Motion and Time Class 7 Worksheet Science Chapter 9
Q.1. True/False
(i) The basic unit of time is second.
True
The second is the standard unit of time in the International System of Units (SI). It is defined as:
Understanding these units helps in measuring time accurately.
- The basic unit of time.
- Symbol: s.
- Related units include minutes (min) and hours (h).
(ii) Every object moves with a constant speed.
False
- Objects do not always move at a constant speed.
- The speed of an object can change due to various forces acting on it.
- Some objects may accelerate or decelerate, leading to varying speeds.
(iii) Distances between two cities are measured in kilometres.
True
Kilometers are the standard unit for measuring distances between cities in many countries. Key points include:
- Kilometers are widely used for long distances.
- They provide a clear understanding of distance.
- This measurement is common in road signs and maps.
(iv) The time period of a given pendulum is not constant.
False
The time period of a simple pendulum is:
- Constant for a specific length.
- Not affected by the mass of the bob.
- Remains the same regardless of slight changes in initial displacement.
(v) The speed of a train is expressed in m/h.
False
The speed of a train is usually expressed in kilometres per hour (km/h), not in metres per hour (m/h).
(vi) Clocks that measure such small time intervals are used for scientific research.
True
- High-precision clocks, like atomic clocks, are crucial in scientific research.
- They accurately measure very small time intervals.
- Such measurements are essential for various scientific applications.
Q.2. Fill in the blanks.
(i) The metallic ball is called the ____ of the pendulum.
bob
The term 'bob' refers to the weight or mass at the end of a pendulum, which swings back and forth during oscillation.
(ii) The symbols of all units are written in ____.
singular
Unit symbols are conventionally written in singular form to maintain consistency and clarity in scientific communication.
(iii) The time taken by the pendulum to complete one oscillation is called its ____.
time period
The 'time period' is defined as the duration it takes for a pendulum to return to its original position after completing one full swing.
(iv) One microsecond is one ____ of a second.
millionth
A microsecond is a unit of time equal to one millionth (10-6) of a second, commonly used in scientific contexts.
(v) A nanosecond is one ____ of a second.
billionth
A nanosecond is a unit of time equal to one billionth (10-9) of a second, often used in computing and telecommunications.
(vi) The distance-time graph for the motion of an object moving with a constant speed is a ____.
straight line
A straight line on a distance-time graph indicates uniform motion, where the distance covered is directly proportional to time.
Q.3. Give an example of oscillatory motion.
- The to and fro motion of a simple pendulum is a clear example of oscillatory motion.
Here’s a brief overview:
- A simple pendulum consists of a small weight, known as the bob, attached to a string or thread.
- When the bob is pulled to one side and released, it swings back and forth around its mean position.
- This back-and-forth movement is repeated in a regular pattern, making it a periodic motion.
Q.4. What is uniform motion?
An object that moves in a straight line at a constant speed is described as being in uniform motion.
This means:
- The speed does not change over time.
- The distance covered is proportional to the time taken.
- The motion can be represented by a straight line on a distance-time graph.
Q.5. An object moving along a straight line with a constant speed is said to be in uniform motion.
Vehicle A is moving faster. The speed of a vehicle is determined by the distance it covers in a specific time frame.
Key points include:
- A vehicle that travels a greater distance in the same time interval has a higher speed.
- For example, if Vehicle A covers 100 metres in 5 seconds and Vehicle B covers 80 metres in the same time, Vehicle A is faster.
- Speed can vary; the same vehicle may move faster or slower at different times.
Q.6. Write down the steps to draw a graph.
Steps
(i) Draw two perpendicular lines to represent the two axes and mark them as OX and OY.
(ii) Decide the quantity to be shown along the x-axis and that to be shown along the y-axis.
(iii) Choose a scale to represent the distance and another to represent the time on the graph.
(iv) Mark values for the time and the distance on the respective axes according to the scale you have chosen.
(v) Mark the points on the graph paper to represent each set of values for distance and time. Join the points.
Q.7. What is distance-time graph?
A distance-time graph visually represents how far an object travels over time. Key points include:
- It shows the speed of an object.
- A straight line indicates constant speed.
- If the line is curved, the object's speed is changing.
Q.8. What is oscillatory motion?
The to and fro motion of an object is known as oscillatory motion.
Q.9. What is circular motion?
Circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path. Key points include:
- It involves a constant distance from a central point.
- The direction of the object continuously changes.
- Examples include planets orbiting the Sun and a car turning around a curve.
Q.10. What is non-uniform motion?
Non-uniform motion occurs when an object's speed changes while moving along a straight line.
Key points include:
- The speed is not constant.
- Motion can vary from slow to fast.
- It contrasts with uniform motion, where speed remains constant.
Q.11. What is the basic unit of speed?
The basic unit of speed is the metre per second (m/s).
Q.12. A simple pendulum takes 32 s to complete 20 oscillations. What is the time period of the pendulum?
Number of oscillations = 20
Total time taken to complete 20 oscillations = 32 s
Time period = Total time taken/Number of oscillations = 32/20 = 1.6s
Q.13. When pendulum is said to have one complete oscillation?
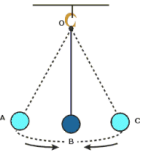
The pendulum is said to have completed one oscillation when its bob, starting from its mean position B, moves to A, to C and back to B.
Q.14. What are the points that should be considered while choosing the most suitable scale for drawing a graph?
Some of the points to be kept in mind while choosing the most suitable scale for drawing a graph are:
(i) the difference between the highest and the lowest values of each quantity.
(ii) the intermediate values of each quantity, so that with the scale chosen it is convenient to mark the values on the graph, and
(iii) to utilise the maximum part of the paper on which the graph is to be drawn.
Q.15. Explain how in ancient time a day, a month and a year were measured?
Our ancestors observed that many natural events occur at regular intervals:
- The day was defined as the time between one sunrise and the next.
- A month was measured from one new moon to the next.
- A year was determined by the time it takes for the Earth to complete one revolution around the sun.
Q.16. The distance between two stations is 240 km. A train takes 4 hours to cover this distance. Calculate the speed of the train.
Distance between two stations = 240 km
Time taken to cover this distance = 4 hours
Speed = Distance/Time Taken = 240/4 = 60km/h
Q.17. Salma takes 15 minutes from her house to reach her school on a bicycle. If the bicycle has a speed of 2 m/s, calculate the distance between her house and the school.
Time taken = 15 min = 15 x 60 = 900 seconds
Speed = 2 m/s
Distance = Speed x Time
= 2 x 900 = 1800 m = 1800/1000 = 1.8 km
Q.18. What is the basic unit of time?
The basic unit of time is a second. Its symbol is s.
Q.19. What is speedometer?
A speedometer is a device that measures and displays the speed of a vehicle.
- It is commonly found on the dashboards of cars, motorcycles, and scooters.
- The speed is usually shown in kilometres per hour (km/h).
- Speedometers help drivers maintain safe speeds while driving.
Q.20. What are quartz clocks?
Quartz clocks are timekeeping devices that use an electric circuit powered by one or more cells.
- They are known for their high accuracy in measuring time.
- Quartz clocks have largely replaced older clock technologies.
- The precision of quartz clocks is significantly better than traditional clocks.
|
111 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on Motion and Time Class 7 Worksheet Science Chapter 9
| 1. What is motion and time? |  |
| 2. How can motion be described? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of motion? |  |
| 4. How is motion measured? |  |
| 5. What is the relationship between motion and time? |  |