Judiciary Class 8 Worksheet Civics Chapter 5
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| True or False Statements |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the primary function of the judiciary in India?
A) Enforcing laws
B) Resolving disputes
C) Making laws
D) All of the above
Ans: B) Resolving disputes
The judiciary primarily resolves legal conflicts between individuals, organizations, and the government while ensuring justice.
Q2: Which court is at the apex level in the Indian judicial system?
A) High Court
B) District Court
C) Supreme Court
D) Session Court
Ans: C) Supreme Court
The Supreme Court is the highest court in India, overseeing the entire judicial system and handling constitutional matters.
 Supreme Court of India
Supreme Court of India
Q3: What does the term 'judicial review' refer to?
A) The review of court cases
B) The power to strike down laws
C) The appointment of judges
D) None of the above
Ans: B) The power to strike down laws
Judicial review allows courts to declare laws unconstitutional if they violate the Constitution.
Q4: Which of the following is true about the independence of the judiciary?
A) Judges can be easily removed by politicians
B) The judiciary is separate from the executive and legislature
C) The judiciary is under government control
D) All of the above
Ans: B) The judiciary is separate from the executive and legislature
The judiciary operates independently to ensure fair and impartial judgments, free from political influence.
Q5: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) was introduced to:
A) Increase access to justice
B) Protect the rights of politicians
C) Speed up the court procedures
D) Reduce the number of judges
Ans: A) Increase access to justice
PIL allows citizens, even without personal stakes, to file cases for public welfare and protect rights.

Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The __________ is responsible for upholding the law and enforcing the Fundamental Rights of citizens.
Ans: The Supreme Court is responsible for upholding the law and enforcing the Fundamental Rights of citizens.
Q2: The __________ system allows individuals to appeal to a higher court if they believe a judgment is unjust.
Ans: The Appellate system allows individuals to appeal to a higher court if they believe a judgment is unjust.
Q3: The __________ of India protects against the misuse of power by the legislature and executive.
Ans: The Constitution of India protects against the misuse of power by the legislature and executive.
Q4: The __________ courts are usually where most citizens first interact with the judicial system.
Ans: The District courts are usually where most citizens first interact with the judicial system.
Q5: __________ law deals with conduct defined as offenses, such as theft and murder.
Ans: Criminal law deals with conduct defined as offenses, such as theft and murder.
True or False Statements
Q1: The High Court is the highest court in a state.
Ans: True
The High Court is the highest judicial authority at the state level. It has the power to hear appeals from lower courts and oversee the functioning of the judiciary within the state.
Q2: The Supreme Court's decisions are not binding on lower courts.
Ans: False
The Supreme Court's decisions are binding on all lower courts to ensure uniformity in law interpretation.
Q3: All citizens in India have easy access to the courts.
Ans: False
High costs, delays, and complex procedures make it difficult for marginalized groups to access courts.
Q4: Judicial review allows the courts to strike down unconstitutional laws.
Ans: True
Q5: The judiciary is controlled by the executive branch of government.
Ans: False
The judiciary in India is independent and not controlled by the executive or legislature.
Match the Following
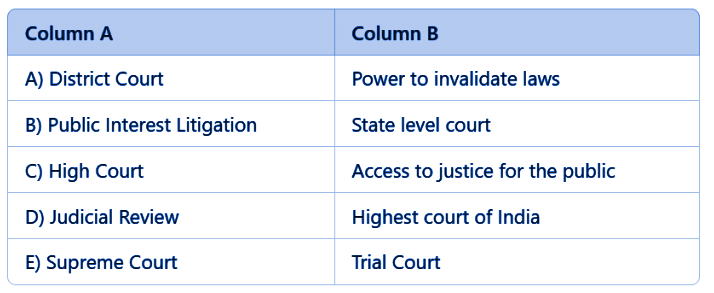
Ans: 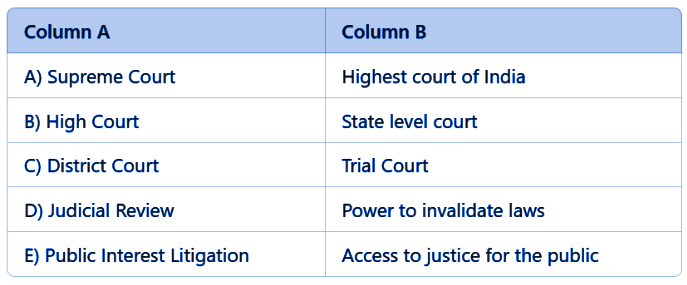
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: What is the primary role of the judiciary in India?
Ans: The judiciary resolves disputes, interprets the Constitution, and protects Fundamental Rights.
Q2: What does judicial review allow the judiciary to do?
Ans: Judicial review allows the judiciary to strike down laws that violate the Constitution.
Q3: How many levels of courts exist in India?
Ans: There are three levels of courts: subordinate courts, High Courts, and the Supreme Court.
Q4: What is the purpose of Public Interest Litigation (PIL)?
Ans: PIL allows individuals or organizations to seek justice for those whose rights are violated.
Q5: What is the significance of the separation of powers in the judiciary?
Ans: It ensures that the judiciary operates independently without interference from the legislature or executive.
 Judiciary
Judiciary
Short Answer Questions
Q1: What does the judiciary do in India?
Ans: The judiciary in India helps solve problems between people, the government, and different states. It makes sure everyone follows the law and protects the rights of citizens. It can also decide if laws are fair or not.
Q2: Why is an independent judiciary important?
Ans: An independent judiciary is important because it means judges can make fair decisions without being influenced by powerful people. This helps protect ordinary citizens' rights and ensures justice is served.
Q3: What are the three levels of courts in India?
Ans: The three levels of courts in India are:
1) District or Subordinate Courts, which are the lowest level,
2) High Courts, which are above the district courts, and
3) The Supreme Court, which is the highest court in the country.
Q4: How can a person appeal a court decision in India?
Ans: A person can appeal a court decision by asking a higher court to look at the case again. This is done if they believe the lower court made a mistake in its judgment.
Q5: What is Public Interest Litigation (PIL)?
Ans: Public Interest Litigation (PIL) allows anyone to file a case in court to help those whose rights are being violated. It makes it easier for people to seek justice, especially for the poor and those who cannot afford a lawyer.
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Judiciary Class 8 Worksheet Civics Chapter 5
| 1. What is the role of the judiciary in India? |  |
| 2. How does the judiciary maintain the rule of law? |  |
| 3. What are the different levels of courts in the Indian judiciary? |  |
| 4. Can the judiciary review laws passed by the legislature? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of public interest litigation (PIL) in the Indian judiciary? |  |















