Networking | Cyber Olympiad for Class 9 PDF Download
The generic term ‘network’ refers to a group of entities (objects, people, etc.) which are connected to one another. A network, therefore, allows material or immaterial elements to be circulated among all of these entities, based on welldefined rules.Network: A group of computers and peripheral devices connected to each other form a network. The smallest possible network is two computers connected together.
Networking: Implementing tools and tasks for linking computers so that they can share resources over the network is called networking.
A computer network is useful for several distinct purposes:
- Sharing resources (files, applications or hardware, an Internet connection, etc.)
- Communication between people (email, live discussions, etc.)
- Communication between processes (such as between industrial computers)
- Guaranteeing full access to information for a specified group of people (networked databases)
- Multiplayer video games
Advantages of Networking
Networks are also used for standardizing applications. Here’s a glimpse of the advantages that such systems have:
- Lower costs, due to sharing data and peripherals,
- Standardizing applications
- Timely access to data,
- More efficient communication and organization.
The different types of networks generally have the following points in common:
- Servers: The computers which provide shared resources to users, by means of a network server
- Clients: The computers which access the shared resources provided by a network server.
- Connection medium: Devices though which computers are liked to another in a network.
- Shared data: The files that can be accessed on the network servers
- Printers and other shared peripherals: The files, printers, or other elements employed by the network’s users
Following is the list of hardware’s required to setup a computer network.
- Network Cables
- Distributors
- Routers
- Network Cards
(i) Network Cables: Network cables are used to connect computers.
(ii) Distributors: A computer can be connected to another through a serial port but if we need to connect many computers to produce a network, one has to use a central body to which other computers, printers, scanners etc. can be connected and then this body will manage or distribute network. This hardware is called the distributor.
(iii) Router: A router is a type of device which acts as the central point in a network. A router has holes called ports and computers and other devices are connected to a router using network cables.
(iv) Network Card: Without this device, a computer cannot be connected over a network. It is also known as network adapter or Network Interface Card (NIC). Most branded computers have network cards preinstalled. Network cards are of two types: Internal and External Network Cards.
Types of networks
Generally there are two types of networks:
- Peer-to-peer networks
- Networks organized around servers (Client/Server)
These two types of networks have different capabilities.
Which type of network is to be installed depends on the following criteria:
- Size of the business
- Level of security required
- Type of activity done
- Skills of the administrators available
- Volume of traffic over the network
- Needs of the users
- Budget set aside for operating the network (not for purchasing it, but for upkeeping and maintenance also only)
Topology
A computer network is made of computers which are linked to one another with communication lines (network cables, etc.) and hardware elements (network adapters, as well as other equipments for ensuring that data travels correctly). The physical arrangement such as the spatial configuration of the network is called the physical topology.
 |
Test: Networking- 2
|
Start Test |
Kinds of Topology
Different kinds of topologies are the following:
- Bus topology
- Star topology
- Ring topology
(i) Bus topology
Bus topology is the simplest way to organize a network. In this topology, all computers are linked to the same transmission line by using a cable, usually coaxialy.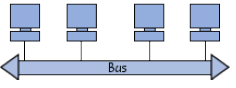
The advantages of this topology are:
- Easy to implement
- Functions easily
Disadvantages of this topology, it is highly vulnerable, that is if one of the connections is defective, the whole network is affected.
(ii) Star topology
- In this topology, the computers are linked to a piece of hardware called a hub. This is a box which contains a certain number of sockets into which cables coming out of the computers can be plugged. Its role is to ensure communications between those sockets.
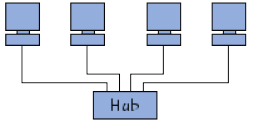
- Unlike bus topology, the network with star topology are much less vulnerable, a connections can be easily removed by disconnecting it from the hub, without paralysing the rest of the network.
(iii) Ring topology
In this topology network, each computer takes turns communicating, creating a loop of computers in which each of them has its turn to speak” one after another.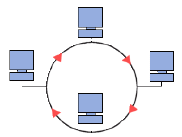
Different Types of Networks
Different types of (private) networks are distinguished based on their size (in terms of the number of machines), their data transfer speed, and their reach. Private networks are networks that belong to a single organization.
Generally there are three categories of such networks:
- LAN (local area network)
- MAN (metropolitan area network)
- WAN (wide area network)
(i) LAN (Local Area Network)
LAN stands for Local Area Network. It is a group of computers which belong to the same organization, and are linked within a small geographic area using a network, and often the same technology (the most widespread being Ethernet).
A local area network is a network in its simplest form. Data transfer speeds over a local area network can reach up to 10 Mbps (such as for an Ethernetnetwork) and 1 Gbps (as with FDDI or Gigabit Ethernet).
Two different operating modes can be defined:
- Peer-to-peer network, in which communication is carried out from one computer to another, without a central computer, and where each computer has the same role.
- Client/server environment, in which a central computer provides network services to users.
(ii) MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
MAN (Metropolitan Area Networks) connects multiple geographically nearby LAN to one another (over an area of up to a few dozen kilometres) at high speeds. Thus, a MAN lets two remote nodes communicate as if they were a part of the same local area network.
(iii) WAN (Wide Area Network)
A WAN (Wide Area Network or extended network) connects multiple LANs to one another over large geographic distances. The speed available on a WAN varies depending on the cost of the connections (which increases with distance) and may be low. The most well-known WAN is the Internet.
Intranet
An intranet is a private network which utilizes Internet-type tools, but are available only within that organization. For large organizations, the intranet provides an easy access mode to corporate information for employees.With the advancements made in browser-based software for the Internet, many private organizations are implementing intranets.
 |
Download the notes
Networking
|
Download as PDF |
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPN uses a technique known as tunneling to transfer data securely on the Internet to a remote access server on your workplace network.VPN helps user save money by using the public Internet instead of making long distance phone calls to connect securely with your private network. There are two ways to create a VPN connection, by dialing an Internet service provider (ISP), or connecting directly to the Internet.
Some important protocols and their jobs are shown in the table given below:
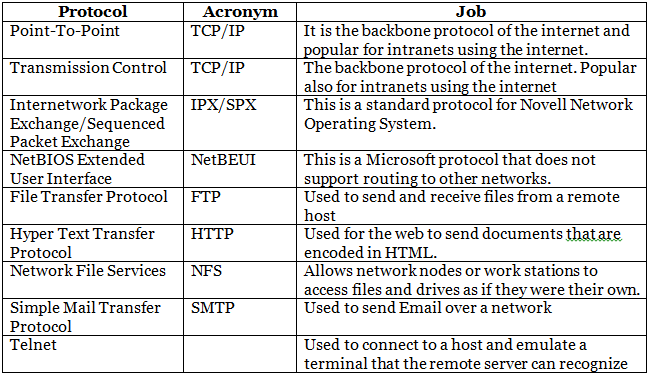
Protocols
Network protocols are the standards that allow computers to communicate. A protocol defines how computers identify one another on a network, the form that the data should take in transit, and how this information is processed once it reaches its final destination.
Similarities between Internet and Intranet
- Both use the internet protocols such as TCP/IP and FTP.
- Intranet sites are accessible via web browser in similar way as websites in internet.
- In Intranet, own instant messengers can be used as similar to yahoo messenger used over the internet.
Differences between Internet and Intranet
- Internet is general to PCs all over the world whereas Intranet is specific to few PCs.
- Internet has wider access and provides a better access to websites to large population whereas Intranet is restricted.
- Internet is not as safe as the Intranet as Intranet is private network within an organization.
Ethernet Products
The following text discusses the key products needed to build an Ethernet LAN.
Transceivers
Transceivers are used to connect nodes to various Ethernet media. Most computers and network interface cards containing a built-in 10BASE-T or 10BASE2 transceiver, to get connected directly to Ethernet without requiring any external transceiver.
Network Interface Cards
Network interface cards, commonly referred to as NICs, are used to connect a PC to a network. The NIC provides a physical connection between the networking cable and the computer’s internal bus.
Hubs/Repeaters
Hubs/repeaters are used to connect together two or more Ethernet segments of any media type. Hubs provide the signal amplification required to allow a segment to be extended to a greater distance. A hub takes any incoming signal and repeats it out to all other ports.
Bridges
The function of a bridge is to connect separate networks together. Bridges connect different network types (such as Ethernet and Fast Ethernet) or networks of the same type. Bridges map the Ethernet addresses of the nodes residing on each network segment and allows only necessary traffic to pass through the bridge. When a packet is received by the bridge, the bridge determines the destination and source segments. If the segments are the same, the packet is dropped ‘filtered’.
If the segments are different, then the packet is forwarded to the correct segment.
Ethernet Switches
Ethernet switches are an expansion of the concept in Ethernet bridging. LAN switches can link four, six, ten or more networks together, and have two basic architectures: cut-through and store-andforward.
Routers
Routers filter out network traffic by specific protocol rather than by packet address. Routers also divide networks logically instead of physically. An IP router can divide a network into various subnets so that only traffic destined for particular IP addresses can pass between segments.
|
7 videos|27 docs|69 tests
|





















