Class 5 Exam > Class 5 Notes > English Grammar Class 5 > Gender of Nouns
Gender of Nouns | English Grammar Class 5 PDF Download
Gender is a grammatical category that classifies nouns (and sometimes pronouns) into different classes. It often indicates the biological sex of the referent, but not always. In English, gender is mostly indicated through pronouns, while in many other languages, nouns and their modifiers also reflect gender.
Types of Gender
Masculine Gender
- Refers to male persons or animals.
- Examples: man, boy, father, uncle, son, brother, king, lion, tiger, bull.
Feminine Gender
- Refers to female persons or animals.
- Examples: woman, girl, mother, aunt, daughter, sister, queen, lioness, tigress, cow, hen, female dog.
Neuter Gender
- Refers to non-living things and plants.
- Examples: book, pen, cup, cot, shirt, house, flower, leaf, stem, gem, knife, tree, chair, table, computer, desk, ball, mobile, television.
Common Gender
- Refers to names that can be used for both males and females.
- Examples: baby, child, friend, cousin, parent, person, pupil, student, teacher, doctor, engineer, architect, writer, orphan, minister.
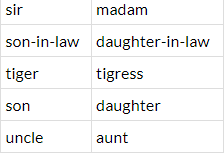
- The feminine form of a noun can often be made from its masculine version by adding a suffix such as -ess, -ine, -trix, or -a.
Formation of Feminine Gender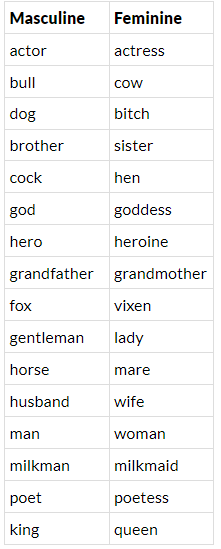
The document Gender of Nouns | English Grammar Class 5 is a part of the Class 5 Course English Grammar Class 5.
All you need of Class 5 at this link: Class 5
|
37 videos|529 docs|53 tests
|
FAQs on Gender of Nouns - English Grammar Class 5
| 1. What is the concept of gender of nouns? |  |
Ans. Gender of nouns refers to the classification of nouns into masculine, feminine, or neuter gender. In many languages, including English, nouns do not have inherent gender and are not assigned a specific gender. However, in languages like French, Spanish, and German, nouns are classified into gender categories, which can affect the form of the article, adjective, or pronoun used with the noun.
| 2. How does gender of nouns impact sentence structure? |  |
Ans. The gender of nouns can impact sentence structure in languages where gender is assigned to nouns. For example, in French, the form of the article and adjective used with a noun depends on its gender. This means that the gender of a noun determines how it interacts with other words in a sentence, potentially altering the word order or agreement of other elements in the sentence.
| 3. Are there any rules for determining the gender of nouns in languages with gender categories? |  |
Ans. Yes, in languages with gender categories, there are usually some rules or patterns that can help determine the gender of a noun. These rules can vary depending on the language, but they may consider factors such as the ending of the noun, its meaning, or its grammatical category. However, it is important to note that not all nouns will follow these rules, and some may have irregular gender assignments.
| 4. What are the implications of using the wrong gender for a noun in languages with gender categories? |  |
Ans. Using the wrong gender for a noun in languages with gender categories can result in grammatical errors and may affect the overall clarity and correctness of the sentence. In such languages, incorrect gender assignment can lead to mismatches between articles, adjectives, and pronouns, causing the sentence to sound awkward or confusing to native speakers. It is important to learn and understand the gender rules of a language to ensure proper usage.
| 5. Can the gender of nouns change over time or vary between dialects in languages with gender categories? |  |
Ans. Yes, the gender of nouns can change over time in some languages with gender categories. This phenomenon is known as noun gender shift and can occur due to various linguistic, historical, or sociolinguistic factors. Additionally, the gender of nouns can sometimes vary between different dialects or regional varieties of a language. These variations can add complexity to the learning and usage of gender in such languages.
Related Searches
















