Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > English Grammar Class 8 > Pronouns
Pronouns | English Grammar Class 8 PDF Download
Introduction
- A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun or a group of words acting as a noun.
- Pronouns make sentences shorter and clearer by preventing repetition.
- When using pronouns, it's important to ensure they match the number (singular or plural) and gender (masculine, feminine, or neuter) of the nouns they replace.
Types of Pronouns
1. Personal Pronouns:
- Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things.
- They can be in the subjective case (when they function as the subject of a sentence) or the objective case (when they function as the object of a verb or preposition).
2. Possessive Pronouns:
- Possessive pronouns show ownership or possession.
- They include words like mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs.
3. Reflexive Pronouns:
- Reflexive pronouns are used when the subject of a sentence and the object are the same person or thing.
- Examples: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
4. Demonstrative Pronouns:
- Demonstrative pronouns are used to point out specific people or things.
- Examples: this, that, these, those.
5. Interrogative Pronouns:
- Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, what.
6. Relative Pronouns:
- Relative pronouns are used to introduce a relative clause that provides additional information about a noun or pronoun in the main clause.
- Examples: who, whom, whose, which, that.
7. Indefinite Pronouns:
- Indefinite pronouns refer to nonspecific people or things.
- Examples: everyone, someone, anybody, nobody, something, anything.
Agreement of Pronouns
- Pronouns must agree in number and gender with the nouns they replace.
- If the noun is singular, the pronoun should be singular. If the noun is plural, the pronoun should be plural.
- Examples: He is a doctor. They are doctors.
Antecedents of Pronouns
- The noun or pronoun that a pronoun refers to is called its antecedent.
- The antecedent must be clear and unambiguous to avoid confusion.
Common Errors with Pronouns
1. Pronoun-Antecedent Agreement:
- Ensure that the pronoun agrees in number and gender with its antecedent.
- Example of correct agreement: The boy did his homework.
- Example of incorrect agreement: The boy did their homework.
2. Ambiguous Pronoun Reference:
- Avoid using pronouns that could have multiple possible antecedents, leading to confusion.
- Example of ambiguous reference: The cat scratched the dog, which was painful. (It is unclear whether the cat or the dog was painful.)
Look at the following table. It will help you to use correct pronoun or possessive adjective: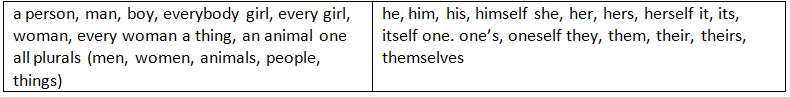
The table above gives only the third person. The one below is more exhaustive: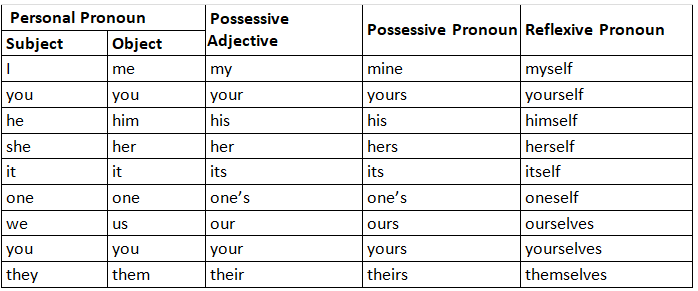
The document Pronouns | English Grammar Class 8 is a part of the Class 8 Course English Grammar Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
28 videos|103 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Pronouns - English Grammar Class 8
| 1. What are pronouns and why are they important in language? |  |
Ans. Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence, helping to avoid repetition and making sentences clearer and more concise. They are important because they facilitate smoother communication and help convey meaning more efficiently.
| 2. What are the different types of pronouns? |  |
Ans. There are several types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (I, you, he, she, it, we, they), possessive pronouns (mine, yours, his, hers, ours, theirs), reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, himself, etc.), demonstrative pronouns (this, that, these, those), and interrogative pronouns (who, what, which).
| 3. How do pronouns agree with their antecedents? |  |
Ans. Pronouns must agree in number (singular or plural) and gender (masculine, feminine, or neutral) with the noun they replace, known as the antecedent. For example, if the antecedent is singular and feminine, the pronoun must also be singular and feminine (e.g., "The girl lost her book").
| 4. Can pronouns change depending on the case? |  |
Ans. Yes, pronouns can change based on their grammatical case—subjective, objective, or possessive. For instance, the subjective case pronoun "I" becomes "me" in the objective case, and the possessive form is "my." This change is essential for maintaining grammatical correctness in sentences.
| 5. What are some common mistakes people make with pronouns? |  |
Ans. Common mistakes include using the wrong pronoun case (e.g., saying "Me went to the store" instead of "I went to the store"), failing to ensure pronoun-antecedent agreement, and using ambiguous pronouns that can confuse the reader about what noun they refer to.
Related Searches
















