Explained: Language and Literature | GK Olympiad for Class 6 PDF Download
Introduction
- Language is a means of communication, ideas or feelings by the use of conventionalized sounds and signs, thus being the spoken and written language. Language is a set of words to express our ideas to others. Thus it is clear that without language, there is no existence of literature because without language we cannot express our thoughts. Language is the fundamental unit of literature. It can be said that language makes literature.
- Literature is produced by the creation of works in a particular language by the writer of the language. On the other hand, language is a mode of expression of thoughts by means of articulate sound. A language comprises of sounds, words and sentences. While literature is made up of the thoughts expressed in any given language.
- The language that was spoken in earlier times is called the Early Dravidian language. The languages that evolves from this are Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Malayalam, etc.
- There is another language called the Indo-Aryan language and the languages that are influenced rather born from this include Sanskrit, Hindi, Bengali, Marathi, etc.
- There are number of languages that are in existence in the world. Some of the widely used languages include Chinese, English, French, Spanish, Italian, German, Arabic, and Russian apart from the native Indian languages. English being the most widely spoken language across the world.
Literary devices
There are some techniques used by writers in their writings in order to make the readers think in a particular way. These techniques can be used to inspire, surprise, persuade or simply convey some message to the reader.
- Simile: It is used to compare two things of different kinds but have atleast one point in common.
For example: words are like leaves and where they most abound. - Metaphor: It is an implied simile. Here we don’t say one thing is like another, but takes that for granted and think as if the two things are one.
For example:
(i) He was a lion in the fight,
(ii) Life is a dream,
(iii) Variety is the spice of life. - Personification: In this, inanimate objects are spoken of as having life and intelligence.
For example:
(i) Laughter holding both her sides.
(ii) Death lays his icy hand on kings. - Hyperbole: A statement is made emphatic by overstatement, a kind of exaggeration.
For example:
(i) O Hamlet! Thou hast left my heart in twain.
(ii) Here’s the smell of blood still; all the perfumes of Arabia will not sweeten this little hand. - Irony - In this the real meaning is exactly the opposite of that which is literally conveyed.
For example
(i) No doubt but you are the people, and wisdom shall die with you.
(ii) The bread is soft as a stone. - Satire: A kind of humour at someone’s or something’s expense, often with the intention of hurting them.
- Onomatopoeia: A word that sounds like the sound it represents.
For example: The autumn leaves cracked and crunched underfoot. - Allegory: In this technique, an abstract idea is given a form of characters, actions or events.
- Analogy: It is a comparison in which an idea or thing is compared to another thing that is quite different from it.
For example: Life is like a race.
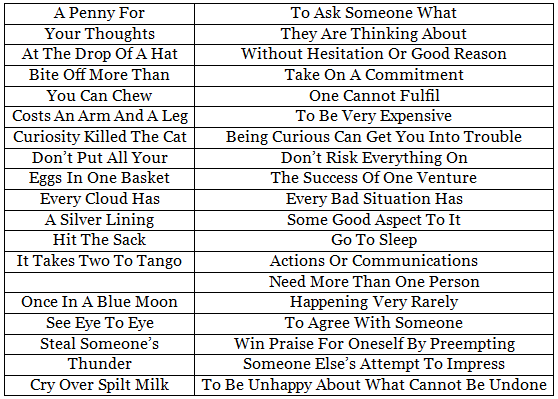
Similes
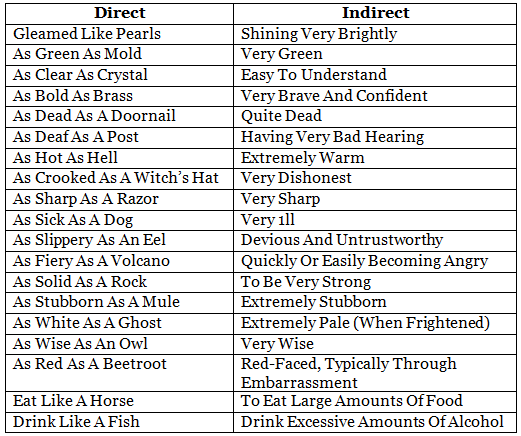
Idioms
English Literature
The English literature can be divided into various genres. It’s two main categories are fiction and non-fiction. Fiction includes poetry, drama, fairy tales, science fiction folklore, historical fiction, mythology and epic. The non-fiction includes essays, biography, autobiography. It is the broadest category of literature.
Graphic Novels
- Graphic novels are illustrated stories. It is somewhat similar to a comic strip but has a more complex plot with a beginning and an end, and lot more characters.
- World’s first graphic novel form was perhaps the carvings on pillars made by ancient Roman ruler Trajan of accounts of his victories as a continuous picture story.
- Picture jokes were published in newspapers and were called ‘Funnies’ or the ‘Comic Papers’. After WWI, publishers assembled weekly funnies into comic books.
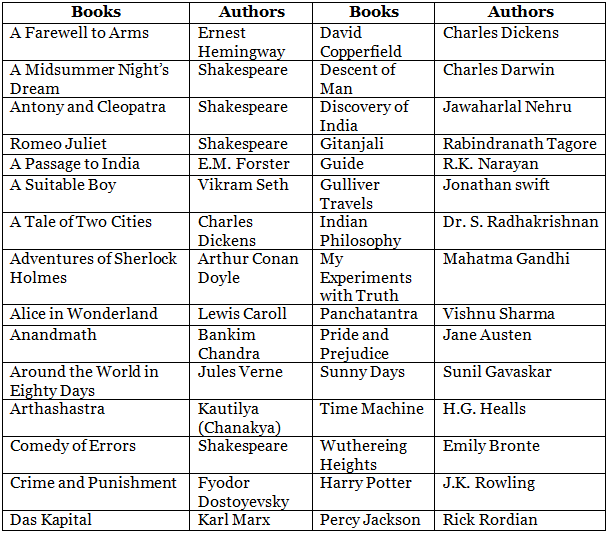
Famous Books and Authors
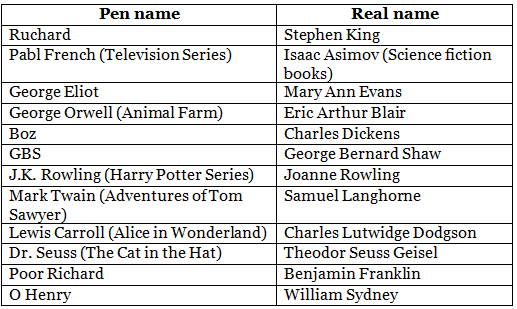
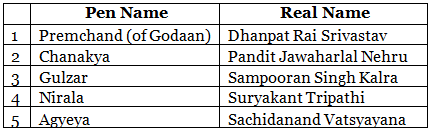
Pseudonym/Pen Name Of Writers
It would be quite an achievement to have one’s name listed as an author or writer of a book. However, there are some authors who, for various reasons, decided to use a pen name on their books. It maybe for private reasons, or to get a fresh start or even to hide their gender.
Indian writers
|
39 videos|80 docs|102 tests
|