Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age Class 8 Worksheet History Chapter 4
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| True or False |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Very Short Answer Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: Who was Birsa Munda?
A) A British official
B) A tribal leader
C) A landlord
D) A missionary
Ans: B) A tribal leader
Q2: What type of cultivation did jhum cultivators practice?
A) Settled cultivation
B) Shifting cultivation
C) Commercial cultivation
D) Industrial agriculture
Ans: B) Shifting cultivation
 Shifting Cultivation
Shifting Cultivation
Q3: What was the primary occupation of the Khonds?
A) Farming
B) Hunting and gathering
C) Herding animals
D) Settled agriculture
Ans: B) Hunting and gathering
Q4: Which of the following was considered a diku?
A) A tribal member
B) The British
C) A local farmer
D) A forest dweller
Ans: B) The British
Q5: What did Birsa Munda aim to achieve with his movement?
A) Establish British rule
B) Restore tribal rights
C) Promote Christianity
D) Develop industrial agriculture
Ans: B) Restore tribal rights
Fill in the Blanks
Q1: The British described the tribal people as __________.
Ans: The British described the tribal people as savages.
Q2: The method of sowing seeds in jhum cultivation is known as __________.
Ans: The method of sowing seeds in jhum cultivation is known as broadcasting.
Q3: The tribal chiefs got __________ titles in central India under the British land settlements.
Ans: The tribal chiefs got land titles in central India under the British land settlements.
Q4: Tribals went to work in the __________ of Assam and the ____________ in Bihar.
Ans: Tribals went to work in the tea plantations of Assam and the coal mines in Bihar.
Q5: Birsa Munda's movement aimed at establishing a __________.
Ans: Birsa Munda's movement aimed at establishing a Munda Raj.
True or False
Q1: Jhum cultivators plough the land and sow seeds.
Ans: False
Jhum cultivators scatter seeds without ploughing.
Q2: Cocoons were bought from the Santhals and sold by the traders at five times the purchase price.
Ans: True
Q3: Birsa urged his followers to purify themselves, give up drinking liquor and stop believing in witchcraft and sorcery.
Ans: True
Q4: The British wanted to preserve the tribal way of life.
Ans: False
The British altered tribal ways of life with policies that forced them to settle and change their practices
Q5: The Baigas were known as the best hunters among all adivasis in Central India.
Ans: True
Match the Following
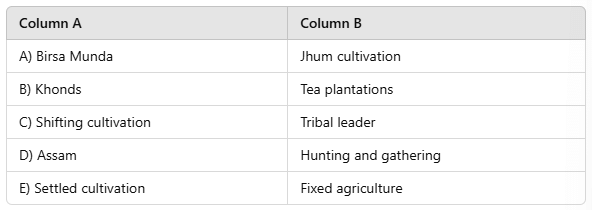 Ans:
Ans: 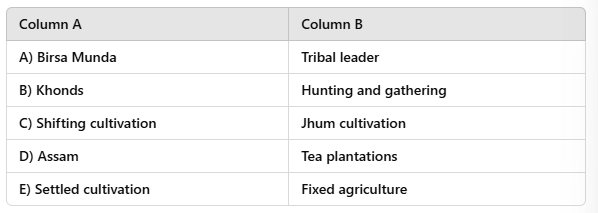
Very Short Answer Questions
Q1: Who was Birsa Munda?
Ans: Birsa Munda was a tribal leader born in the mid-1870s, known for his movement against the British colonial rule and for the rights of the Mundas. Postal Stamp issued in memory of Birsa Munda
Postal Stamp issued in memory of Birsa Munda
Q2: What did Birsa Munda urge his followers to give up?
Ans: Birsa urged his followers to give up drinking liquor and stop believing in witchcraft and sorcery.
Q3: What was jhum cultivation?
Ans: Jhum cultivation is a method of shifting cultivation practiced by tribal groups, involving moving to different patches of land for farming.
Q4: How did British rule affect tribal chiefs?
Ans: Under British rule, tribal chiefs lost much of their administrative power and were forced to follow British laws.
Q5: What was the vision of a golden age?
Ans: Birsa's vision of a golden age referred to a time when the Mundas lived a good life, free from oppression and in harmony with their traditions.
FAQs on Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age Class 8 Worksheet History Chapter 4
| 1. What were the primary concerns of tribals regarding the Dikus in the article "Tribals, Dikus and the Vision of a Golden Age"? |  |
| 2. How did the arrival of Dikus impact the lifestyle of tribal communities? |  |
| 3. What was the vision of a Golden Age for tribals as discussed in the article? |  |
| 4. In what ways did the tribals resist the changes brought by the Dikus? |  |
| 5. What role did the government play in the relationship between tribals and Dikus? |  |















