Class 12 Biology: CBSE Sample Question Paper- Term II (2021-22)- 4 | Sample Papers for Class 12 Medical and Non-Medical PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class-XII |

|
| Time: 120 Minutes |

|
| Max. Marks: 35 |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
Class-XII
Time: 120 Minutes
Max. Marks: 35
General Instructions :
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 13 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section–A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Section–B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section–C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section - A
Q.1. HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) gains entry into the cells after infecting the human body. Name the cells into which HIV enters and explain the events that occur in these cells.
HIV (Human immuno deficiency virus) The HIV gains entry into the macrophages and the helper T-cells after infecting the human body.
Events that occur in the human host after the entry of HIV:
(a) After entering the human body, the HIV virus attacks and enters the macrophages.
(b) Inside the macrophages, the RNA of the virus replicates with the help of enzyme reverse transcriptase and give rise to viral DNA.
(c) Then, this viral DNA incorporates into the host cell DNA, uses raw materials and infected cell machinery and directs the synthesis of virus particles.
(d) At the same time, HIV enters the helper T-lymphocytes, replicates and produces progenies.
(e) As a result, T-lymphocytes start decreasing in number and immune response of the person becomes weak.
Q.2. "Large scale cultivation of Spirulina is highly advantageous for human population." Give two reasons for the above statement.
OR
Not all microbes are pathogenic. Several microbes are useful to man in diverse ways. Name the microbes that help in the production of the following products commercially:
(a) Statin
(b) Citric acid
(c) Penicillin
(d) Butyric acid
Source of good protein, fats, carbohydrates, minerals and vitamins for undernourished humans and animal population, its cultivation reduce environmental pollution / can be grown in wastewater / molasses / straw / animal manure, easy to cultivate.
OR
(a) Monascus purpureus
(b) Aspergillus niger
(c) Penicillium notatum
d) Clostridium butylicum
Q.3. Name two drugs obtained from the latex of the plant given below. “These drugs are medically useful but are often abused“. Taking the mentioned examples, justify your answer by giving reasons. 
Morphine and heroin are the drugs that are extracted from the latex of unripe capsules of poppy plant (Papaver somniferum). Morphine acts as an effective pain killer and sedative. Heroin (a derivative of morphine) is used as depressant. If these drugs are used in excess, then it may impair the physical and mental state of a person and is said to be abused.
Q.4. Given below is a table depicting population interactions between species A and species B.

Name the types of interactions (a) and (b) in the above table.
(a) Amensalism
(b) Predation
Q.5. The image shown below is of a typical biogas plant.
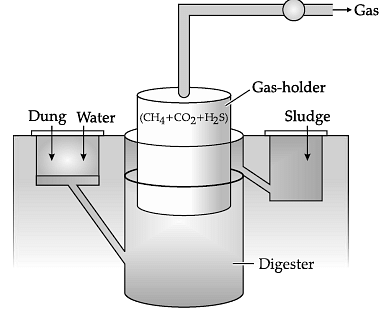
List the events that lead to biogas production from wastewater whose BOD has been reduced significantly.
Events that lead to biogas production from waste water with reduced BOD are :
(a) Once the BOD of wastewater is significantly reduced, the effluent is passed into a settling tank for sedimentation.
(b) From the settling tank, the major part of sedimented material called activated sludge (bacterial flocs) is pumped into large tanks called anaerobic sludge digester and a small part is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as inoculum.
(c) In these tanks, the sludge is anaerobically digested by bacteria and fungi and the biogas is produced which is a mixture of methane, hydrogen sulphide and CO2. The biogas can be used as a source of energy as it is inflammable.
Q.6. Ronit has gone on a trek. After reaching high altitude, he started feeling sick. A doctor suggested that he is suffering from “Altitude sickness’.
Why does Ronit suffers from altitude sickness after reaching the high-altitude regions? Give any two ways by which his body will acclimatize after a couple of days?
OR
In the absence of an external source of water, the kangaroo rat and desert plants in North American deserts are capable of meeting all their water requirements.
How do kangaroo rats and desert plants adapt themselves to survive in their extreme habitat?
“Altitude sickness” is because of low atmospheric pressure at high altitude and as a result, the body does not get sufficient oxygen.
The body compensates low oxygen availability by increasing RBCs production, decreasing the binding capacity of haemoglobin, and by increasing the breathing rate.OR
Kangaroo rats fulfil the water requirement by internal oxidation of fat in the absence of water. It also has the ability to concentrate its urine, so that minimal volume of water is used to remove excretory products.
Desert plants have thick cuticle to prevent loss of water. CAM plants open their stomata during the night time to reduce the loss of water during photosynthesis.
Section - B
Q.7. How do normal cells get transformed into cancerous neoplastic cells? Elaborate by giving three examples of inducing agent.
OR
A person is suffering from a high-grade fever. Which symptoms will help to identify if he/she is suffering from typhoid, pneumonia or malaria?
Transformation of normal cells into cancerous neoplastic cells may be induced by following physical, chemical or biological agents causing DNA damage:
- Ionizing radiations like X-rays and gamma rays.
- Non-ionizing radiations like UV.
- Chemical carcinogens present in tobacco smoke.
- Cellular oncogenes (c-onc) or protooncogenes, when activated under certain conditions causes cancer. Viruses with oncogenes can transform normal cells to cancerous cells.
OR
If the person has sustained high fever (39° to 40°C), weakness, stomach pain, constipation, headache and loss of appetite, then the person is suffering from typhoid.
If the person has fever, chills, cough and headache; and the lips and fingernails turn grey to bluish in color, it is pneumonia.
If the person has chills and high fever recurring every three to four days then, it is malaria.
Q.8. Recognition of an antigenic protein of a pathogen or exposure to a pathogen occurs during many types of immune responses, including active immunity and induced active immunity.
Specify the types of responses elicited when human beings get encountered by a pathogen.
- When our body encounters an antigenic protein or a pathogen for the first time, it produces a response which is of low intensity and our body retains memory of the first encounter.
- The subsequent encounter with the same pathogen elicits a highly intensified response carried out with the help of two special types of lymphocytes present in our blood, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes.
- The B-lymphocytes produce an army of proteins in response to these pathogens into our blood to fight with them. These proteins are called antibodies. The T-cells themselves do not secrete antibodies but help B-cells to produce them.
Q.9. In a pathological lab, a series of steps were undertaken for finding the gene of interest. Describe the steps, or make a flow chart showing the process of amplification of this gene of interest.
The flow chart showing the three steps involved in the process of PCR:
Step-I: Denaturation: The DNA strands are treated at a temperature of 94°C – 98°C (Heat) and the strands are separated.
Step-II: Annealing: The primers anneal to the complementary strands.
Step-III: Extension: The DNA polymerase facilitates the extension of the strands.OR
Q.10. (a) ‘The Evil Quartet’ describes the rates of species extinction due to human activities. Explain how the population of organisms is affected by fragmentation of the habitats.
(b) Introduction of alien species has led to environmental damage and decline of indigenous species. Give any one example of how it has affected the indigenous species?
(c) Could the extinction of Steller’s sea cow and passenger pigeon be saved by man? Give reasons to support your answer.
(a) When a large habitat is broken into small fragments due to various activities, mammals and birds requiring large territories and certain animals with migratory habitats are badly affected, leading to population decline.
(b)
- Nile perch introduced in Lake Victoria eventually led to the extinction of an ecologically unique assemblage of more than 200 species of cichlid fish.
- Parthenium/Lantana/water hyacinth caused environmental damage and threat to our native species.
- African catfish-Clarias gariepinus intro- duced for aquaculture purposes is posing a threat to the indigenous catfishes in our rivers.
(c) Yes; Humans have overexploited natural resources for their ‘greed’ rather than ‘need’ leading to extinction of these animals. Sustainable harvesting could have prevented extinction of these species.
Q.11. (a) The image shown below is of a sacred grove found in India. Explain how has human involvement helped in the preservation of these biodiversity rich regions.

(b) Value of Z (regression coefficient) is considered for measuring the species richness of an area. If the value of Z is 0.7 for area A, and 0.15 for area B, which area has higher species richness and a steeper slope?
(a) India’s history of religious and cultural traditions emphasized the protection of nature. In many cultures, tracts of forest are set aside, all the trees and wildlife within are venerated and given total protection. Sacred groves in many states are the last refuges for a large number of rare and threatened plants.
(b) Area A will have more species richness and a steeper slope.
Q.12. The image below depicts the result of gel electrophoresis.

If the ladder represents the sequence length upto 3000 base pairs (bp),
(a) Which of the bands (I - IV) correspond to 2500 bp and 100 bp respectively?
(b) Explain the basis of this kind of separation and also mention the significance of this process.
(a) Band III corresponds to 2500 bp (base pairs) and Band IV corresponds to 100 bp.
(b) The fragments will resolve according to their size. The shorter sequence fragments would move farthest from well as seen in Band IV (100 bp) which is lighter as compared to Band III which is heavier being 2500 base pairs.
The significance of electrophoresis is to purify the DNA fragments for use in constructing recombinant DNA by joining them with cloning vectors.
Section - C
Q.13. Read the following passage and answer the following questions.
Restriction endonuclease was isolated for the first time by W. Aber in 1962 in bacteria. Restriction endonuclease cut the DNA duplex at specific points, therefore they are also called as molecular scissors or biological scissors. Three types of restriction endonuclease are Type I, Type II and Type III. But only Type II restriction endonuclease are used in recombinant DNA technology. Restriction endonuclease EcoRI recognises the base sequence GAATTC in DNA duplex and cut strands between G and A.
(a) Why only type II restriction enzymes are used in gene manipulation?
(b) Name the ions used by restriction endonuclease for restriction activity.
(c) Why are molecular scissors so called? Write their use in biotechnology.
(d) Restriction enzymes present in the cloning site of a vector should not have more than one recognition site. Comment.
OR
Given diagram shows the process of gel electrophoresis.
 Gel electrophoresis is performed in a gel matrix so that molecules of similar electric charges can be separated on the basis of their size. Most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is agarose. The fragments are separated under the influence of an electric field. The separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining the DNA with compound known as ethidium bromide (EtBr) followed by exposure to UV radiation as bright orange band.
Gel electrophoresis is performed in a gel matrix so that molecules of similar electric charges can be separated on the basis of their size. Most commonly used matrix in gel electrophoresis is agarose. The fragments are separated under the influence of an electric field. The separated DNA fragments can be seen only after staining the DNA with compound known as ethidium bromide (EtBr) followed by exposure to UV radiation as bright orange band.
(a) What is the principle of gel electrophoresis?
(b) Why EtBr is used in gel electrophoresis inspite of it being highly carcinogenic?
(a) Type II enzymes are simpler and don't require ATP as an energy source, unlike Type I, it makes cleavage or cut in the DNA sequence within or in close proximity of the recognition site.
(b) The restriction endonuclease binds with two magnesium ions. One of these ions, binds to the phosphate group where the cleavage occurs and is required for catalysis.
(c) The restriction enzymes are known as molecular scissors as they cut the DNA at specific sites or locations.
They help (in genetic engineering) to form recombinant molecules of DNA, which are composed of DNA from different genomes.
(d) If the restriction enzymes have more than one recognition site in a vector, then the vector itself will get fragmented on treatment with the restriction enzymes.OR
(a) Gel electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation and analysis of macro molecules (DNA, RNA and proteins) and their fragments, based on their size and charge.
(b) Ethidium bromide (EtBr) exchanges its visible range of wavelength with the invisible wavelength of DNA to make it visible under UV light.
|
159 docs|4 tests
|
|
159 docs|4 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|


















