Force, it's Effects & Types | Science Olympiad Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Force? |

|
| Effects of Force |

|
| What are Balanced Forces? |

|
| What are Unbalanced Forces? |

|
What is Force?
What is Force?
It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts.
It is believed that rest is the natural state of an object. We put in some effort like pushing, pulling, stretching, pressing, hitting, etc. in order to move the object at rest into motion. The objects move because we apply a force on them.
Examples :
- A force is used when we push the door to open it.
- When we pull the drawer of a table, a force is used.
- A force is used in lifting a heavy box.
- A force is used when we squeeze out water by twisting wet clothes.
- Dry leaves from trees fly away because the force of wind pushes them.
Effects of Force
Effects of Force
We cannot see force. A force can be judged only by the effects by it. A force can produce the following effects :
- A force can move a stationary object.
- A force can stop a moving object.
- A force can change the direction and speed of a moving body.
- A force can change the shape and size of a body.
What are Balanced Forces?
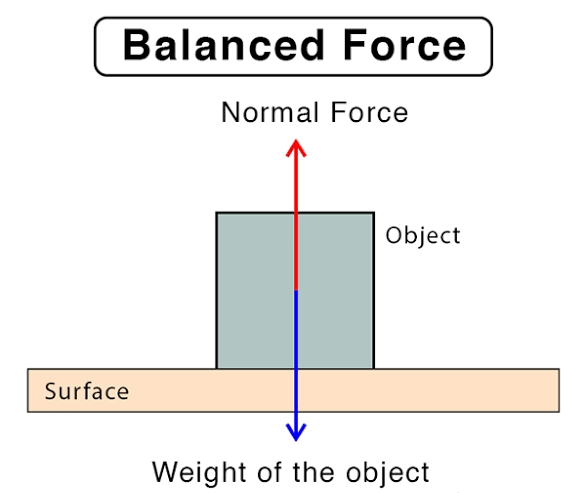
If the resultant of all the forces acting on a body is zero the forces are called balanced forces.
Example :
A heavy box placed on the table is pushed from the left side in order to move it. The four forces are acting on the box are as shown below :
1. Force of our push.
2. Force of friction (which opposes the push and does not allow the box to move).
3. Force of gravity or weight of box (which pulls the box downwards).
4. Force of reaction exerted by the ground on the box (upwards which balances the force of gravity).
Even after application of these four forces, the box does not move at all. Thus, we can conclude that the resultant of all the forces is zero.
Key Note :
- If a number of balanced forces act on a stationary body, the body continues to remain in its stationary position.
- If a number of balanced forces act on a body in uniform motion, the body continues to be in its state of uniform motion.
What are Unbalanced Forces?
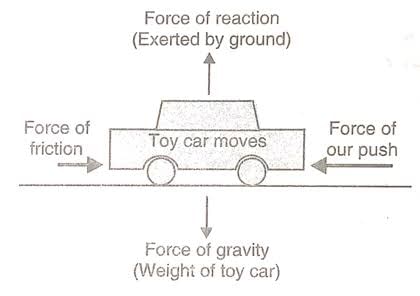
The resultant of all the forces acting on a body is not zero, the forces are called unbalanced forces.
Unbalanced forces can move a stationary body or they can stop a moving body.
Example :
In case of a toy car, again four forces of push, friction, gravity and reaction are applied. Force of gravity on the car acting downwards and the force of reaction of ground acting upwards are equal and opposite, so they balance each other. Due to the wheels of the toy car, the opposing force of friction is much less than the force of our push. The resultant of all the forces is not zero causing an unbalanced force acting on the toy car which makes the car move from its position of rest.
|
31 videos|126 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on Force, it's Effects & Types - Science Olympiad Class 9
| 1. What is force? |  |
| 2. What are the effects of force? |  |
| 3. What are balanced forces? |  |
| 4. What are unbalanced forces? |  |
| 5. What are the types of force? |  |















