Olympiad Notes: Human Eye and Colourful World | Olympiad Preparation for Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Eye |

|
| Eye Defects |

|
| Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism |

|
| Atmospheric Refraction |

|
| Scattering of Light |

|
| Tyndall effect |

|

Human Eye
It is a naturally occurring optical instrument. As you all know, we have a pair of eyes, and their function is to enable us to see. Without it, the whole world would have been a dark place for us.
Structure of Eye
- The eye is shaped like a sphere but has a slight bulge at the front.
- It is located within a protective socket in the skull called the eye socket.
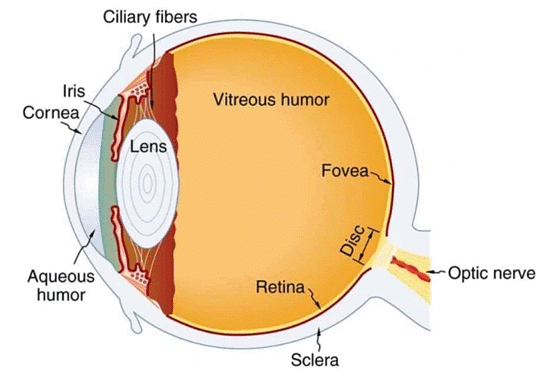
- The eye is covered by two layers: the sclera and the choroid.
Function of the Sclera
The sclera is the outer layer of the eye, made up of tough, white fibrous tissue. Its primary function is to protect the various parts of the eye from injury and damage.
Function of the Choroid
The choroid is the layer beneath the sclera, rich in blood vessels. It has two main functions:
- Nourishment: The blood vessels in the choroid supply essential nutrients and oxygen to the eye, keeping its tissues healthy.
- Reducing Internal Reflection: The choroid helps to minimize internal reflection of light within the eye, which improves the quality of the images formed on the retina.
Apart from these layers, it consists of:
- Cornea: It is the white part of the eye that allows light to enter. It acts as a window to the world.
- Iris: It is a colored part of the eye. It holds the pupil and also adjusts the size of the pupil according to the intensity of light.
- Pupil: It is black in color and absorbs all the light rays falling on it. It gets constricted when the intensity of light is high. It gets expanded when the intensity of light is low.
- Ciliary muscles: They hold the lens. They adjust the focal length of the lens.
- Convex lens A cellular structure resembling a convex lens (diverging lens).
- Retina: It is the screen of an eye where an image is formed.
It consists of two types of cells:
(i) Cone cells: those cells which respond to colors.
(ii) Rod cells: those cells which respond to the intensity of light. - Yellow spot: A point on the retina where the clearest image is formed.
(i) Blindspot: The point on the retina without image formation because the optic nerve exits the eye, lacking photoreceptor cells.
(ii) Optic nerve: A nerve that connects the eye to the brain.
Aqueous Humor
The fluid which is present between the cornea and lens is called aqueous humor.
- Function: It is a watery fluid present in the interior part of the eye and its function is to protect the exterior part of the eye from collapsing when there is a sudden change in the atmospheric pressure. Also, it is the fluid that flows out from the eye when we wink our eyes. So, it washes the eye and also keeps it moist.
Vitreous Humor
The fluid is present between the lens and retina and is called the vitreous humor.
- Function: It is a dense jelly-like fluid present in the posterior part of the eye and its function is to protect the posterior part of the eye from collapsing when there is a sudden change in the atmospheric pressure. It also helps in focusing the image clearly on the retina.
Adjustment of Pupil Size according to the intensity of light:
- In Bright Light: The iris constricts the pupil to limit the amount of light entering the eye, helping to create a clearer image.
- In Dim Light: The pupil expands to allow more light to enter, improving visibility and image clarity.
Accommodation of the Eye
It is the ability of the eye lens to adjust its focal length so that a clear image is formed on the retina that can be easily recognized by our brain.
In the case of far-off objects.
In order to see a far-off object, our ciliary muscles, lens, and focal length undergo a change i.e. the ciliary muscles relax, the lens becomes thin and elongated, and the focal length increases.
In the case of nearby objects. In order to see nearby objects, the focal length of the lens and ciliary muscles undergo a change. ciliary muscles contract, the lens becomes thick and short and the focal length decreases.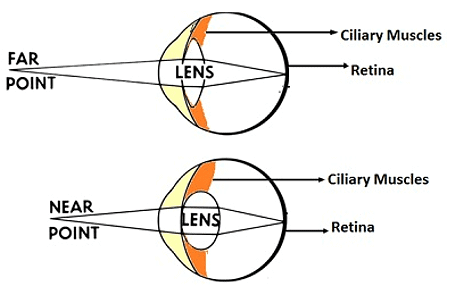
Eye Defects
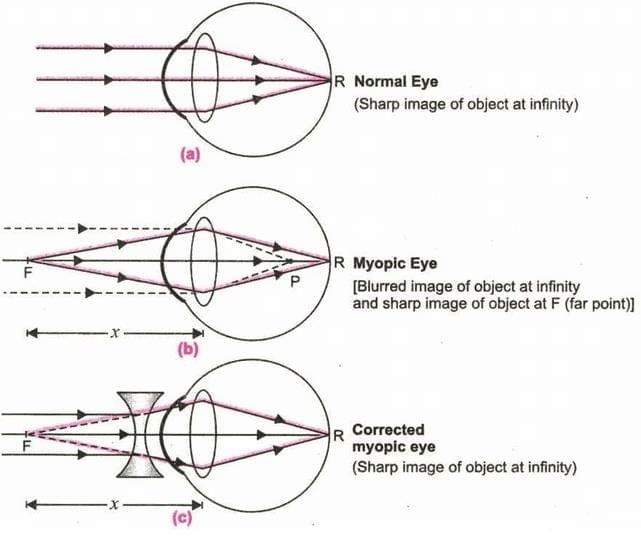
Myopia (Short-sightedness)
In myopia, distant objects appear blurry while nearby objects are clear.
It occurs because the ciliary muscles and lens do not work together properly to focus light on the retina.
The eyeball is often too long, causing images to form in front of the retina.
Correction: Concave lenses in glasses help by allowing light to focus correctly on the retina.
Hypermetropia (Long-sightedness)
In hypermetropia, it is difficult to see close objects, but distant objects appear clear.
This happens when the ciliary muscles and lens fail to thicken and shorten properly, resulting in a focal length that is too long.
The eyeball is too short, so the image forms behind the retina.
Correction: Convex lenses in glasses increase the lens’s focusing power, allowing light to converge on the retina correctly.
 Hypermetropia
Hypermetropia
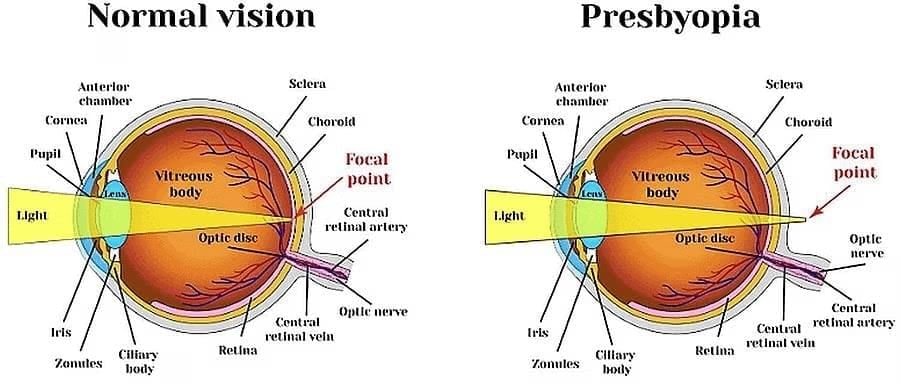
Presbyopia
Presbyopia is an age-related condition where ciliary muscles weaken, making it hard to focus on both near and distant objects.
It develops gradually with age.
Correction: Bifocal lenses in glasses provide different lens powers for near and far vision.
Refraction through prism
- Definition of a Prism:. prism is a transparent object, often made of glass, with a triangular shape and three rectangular sides. The rectangular sides are called refracting surfaces because they are where the bending of light occurs.
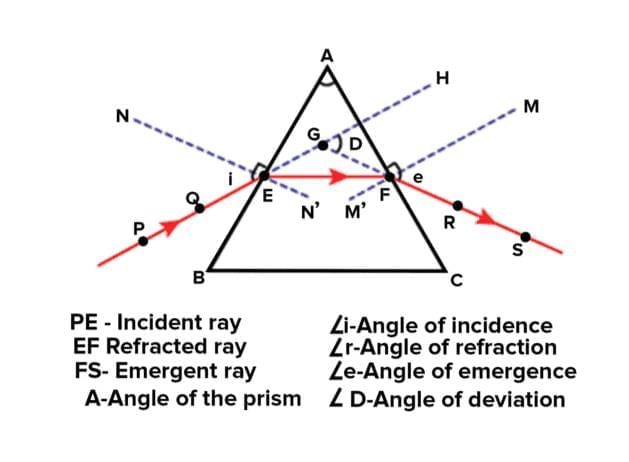
- Angle of the Prism: The angle between the two refracting surfaces of the prism is known as the angle of the prism. This angle is crucial as it determines how much the light will bend when it passes through the prism.
- Refracting Edge: The edge where the two refracting surfaces meet is called the refracting edge. This edge is where the light enters and exits the prism, undergoing refraction.
- Principal Section of the Prism:. cross-section of the prism that is perpendicular to the refracting edge is known as the principal section of the prism. This section helps in understanding the internal structure of the prism and how light interacts with it.
- Difference between Refraction through a Prism and a Glass Slab: In a glass slab, the light beam entering the slab remains parallel to the incident beam after refraction. This is because the opposite faces of the slab are parallel, allowing the light to pass through without changing its direction significantly.
- In contrast, when light passes through a prism, the emergent ray is deflected at an angle and is not parallel to the incident ray. This is due to the fact that the refracting surfaces of the prism are angled and not parallel, causing the light to change direction more significantly as it passes through.
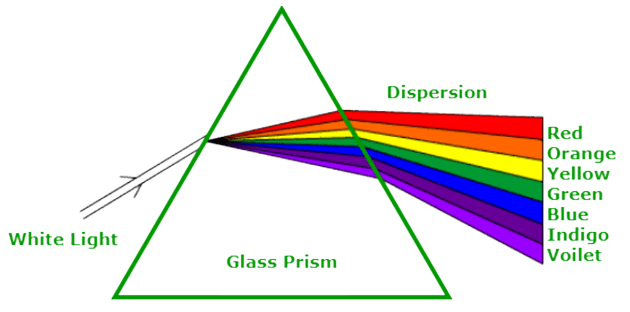
Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism
- When a ray of white light is incident on a glass prism, it splits the incident white light into a band of colours. The various colours seen are Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red (VIBGYOR).
- The band of the coloured components of a light beam is called its spectrum.
- The splitting of light into its component colours is called dispersion.
Why do we get these colours? (Cause of Dispersion of Light)
- Different colors of light bend at varying angles relative to the incident ray as they pass through a prism.
- As a result, each color's rays emerge along separate paths, making them distinct.
- This separation of colors forms the band of distinct hues that we observe in a spectrum.
 Dispersion of Light
Dispersion of Light
V I B G Y O R
- The angle of deviation ∝ 1/wavelength
- Red is the least deviated colour as it has the largest/longest wavelength.
- Violet is the most deviated colour as it has the smallest wavelength in the visible spectrum.
Recombination of White Light
Issac Newton was the first person to proved that sunlight is made up of seven colours :
(i) He passed sunlight through a glass prism to form a band of seven colours.
(ii) He tried to split the colours further by putting another prism ahead of the prism forming spectrum, but he failed to obtain more colours.
(iii) He formed a spectrum from sunlight and placed an identical but inverted prism in front of the prism, forming the spectrum. All the seven colours combined by the inverted prism and emerged as white light.
Rainbow Formation
A rainbow is a natural optical phenomenon that forms when sunlight passes through water droplets in the atmosphere. It results in a spectrum of colors appearing in the sky, usually as a circular arc.
Process of Rainbow Formation:
Rainbow formation involves three main steps:
1. Refraction
When sunlight enters a raindrop, it bends (refracts) because it moves from air (less dense) to water (more dense).
This causes the white light to split into its seven component colors (VIBGYOR — Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red).
2. Internal Reflection
The refracted light reflects off the inner surface of the raindrop.
3. Refraction Again
As the light exits the raindrop, it is refracted again, further separating the colors.
Different colors emerge at slightly different angles, with red emerging at about 42° and violet at about 40° from the direction opposite the sun.
Atmospheric Refraction
The refraction of light by different layers of the atmosphere is called atmospheric refraction.
(i) Twinkling of stars.
(ii) Sun Appear Bigger During Sunrise and Sunset
(iii) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
(iv) Stars near the horizon appear slightly higher than their actual position.
1. Twinkling of stars.
When light from a star passes through the Earth's atmosphere, it gets refracted (bent) multiple times due to varying air densities and temperature layers.
These atmospheric disturbances cause the position and brightness of the star's light to change rapidly, making stars appear to twinkle.
Stars are very far away, so they appear as point sources of light, making them more affected by atmospheric refraction.
Planets, on the other hand, are much closer to Earth and appear as tiny discs (not point sources).
The light coming from different parts of the planet’s disc averages out the twinkling effect, so planets usually do not twinkle or twinkle much less.
2. Sun Appear Bigger During Sunrise and Sunset
During sunrise and sunset, the sunlight travels through a greater thickness of the Earth's atmosphere compared to noon.
The atmosphere acts like a lens, bending the light due to refraction.
This causes the apparent position of the sun to shift, and due to optical illusion and atmospheric scattering, the sun appears larger and reddish.
3. Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset
- The sun appears about two minutes earlier than the actual sunrise, and it remains visible for about two minutes after the actual sunset.
- When the sun is below the horizon, the rays have to pass from rarer to denser medium.
- The time difference between the actual sunset and the apparent sunset is approximately 2 minutes.
- So, rays bend towards the normal. As a result, the sun appears higher than its actual position.

Scattering of Light
Scattering is the process in which light is spread in different directions when it strikes particles that are larger in size than the wavelength of light.
When light hits dust, smoke, or gas particles in the atmosphere, it gets deflected in many directions.
The larger the particle, the more light is scattered.
Scattering is responsible for many natural phenomena, like the blue color of the sky and the reddish appearance of the sun during sunrise and sunset.
Applications of Scattering
1. The Sky Appears Blue
When white sunlight enters the Earth's atmosphere, it interacts with gas molecules and small particles.
Shorter wavelengths like violet, indigo, and blue scatter more than longer wavelengths.
Among them, blue light dominates as our eyes are more sensitive to it (violet is mostly absorbed).
As a result, we see the sky as blue.
2. The Sun Appears Yellow
As sunlight passes through the atmosphere, blue and violet light are scattered away in all directions.
The remaining light reaching our eyes is rich in red, orange, and yellow wavelengths.
This mix gives the sun a yellowish appearance, especially during midday when it is overhead.
3. The Sky Appears Dark to an Astronaut
In outer space, there is no atmosphere and thus no particles to scatter sunlight.
Since there is no scattering, the sky looks black or dark to astronauts, even when the sun is shining.
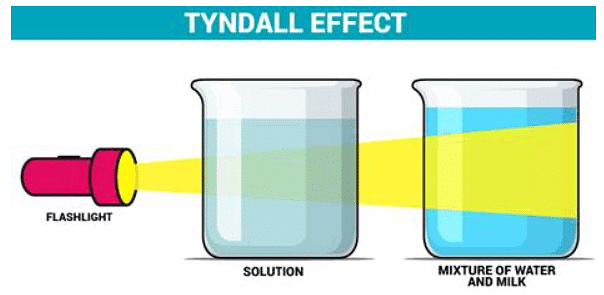
Tyndall effect
The scattering of light by colloidal solution particles is called the Tyndall effect. It makes the path of a light beam visible when it passes through such a mixture.
Examples:
Sunlight through mist or fog: The tiny water droplets scatter the light and make sun rays visible.
Dust particles in a dark room: When sunlight enters through a small window or hole, the dust particles scatter the light and make the beam visible.
Milk in water: Milk scatters light because it is a colloid.
Conditions for Tyndall Effect:
The mixture must be a colloid or contain very fine particles.
The particle size should be large enough to scatter light but small enough to remain suspended.
|
70 videos|242 docs|187 tests
|
FAQs on Olympiad Notes: Human Eye and Colourful World - Olympiad Preparation for Class 10
| 1. What are the main parts of the human eye and their functions? |  |
| 2. How does the human eye perceive colors? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the lens in the human eye? |  |
| 4. What are common vision problems associated with the human eye? |  |
| 5. How can we protect our eyes and maintain good vision? |  |















