Statements and Questions | English Grammar Advanced - Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Types of Statements |

|
| Types of Questions |

|
| Sentences with Question Tags |

|
| Exclamations and Wishes |

|
| Key Points to Remember |

|
Introduction
- A statement is a sentence that conveys a definite meaning. It can be true or false.
- A question is a sentence used to ask something. It usually begins with a helping verb or an interrogative word (What, Why, How, etc.).
Types of Statements
Declarative Statements: Expresses a fact or opinion.
- Example: "The Earth revolves around the Sun."
Positive and Negative Statements:
- Positive: "She is a doctor."
- Negative: "She is not a doctor."
Universal Truths: Always true, scientifically or logically.
- Example: "Water boils at 100°C."
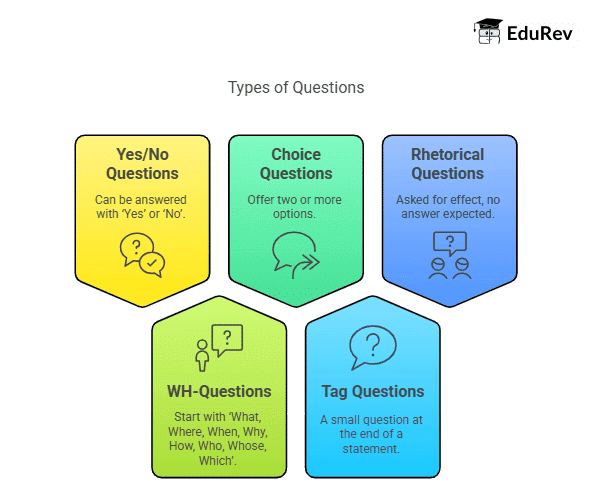
Types of Questions
Yes/No Questions: Can be answered with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’.
- Example: "Is she coming to the party?"
WH-Questions: Start with ‘What, Where, When, Why, How, Who, Whose, Which’.
- Example: "Where do you live?"
Choice Questions: Offer two or more options.
- Example: "Do you prefer tea or coffee?"
Tag Questions: A small question at the end of a statement.
- Example: "You are coming, aren’t you?"
Rhetorical Questions: Asked for effect, no answer expected.
- Example: "Who doesn’t love ice cream?"
- Example: "Who doesn’t love ice cream?"
Sentences with Question Tags
In indirect speech, the question tag is usually omitted.
Examples:
Direct: She said to me, “You didn’t break the window, did you?”
Indirect: She asked me if/whether I had broken the window.Direct: He said to Geeta, “You are going to the station, aren’t you?”
Indirect: He asked Geeta if/whether she was going to the station.
Sentences with ‘Yes’ or ‘No’
In indirect speech, ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ is replaced with a short answer.
Examples:
Direct: He said, “Can you dance?” And I said, “No.”
Indirect: He asked me if I could dance and I replied that I couldn’t.Direct: My mother said, “Will you come home on time?” And I said, “Yes.”
Indirect: My mother asked me if I would come home on time and I replied.
Sentences with ‘Have to’ or ‘Had to’
In indirect speech:
- "Have to" changes according to the tense.
- "Had to" changes to "had had to."
Examples:
Direct: Hari said, “I have to work a lot.”
Indirect: Hari said that he had to work a lot.Direct: Hari said, “I had to work a lot.”
Indirect: Hari said that he had had to work a lot.
Sentences with ‘Sir’, ‘Madam’, or ‘Your Honour’
In indirect speech, these words are removed and replaced with ‘respectfully’ in the reporting clause.
Example:
- Direct: Mahesh said, “Sir, may I go home?”
Indirect: Mahesh respectfully asked his sir if he might go home.
Exclamations and Wishes
In indirect speech, exclamatory words like "Hurrah!", "Alas!", "Oh!", "Bravo!", etc., are removed and replaced with expressions like ‘exclaimed with joy’, ‘exclaimed with sorrow’, etc.
Examples:
Direct: Rohan said, “Hurrah! We won the match.”
Indirect: Rohan exclaimed with joy that they had won the match.Direct: Reema said, “Alas! Karina’s mother is suffering from cancer.”
Indirect: Reema exclaimed with sorrow that Karina’s mother was suffering from cancer.Direct: The captain said to Kapil, “Bravo! You scored 89 runs.”
Indirect: The captain exclaimed with praise that he (Kapil) had scored 89 runs.
Wishes in Indirect Speech
Exclamatory sentences expressing wishes begin with ‘prayed’ or ‘blessed’.
Examples:
Direct: My mother said, “May God bless you!”
Indirect: My mother prayed to God for my well-being.Direct: She said, “May God save the country!”
Indirect: She prayed to God to save the country.Direct: They said to the king, “Long live!”
Indirect: They blessed the king for his long life.
Expressing Surprise or Emotion
Exclamatory sentences are turned into statements in indirect speech.
Examples:
Direct: Mohan said, “What a pity!”
Indirect: Mohan exclaimed that it was a great pity.Direct: I said, “How stupid he is!”
Indirect: I exclaimed that it was very stupid of him.Direct: “What a terrible sight it is!” said the traveller.
Indirect: The traveller exclaimed that it was a very terrible sight.
Key Points to Remember
- In indirect speech, question tags are usually removed.
- ‘Yes’ and ‘No’ are replaced with a short answer.
- ‘Have to’ follows normal tense rules, while ‘had to’ changes to ‘had had to’.
- Words like ‘Sir’, ‘Madam’, and ‘Your Honour’ are replaced with ‘respectfully’.
- Exclamatory words are removed, and expressions like ‘exclaimed with joy’ or ‘prayed’ are used instead.
- Exclamatory sentences become statements in indirect speech.
|
53 videos|210 docs|40 tests
|
FAQs on Statements and Questions - English Grammar Advanced - Class 10
| 1. What are the different types of statements in English? |  |
| 2. How do you form questions in English? |  |
| 3. What are question tags and how are they used in sentences? |  |
| 4. How can exclamations and wishes be formed in English? |  |
| 5. What are the key points to remember regarding statements and questions? |  |















