Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Crop Production and Management- 2 | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Short Answer Type Questions
Q.31. (a) Why is it is necessary to dry the harvested food grains before storage ?
(b) What are the two ways in which farmers store food grains ?
(a) The fresh crop has more moisture. So, the food grains obtained by harvesting the crop are dried before storage. If freshly harvested food grains are stored without drying, they may get spoilt or attacked by organisms, losing their germination capacity.
(b) The farmers store food grains in jute bags and metal bins at home.
Q.32. Out of drip system and sprinkler system of irrigation, which one is more suitable :
(a) for uneven land?
(b) for sandy soil?
(c) for watering fruit plants ?
(d) where availability of water is poor?
(a) Sprinkler system is more suitable for uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
(b) Sprinkler system is very useful for sandy soil.
(c) Drip system is best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
(d) Drip system of irrigation is more suitable where availability of water is poor.
Q.33. (a) What are weeds? Name any one weed found in a crop field.
(b) How do weeds affect the growth of crops?
(a) The undesirable plants which grow along with a cultivated crop are called weeds. Wild oat is a weed which is found in wheat crop field.
(b) Weed compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of crops.
Q.34. Explain how, the irrigation requirements depend on the nature of the crop.
Proper watering of crop at right time is called irrigation. Each crop needs a specific amount of water during its various stages of its growth. The irrigation requirements depend on the nature of crop. Some crops like paddy crop (rice crop) need more water whereas other crops like wheat, gram require less water.
Q.35. Explain how, the irrigation requirements of a crop depend on the nature of soil in which the crop is grown.
The irrigation requirements of a crop depend on the nature of soil in which the crop is grown. There are two types of soil- sandy soil and clayey soil. Sandy soil is highly porous having highly permeability. So, the water quickly percolates down to the soil and crop plants standing in the sandy soil, are not able to get adequate amount of water. Thus, crop cultivated in sandy soil need more frequent irrigation of water. On the other hand, the clayey soil is much less permeable than sandy soil due to which it can retain water for a much longer time. Thus, crop cultivated in clayey soil can absorb adequate amount of water. Hence, the crop grown in a clayey soil need irrigation less frequently.
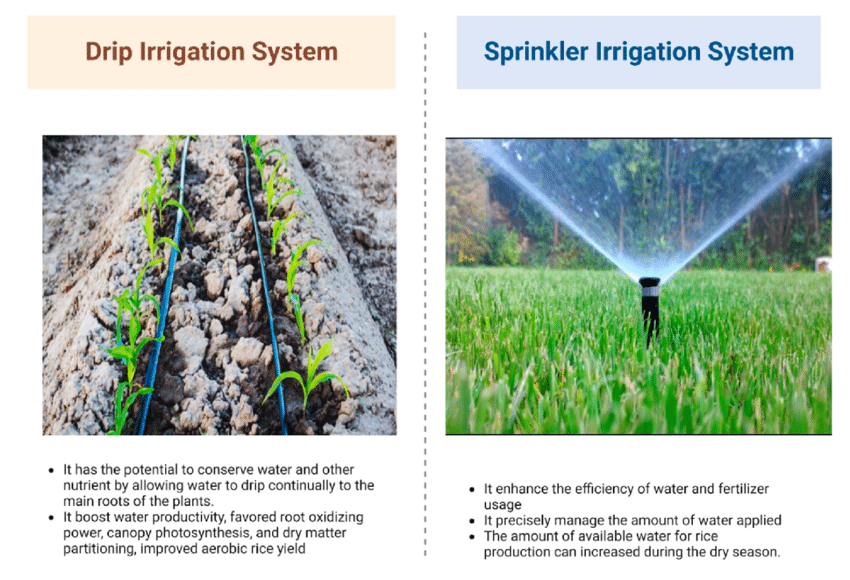
Q.36. Describe the sprinkler system of irrigation. State its advantages.
In the sprinkler system of irrigation, a main pipeline is laid in the field. The perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
Advantages of sprinkler system of irrigation:
- This system is more useful on the uneven land where sufficient water is not available.
- This system is also very useful for sandy soil.
Q.37. Explain the drip system of irrigation. State two advantages of the drip system of irrigation.
In this system, there is a network of narrow pipes with small holes, in the fields. When water flows through these pipes, water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. So, it is called drip system. Water is not wasted at all. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees.
Advantages:
- Drip system is very useful in those regions where availability of water is poor.
- Drip system provides water to plants drop by drop. So, water is not wasted at all.
Q.38. How do the irrigation requirements of a wheat crop differ from that of a paddy crop ?
Each crop needs a specific amount of water during its various stages of its growth. The irrigation requirements depend on the nature of crop. Some crops like need more water whereas other crops require less water. For example, paddy crop requires continuous irrigation whereas wheat crop requires less water.
Q.39. Explain why, the frequency of irrigation of crops is higher in summer season.
The frequency of irrigation of crops is higher in summer season due to the increased rate of evaporation of water from the soil and the leaves.
Q.40. How are weeds removed from the crop fields ? Name one implement used for weeding.
The removal of weeds from the crop fields is known as weeding. It is necessary process as weed competes with the crop plants for water, nutrients and space. Farmers adopt many ways to remove weeds and control their growth. The various ways by which weeds are removed from the crop fields are-
- With hand – In this method, weeds are removed manually by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground.
- By using a khurpa – In this method, weeds can be removed by using a implement called khurpa.
- By using weedicides – Example- 2, 4-D
Q.41. If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
If wheat is sown in the kharif season, it will not grow well as plants cannot tolerate too much water of the rainy season.
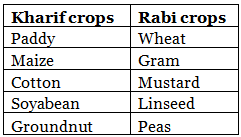
Q.42. Which of the following are kharif crops and which are rabi crops ? Wheat, Paddy, Gram, Maize, Mustard, Cotion, Soyabean, Linseed, Peas, Groundnut
Q.43. What is a crop? Give two examples of crops.
When plants of the same kind are grown and cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Examples- Wheat and Maize.
Q.44. What are the two types of crops based on seasons ? Give one e ample of each type.
Based on seasons, all crops are classified into two main groups:
- Kharif crops: The crops which are sown in the rainy season are called kharif crops.
Example: paddy, maize.- Rabi crops: The crops grown in winter season are called rabi crops.
Examples: wheat, gram, etc.
Q.45. Name the various agricultural practices in the right sequence in which they are undertaken by the farmers.
The various agricultural practices which they are undertaken by the farmers are:
- Preparation of soil
- Sowing
- Adding manure and fertilisers
- Irrigation
- Protecting from weeds
- Harvesting
- Storage
Q.46. Describe briefly, how soil is prepared for sowing the seeds.
The preparation of soil is the first step before growing a crop. The soil is prepared for sowing the seeds of crop by ploughing, levelling and manuring. The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing. It is done by using a tool called plough. It is made up of wood or iron. One of the important task in agriculture is to turn the soil and loosen it. It allows the roots to penetrate deep into the soil so that plants are held more firmly to the soil. The ploughed field may have big pieces of soil called crumbs. It is necessary to break these crumbs with a plank. The levelling of ploughed soil is done by using an implement called leveller. Sometimes, manure is added to the soil before tilling. This helps in proper mixing of manure with soil. Once the soil is ploughed, levelled and manured, it is ready for sowing of seeds.
Q.47. Why do farmers carry out levelling of the ploughed fields?
Top layer of soil supports plant growth. It gets loss due to ploughing because of which it can easily washed away by rain or blown away by wind. So, ploughed soil is levelled by pressing it with a wooden leveller, so that top soil is not blown away by wind or washed away by water.
Q.48. What are the advantages of sowing seeds. with a seed drill?
Following are the advantages of sowing seeds with a seed drill:
- Seed drill sows the seeds uniformly at proper distance and correct depths.
- It sows the seeds in regular rows.
- It ensures that seeds get covered by the soil after sowing as a result of which seeds cannot be picked by birds
- Sowing by using a tractor joined with seed drill saves time and labor.
Q.49. Explain why, the seeds should be sown at right spacings.
Seeds should be sown at right spacings. They should be neither sown too close nor too far apart. If seeds are placed too close, then plants formed form them will be also too close and will not get enough sunlight, water and nutrients to grow. On the other hand, if seeds are placed too far, then it will be a wastage of field space. Thus, the seeds should be sown at right spacing to proper growth.
Q.50. What is ploughing (or tilling)? Name any two implements used for tilling the fields.
The process of loosening and turning the soil is called ploughing or tilling. The agricultural implements used for tilling (loosening and turning) the soil are plough and hoe.
Ploughing with Bulls
Q.51. State two beneficial effects of – ploughing the fields (or loosening and turning the soil).
Loosening and turning the soil is very important for cultivation of crops. The loosening and turning the soil by ploughing is beneficial because of the following reasons:
- The loose soil allows the roots to breathe easily even when they go deep into the soil.
- The loosened soil helps in the growth of earthworms and microbes present in the soil.
Q.52. (a) State the function of Food Corporation of India.
(b) What is done to protect tile grains stored in gunny bags in big go downs from damage ?
(a) The government agency like food corporation of India (FCI) buy food grains from farmers and storing them properly so that they can be supplied throughout the country.
(b) Pesticide solution are sprayed on the gunny bags in big go downs from time to time to protect the grains from damage.
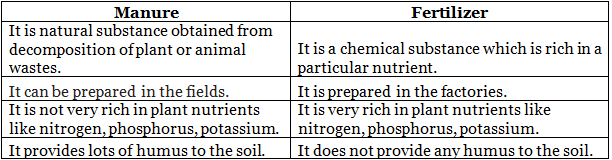
Q.53. Define manure. What are the advantages of manure ?
Manure is an organic substance obtained by the decomposition of plants or animals wastes.
Advantages of manure:
- It enhances the water holding capacity of the soil.
- It makes the soil porous due to which exchange of gases becomes easy.
- It increases the number of friendly microbes.
- It improves the texture of the soil
Q.54. What is a fertilizer ? Name any two fertilizers. State two harmful effects caused by the excessive use of fertilizers.
Fertilisers are chemical substances which are rich in a particular nutrient. Some examples of fertilizers are urea, potash, NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium), etc.
Harmful effects caused by the excessive use of fertilizers are-
- Excessive use of fertilizers makes the soil less fertile.
- Excessive use of fertilizers causes water pollution.
Q.55. Explain how, soil gets affected by the repeated growing of croping the same fields. How does use of fertilizers help the farmers ?
Plants require nutrients for their proper growth and functioning. If continuous plantation of crops is done in the fields then the soil will become poor in necessary nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, etc. This affect the yield and also affects the quality of soil. So, the nutrients once consumed by crop must be replenished so that soil get all its nutrients back and it will be ready for the next harvest.
Fertilizers help the farmers to get better yield of crops such as wheat, paddy and maize.
Q.56. What is weeding? Why is weeding necessary ?
The removal of weeds is called weeding. Weeding is necessary since weeds compete with the crop plants for water, nutrients, space and light. Thus, they affect the growth of the crop. Some weeds interfere even in harvesting and may be poisonous for animals and human beings.
Q.57. What are weedicides? Name one weedicide.
Weedicides are special chemicals which are used to control weeds. 2,4-D is an example of weedicide.
Q.58. What precaution should be taken while spraying weedicides ? Why
Weedicides affects the health of farmer. So, weedicides should be used vary carefully. During spraying of weedicides, the nose and mouth of farmer should be covered with a piece of cloth.
Q.59. Give any four differences between manures and fertilizers.
Differences between manures and fertilizers:
Q.60. Define the terms:
(i) harvesting,
(ii) threshing, and
(iii) winnowing.
(i) Harvesting: The cutting and gathering of mature food crop like wheat or paddy is known as harvesting.
(ii) Threshing: The process of removal of the grains of harvested crop from the chaff is called threshing.
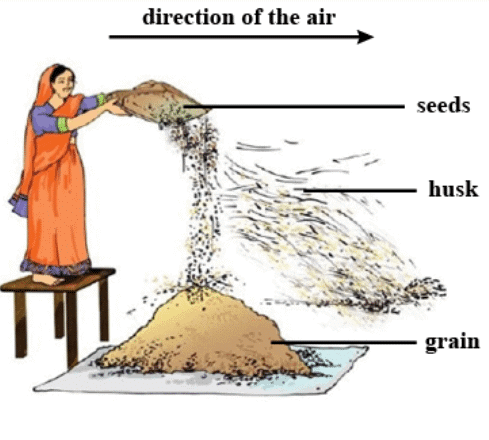
(iii) Winnowing: The process in which grains are separated from chaff with the help of wind is called winnowing.
Q.61. (a) What are the two ways in which food grains are stored on a large scale?
(b) What is the advantage of storing food grains in gunny bags?
(a) Food grains are stored on a large scale in silos and granaries (gunny bags).
(b) The advantage of storing food grains in gunny bags is that food grains filled in gunny bags can be easily transported and distributed at various parts of country.
Q.62. Name two traditional methods of irrigation and two modem methods of irrigation.
(i) Traditional methods of irrigation are chain pump and dhekli.
(ii) Modern methods of irrigation are sprinkler and drip system.
Q.63. What is a ‘combine’ which is used in agriculture ? State its functions.
The process of threshing is done with the help of a machine called combine. It is in fact a combined harvester and thresher. Combine separates the grains from chaff.
Q.64. What is ‘animal husbandry’?
The branch of agriculture which deals with feeding, shelter, health and breeding of domestic animals is called animal husbandry.
Q.65. What are the various practices necessary for raising animals for food and Other purposes.
The various practices necessary for raising animals for food and Other purposes are:
- Proper food of animals,
- Proper shelter of animals, and
- Proper care of animals.
|
136 videos|530 docs|57 tests
|
FAQs on Lakhmir Singh & Manjit Kaur: Crop Production and Management- 2 - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the steps involved in crop production and management? |  |
| 2. What is the importance of crop production and management? |  |
| 3. What are the different methods of irrigation used in crop production and management? |  |
| 4. How can farmers protect their crops from pests? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of crop protection practices? |  |