Tenses | English Grammar for Junior Classes - Class 1 PDF Download
Introduction to Tenses
- Tenses are used to indicate when an action occurred.
- They help us understand if something happened in the past, is happening in the present, or will happen in the future.
- There are three main types of tenses:
- Past Tense: This tense shows that an action has already occurred.
- Present Tense: This tense indicates that an action is currently taking place.
- Future Tense: This tense is used for actions that will happen later.

1. Present Tense:
- Present Tense talks about things happening now.
- Use the base form of the verb (the verb without 'to') for most actions in the present.
Examples:
- I eat an apple. (action happening now)
- She plays with her toys. (action happening now)
2. Past Tense:
- Past Tense talks about things that happened before now.
- Add 'ed' to regular verbs to make them past tense.
Examples:
- I ate an apple. (action happened in the past)
- He watched a movie yesterday. (action happened in the past)

3. Future Tense:
- Future Tense talks about things that will happen later.
- Use "will" before the base form of the verb for most future actions.
Examples:
- I will eat an apple. (action will happen in the future)
- They will go to the park tomorrow. (action will happen in the future)

4. Present Continuous Tense:
- Present Continuous Tense talks about actions happening right now.
- Use "am/is/are" + the base form of the verb + 'ing'.
Examples:
- I am eating an apple. (action happening right now)
- She is playing with her toys. (action happening right now)
5. Past Continuous Tense:
- Past Continuous Tense talks about actions that were happening in the past.
- Use "was/were" + the base form of the verb + 'ing'.
Examples:
- I was eating an apple when the phone rang. (action happening in the past)
- They were playing in the garden yesterday. (action happening in the past)
6. Future Continuous Tense:
- Future Continuous Tense talks about actions that will be happening at some point in the future.
- Use "will be" + the base form of the verb + 'ing'.
Examples:
- I will be eating dinner at 7 PM. (action in the future)
- She will be playing with her friends tomorrow. (action in the future)
7. Present Perfect Tense:
- Present Perfect Tense talks about actions that happened at an unspecified time before now.
- Use "have/has" + the past participle form of the verb.
Examples:
- I have eaten lunch. (action happened at an unspecified time before now)
- He has visited the museum. (action happened at an unspecified time before now)
8. Past Perfect Tense:
- Past Perfect Tense talks about actions that happened before another action in the past.
- Use "had" + the past participle form of the verb.
Examples:
- I had already eaten lunch when she called. (action happened before another action in the past)
- They had finished their homework before going out. (action happened before another action in the past)
9. Future Perfect Tense:
- Future Perfect Tense talks about actions that will be completed before some point in the future.
- Use "will have" + the past participle form of the verb.
Examples:
- By 5 PM, I will have finished my work. (action will be completed before a point in the future)
- She will have read the book by next week. (action will be completed before a point in the future)
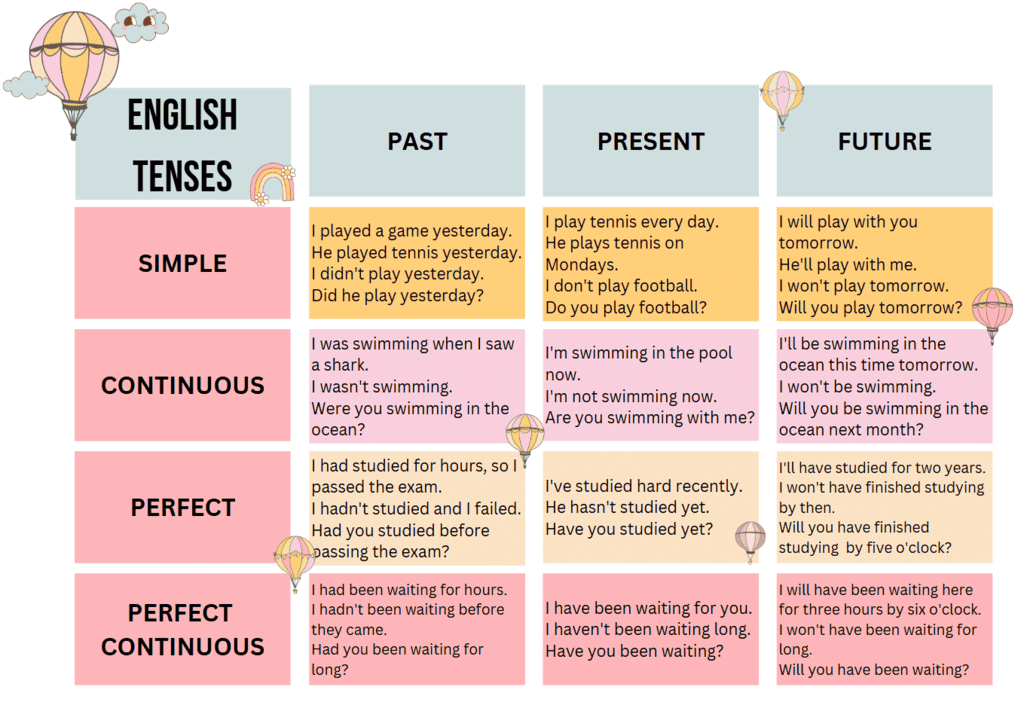
Summary
In this table, you can learn about different tenses in the English language, which are used to describe actions that happen at different times. Let’s get started! You will see how each form is used in sentences.
Some Solved Questions
Q1. What tense is used in this sentence: "I went to market."
Ans. Simple past tense
Q2. What tense is used in this sentence: "I will call you tomorrow."
Ans. Simple future tense
Q3. What tense is used in this sentence: "I play football very well."
Ans. Simple present tense
Q4. What tense is used in this sentence: "Mr Ravi taught us English."
Ans. Simple past tense
Q5. Complete the sentences with the correct continuous forms of the verbs in brackets.
a) I ………………………………. for the shops to open last evening. (wait)
Ans. I was waiting for the shops to open last evening.
b) Yes, she ………………………………. the conference. (attend)
Ans. Yes, she will be attending the conference.
c) The universe ………………………………. and has been doing so since its
beginning. (expand)
Ans. The universe is expanding and has been doing so since its beginning.
|
18 videos|286 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Tenses - English Grammar for Junior Classes - Class 1
| 1. What are the three main tenses in English? |  |
| 2. How do I identify the tense of a verb in a sentence? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between simple and continuous tenses? |  |
| 4. Can you give examples of perfect tenses? |  |
| 5. Why is it important to use correct tenses in writing? |  |





















