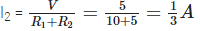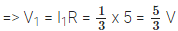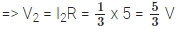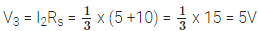Viva Voce: Resistors in Series | Lab Manuals for Class 10 PDF Download
Q.1. Can you mention one disadvantage of series connection?
In series connection, if any one component fails to work, the circuit breaks and none of the components works.
Q.2. Why current should be passed for a short time through the circuit while taking observations?
Current passed through the circuit for longer time while taking observations, can cause unnecessary heating in the circuit, which may change the resistance of resistors.
Q.3. When do we put the resistances in series combination?
A, When we have the smaller value of resistance and need the greater value of resistance, we put them in series combination.
Q.4. What happens to the ammeter reading if two resistors of the same value are connected in series in the circuit?
The deflection in ammeter is reduced to half of the previous value, i.e. ammeter shows half of the previous reading.
Q.5. What happens to the resistance of the resistor, if the current through it increases?
It remains unchanged because the resistance does not depend on the current flowing through it.
Q.6. How will you find the equivalent resistance, when they are connected in series?
The equivalent resistance of two resistors R1 and R2, is determined by
Rs = R1 + R2
Q.7. In an electric circuit, a resistor of 5 Ω resistance is connected to a battery (5V), through an ammeter and a plug key. Now in this circuit, an another resistor of 10 Ω is connected in series with the 5 Ω resistor. Will there be any change in the ammeter reading? How much?
Since, resistors are added in series, therefore there will be a change in the current.
I1 = V/R = 5/5 = 1A
and
Therefore, change in ammeter reading will be from 1 A to 0.33 A.
Q.8. Mention the use of rheostat in the circuit.
To change the current in the circuit which can be done by changing the sliding contact of the rheostat.
Q.9. In a circuit, if two resistors of resistances 5Ω and 10Ω are connected in series. Compare the current passing through the two resistors.
In a series combination, same current passes through all the resistors. Thus, the ratio of current will be 1:1.
Q.10. Why resistance becomes more in series combination?
The effective length of all the resistors in series combination increases. Hence, equivalent resistance of the combination increases as R ∝ I
Q.11. When two unequal resistances are connected in series, what will be the potential difference across each resistor?
When two unequal resistances are connected in series, the potential difference across each resistor will be different.
Q.12. What is the relationship between V and R for the series combination?
Voltage applied across combination of resistances is directly proportional to the resistance of series combination.
Q.13. In the above question, what is the potential difference across two ends of the resistor of 5 Ω resistance, when it is alone in the circuit? What is the potential difference across the two ends of resistor of 5 Ω resistance, when it is connected in series with the resistor of 10 Ω resistance? What is the potential difference across the series combination?
Consider V1 be the potential difference across two ends of the resistor of 5 Ω resistance, when it is connected alone.
Consider V2 be the potential difference across two ends of resistor of 5 Ω resistance, when it is connected to 10 Ω resistor in series.
Potential difference across the series combination is
The potential difference across series combination is equal to applied potential difference.
Question 14. If two resistors having resistances of 2 Ω and 4 Ω, respectively are connected in a series combination in an electric circuit, what will be the net resistance in the Circuit?
According to series combination, Rnet = R1 + R2
⇒ Rnet = (2 + 4) Ω {∵ R1 = 2 Ω, R2 = 4Ω}
⇒ Rnet = 6 Ω