing companies as these companies need more clerical staff, salespeople, research and other workers.
(iv) Medical services have also increased in Europe, North America and Japan because of an increase in demand for medical care from the elderly population.
(v) The increasing value of time has led to more household functions being accomplished outside of the home.
Q.8. How is the use of plastic bags harmful for environmental degradation? Evaluate it by citing suitable reasons.
Plastic is a non-biodegradable substance and its use and production should be minimum. Plastic debris is found everywhere, from the Arctic to Antarctica. It clogs street drains in our cities; it litters campgrounds and national parks, and is even piling up on Mount Everest. Thanks to runoff, and to our fondness for directly dumping our trash into the nearest river or lake, plastic is growing increasingly common in the world’s oceans. When plastics are broken down, this simply means one large piece of plastic is reduced into a bunch of smaller pieces of plastic. These smaller pieces of plastic can be consumed by smaller animals, but are still indigestible. It affects all organisms in the food chain from tiny species like plankton to whales. Toxins work their way up the food chain when plastic is ingested and can even be present in the fish people eat. From cell phones to bicycle helmets to IV bags, plastic has molded society in ways that make life easier and safer. But the synthetic material has also left its harmful imprints on the environment.
(i) Chemicals added to plastics are absorbed by human bodies. Some of these compounds have been found to alter hormones or have other potential human health effects.
(ii) Plastic debris, laced with chemicals, is often ingested by marine animals, which injured and poison wildlife.
(iii) Floating plastic waste, which can survive for thousands of years in water, serves as mini transportation devices for invasive species, disrupting habitats.
(iv) Plastic buried deep in landfills can leach harmful chemicals that spread into groundwater.
(v) Around 4 percent of world oil production is used as a feedstock to make plastics, and a similar amount is consumed as energy in the process.
OR
The disposal of urban waste has become a serious concern for the local authorities. Analyze the statement with suitable examples.
The problem of the overcrowded, congested and insufficient infrastructure of urban areas results in the accumulation of huge urban waste. There are two sources of urban waste– Household or domestic sources and industrial or commercial sources. The mismanagement of urban waste disposal is a serious problem in big cities.
(i) Tons of waste come out daily in metropolitan cities and is burnt. The smoke released from the waste pollutes the air.
(ii) Lack of sewers or other means to dispose of human excretes safely and the inadequacy of garbage collection sources adds to water pollution.
(iii) The concentration of industrial units in and around urban centres gives rise to a series of environmental problems. Dumping industrial waste into rivers is the major cause of water pollution. The solid waste generation continues to increase in both absolute and per capita in cities.
(iv) This improper disposal of solid waste attracts rodents and flies which spread diseases. The thermal plants release a lot of smoke and ash in the air. For example, a plant producing 500mw electricity releases 2000 tons of ash which is difficult to manage.
(v) In most cities and towns, about 30 to 50 percent of the waste generated is left uncontrolled which accumulate on streets, in open spaces between houses and in wastelands leading to serious health hazards.
Q.9. Attaining Sustainable development in the command area requires major thrust upon the measures to achieve ecological sustainability. Highlight the measures proposed to promote sustainable development in the command area of Indira Gandhi Rajasthan Canal.
Seven measures proposed to promote sustainable development in the command area are meant to restore ecological balance.
(i) The first requirement is strict implementation of water management policy. The canal project envisages protective irrigation in Stage-I and extensive irrigation of crops and pasture development in Stage-II.(ii) In general, the cropping pattern shall not include water intensive crops. It shall be adhered to and people shall be encouraged to grow plantation crops such as citrus fruits.
(iii) The CAD programmes such as lining of water courses, land development and leveling and warabandi system (equal distribution of canal water in the command area of outlet) shall be effectively implemented to reduce the conveyance loss of water.
(iv) The areas affected by water logging and soil salinity shall be reclaimed.
(v) The eco-development through afforestation, shelterbelt plantation and pasture development is necessary particularly in the fragile environment of Stage-II.
(vi) Social sustainability in the region can be achieved only if the land allottees having poor economic background are provided adequate financial and institutional support for cultivation of land.
(vii) The economic sustainability in the region cannot be attained only through the development of agriculture and animal husbandry. The agricultural and allied activities have to develop along with other sectors of the economy. This shall lead to diversification of economic base and establishment of functional linkages between basic villages, agro-service centers and market centers.
Section - E
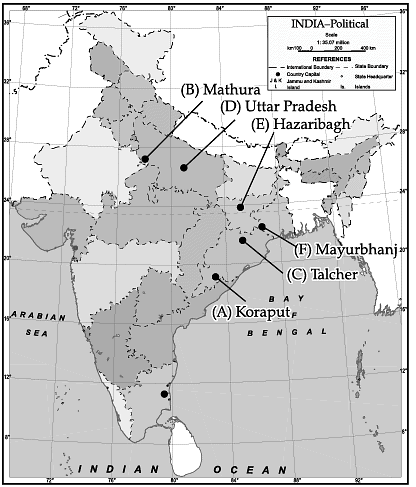
Q.10. On the outline map of India indicate and mark the following features.
(a) The Bauxite mines in Orissa.
(b) The Oil Refineries in Uttar Pradesh.
(c) Coal mines in Orissa.
(d) The state with largest number of out-migrants.
(e) The Copper mines in Jharkhand.
(f) An iron ore mining area in Orissa
(a) Koraput
(b) Mathura(c) Talcher
(d) Uttar Pradesh
(e) Hazaribagh
(f) Mayurbhanj
|
145 docs|4 tests
|