Find the first circular tour that visits all petrol pumps - Class 8 PDF Download
Suppose there is a circle. There are n petrol pumps on that circle. You are given two sets of data.
- The amount of petrol that every petrol pump has.
- Distance from that petrol pump to the next petrol pump.
Calculate the first point from where a truck will be able to complete the circle (The truck will stop at each petrol pump and it has infinite capacity). Expected time complexity is O(n). Assume for 1-litre petrol, the truck can go 1 unit of distance.
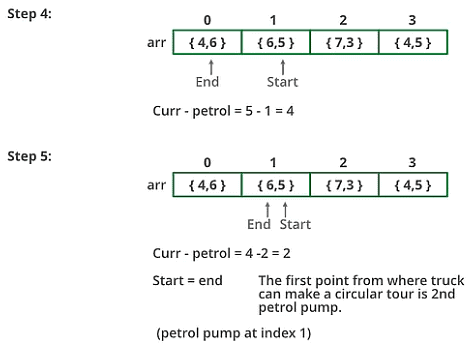
For example: let there be 4 petrol pumps with amount of petrol and distance to next petrol pump value pairs as {4, 6}, {6, 5}, {7, 3} and {4, 5}. The first point from where the truck can make a circular tour is 2nd petrol pump. Output should be “start = 1” (index of 2nd petrol pump).
- A Simple Solution is to consider every petrol pumps as a starting point and see if there is a possible tour. If we find a starting point with a feasible solution, we return that starting point. The worst case time complexity of this solution is O(n^2).
- An efficient approach is to use a Queue to store the current tour. We first enqueue first petrol pump to the queue, we keep enqueueing petrol pumps till we either complete the tour, or the current amount of petrol becomes negative. If the amount becomes negative, then we keep dequeuing petrol pumps until the queue becomes empty.
- Instead of creating a separate queue, we use the given array itself as a queue. We maintain two index variables start and end that represent the rear and front of the queue.
Below image is a dry run of the above approach: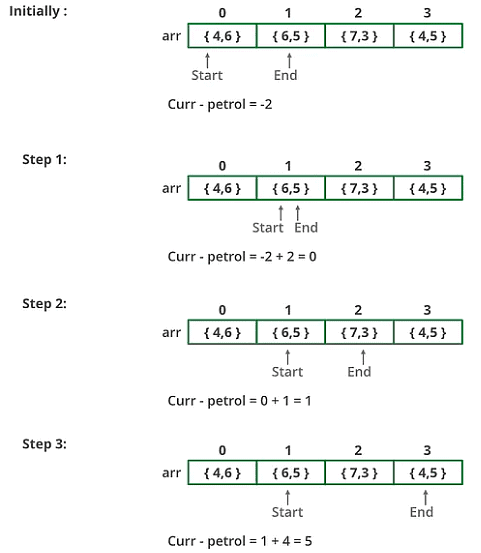
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find circular tour for a truck
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump
{
public:
int petrol;
int distance;
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a possible solution,
// otherwise returns -1
int printTour(petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
// Consider first petrol pump as a starting point
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
int curr_petrol = arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
/* Run a loop while all petrol pumps are not visited.
And we have reached first petrol pump again with 0 or more petrol */
while (end != start || curr_petrol < 0)
{
// If current amount of petrol in truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while (curr_petrol < 0 && start != end)
{
// Remove starting petrol pump. Change start
curr_petrol -= arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
start = (start + 1) % n;
// If 0 is being considered as start again, then there is no
// possible solution
if (start == 0)
return -1;
}
// Add a petrol pump to current tour
curr_petrol += arr[end].petrol - arr[end].distance;
end = (end + 1) % n;
}
// Return starting point
return start;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
petrolPump arr[] = {{6, 4}, {3, 6}, {7, 3}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1)? cout<<"No solution": cout<<"Start = "<<start;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
// C program to find circular tour for a truck
#include <stdio.h>
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
struct petrolPump
{
int petrol;
int distance;
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a possible solution,
// otherwise returns -1
int printTour(struct petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
// Consider first petrol pump as a starting point
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
int curr_petrol = arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
/* Run a loop while all petrol pumps are not visited.
And we have reached first petrol pump again with 0 or more petrol */
while (end != start || curr_petrol < 0)
{
// If current amount of petrol in truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while (curr_petrol < 0 && start != end)
{
// Remove starting petrol pump. Change start
curr_petrol -= arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
start = (start + 1)%n;
// If 0 is being considered as start again, then there is no
// possible solution
if (start == 0)
return -1;
}
// Add a petrol pump to current tour
curr_petrol += arr[end].petrol - arr[end].distance;
end = (end + 1)%n;
}
// Return starting point
return start;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
struct petrolPump arr[] = {{6, 4}, {3, 6}, {7, 3}};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1)? printf("No solution"): printf("Start = %d", start);
return 0;
}
Java
//Java program to find circular tour for a truck
public class Petrol
{
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
static class petrolPump
{
int petrol;
int distance;
// constructor
public petrolPump(int petrol, int distance)
{
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
// The function returns starting point if there is a possible solution,
// otherwise returns -1
static int printTour(petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
int curr_petrol = arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
// If current amount of petrol in truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while(end != start || curr_petrol < 0)
{
// If current amount of petrol in truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while(curr_petrol < 0 && start != end)
{
// Remove starting petrol pump. Change start
curr_petrol -= arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
start = (start + 1) % n;
// If 0 is being considered as start again, then there is no
// possible solution
if(start == 0)
return -1;
}
// Add a petrol pump to current tour
curr_petrol += arr[end].petrol - arr[end].distance;
end = (end + 1)%n;
}
// Return starting point
return start;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
public static void main(String[] args)
{
petrolPump[] arr = {new petrolPump(6, 4),
new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3)};
int start = printTour(arr, arr.length);
System.out.println(start == -1 ? "No Solution" : "Start = " + start);
}
}
//This code is contributed by Sumit Ghosh
Python
# Python program to find circular tour for a truck
# In this approach we will start the tour from the first petrol pump
# then while moving to the next pumps in the loop we will store the cumulative
# information that whether we have a deficit of petrol at the current pump or not
# If there is a deficit then we will add it to the deficit value calculated
# till the previous petrol pump and then update the starting point to the next pump
# and reset the petrol available in the truck as 0
# This function return starting point if there is a possible
# solution otherwise returns -1
def printTour(arr,n):
# Consider first petrol pump as starting point
start = 0
# These two variable will keep tracking if there is
# surplus(s) or deficit(d) of petrol in the truck
s = 0 # petrol available the truck till now
d = 0 # deficit of petrol till visiting this petrol pump
# Start from the first petrol pump and complete one loop
# of visiting all the petrol pumps and keep updating s and d at each pump
for i in range(n):
s += arr[i][0] - arr[i][1]
if s < 0: # the truck has a deficit of petrol
start = i+1 # change the starting point
d += s # storing the deficit of petrol till current petrol pump
s = 0 # starting again from new station
# when we reach first petrol pump again and sum of the petrol available at the truck
# and the petrol deficit till now is 0 or more petrol then return the starting point
# else return -1
return start if (s+d)>=0 else -1
# Driver program to test above function
arr = [[6,4], [3,6], [7,3]]
start = printTour(arr,3)
if start == -1:
print("No Solution Possible !!!")
else:
print("start = {}".format(start))
# This code is contributed by Antara Das(anny)
C#
// C# program to find circular
// tour for a truck
using System;
class GFG
{
// A petrol pump has petrol and
// distance to next petrol pump
public class petrolPump
{
public int petrol;
public int distance;
// constructor
public petrolPump(int petrol,
int distance)
{
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
// The function returns starting point
// if there is a possible solution,
// otherwise returns -1
public static int printTour(petrolPump[] arr,
int n)
{
int start = 0;
int end = 1;
int curr_petrol = arr[start].petrol -
arr[start].distance;
// If current amount of petrol in
// truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while (end != start || curr_petrol < 0)
{
// If current amount of petrol in
// truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while (curr_petrol < 0 && start != end)
{
// Remove starting petrol pump.
// Change start
curr_petrol -= arr[start].petrol -
arr[start].distance;
start = (start + 1) % n;
// If 0 is being considered as
// start again, then there is no
// possible solution
if (start == 0)
{
return -1;
}
}
// Add a petrol pump to current tour
curr_petrol += arr[end].petrol -
arr[end].distance;
end = (end + 1) % n;
}
// Return starting point
return start;
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
petrolPump[] arr = new petrolPump[]
{
new petrolPump(6, 4),
new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3)
};
int start = printTour(arr, arr.Length);
Console.WriteLine(start == -1 ? "No Solution" :
"Start = " + start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Shrikant13
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find circular tour for a truck
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump {
constructor(petrol, distance) {
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a possible solution,
// otherwise returns -1
const printTour = (arr, n) => {
// Consider first petrol pump as a starting point
let start = 0;
let end = 1;
let curr_petrol = arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
/* Run a loop while all petrol pumps are not visited.
And we have reached first petrol pump again with 0 or more petrol */
while (end != start || curr_petrol < 0) {
// If current amount of petrol in truck becomes less than 0, then
// remove the starting petrol pump from tour
while (curr_petrol < 0 && start != end) {
// Remove starting petrol pump. Change start
curr_petrol -= arr[start].petrol - arr[start].distance;
start = (start + 1) % n;
// If 0 is being considered as start again, then there is no
// possible solution
if (start == 0)
return -1;
}
// Add a petrol pump to current tour
curr_petrol += arr[end].petrol - arr[end].distance;
end = (end + 1) % n;
}
// Return starting point
return start;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [new petrolPump(6, 4), new petrolPump(3, 6), new petrolPump(7, 3)];
let n = arr.length;
let start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1) ? document.write("No solution") : document.write(`Start = ${start}`);
// This code is contributed by rakeshsahni
</script>
Output
Start = 2
- Time Complexity: We are visiting each petrol pump exactly once, therefore the time complexity is O(n)
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Another efficient solution can be to find out the first petrol pump where the amount of petrol is greater than or equal to the distance to be covered to reach the next petrol pump. Now we mark that petrol pump as start and now we check whether we can finish the journey towards the end point. If in the middle, at any petrol pump, the amount of petrol is less than the distance to be covered to reach the next petrol pump, then we can say we cannot complete the circular tour from start. We again try to find out the next point from where we can start our journey i.e. the next petrol pump where the amount of petrol is greater than or equal to the distance to be covered and we mark it as start. We need not look at any petrol pump in between the initial petrol pump marked as start and the new start as we know that we cannot complete the journey if we start from any middle petrol pump because eventually we will arrive at a point where amount of petrol is less than the distance. Now we repeat the process until we reach the last petrol pump and update our start as and when required. After we reach our last petrol pump, we try to reach our first petrol pump from the last and let’s say we have a remaining amount of petrol as curr_petrol. Now we again start traveling from the first petrol pump and take the advantage of our curr_petrol and try to reach the start. If we can reach the start, then we may conclude that start can be our starting point.Now you might be wondering even after reaching the end of the array why we are not making any circular tour and after reaching the end we’re concluding the result.
The main concept is that :
Let’s suppose we start at the 0’th pump moving on and at the middle we’ve negative fuel so we’ll restart our journey from the middle position. Now let’s suppose after reaching the end we’ve some fuel in our tank. We’re saying that the middle position will be the starting position. But why we’re not going back to the middle element ( from where we’ve started our journey) from the end to just check whether it’s possible to make circular tour or not? It’s because we’ve already checked previously that it’s possible to come from the 0’th index to the middle. So no need to check for the remainig part of the circular tour since it will always be a valid tour.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to find circular tour for a truck
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump {
public:
int petrol;
int distance;
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
int printTour(petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
int start;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Identify the first petrol pump from where we
// might get a full circular tour
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
// To store the excess petrol
int curr_petrol = 0;
int i;
for (i = start; i < n;) {
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance);
// If at any point remaining petrol is less than 0,
// it means that we cannot start our journey from
// current start
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
// We move to the next petrol pump
i++;
// We try to identify the next petrol pump from
// where we might get a full circular tour
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
// Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0;
break;
}
}
}
else {
// Move to the next petrolpump if curr_petrol is
// >= 0
i++;
}
}
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach the
// first petrol pump, it means no circular tour is
// possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < start; j++) {
curr_petrol += (arr[j].petrol - arr[j].distance);
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any point
// before we reach initial start, it means no
// circular tour is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
// If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
// means can get a circular tour from final_start, hence
// return it
return start;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
petrolPump arr[] = { { 6, 4 }, { 3, 6 }, { 7, 3 } };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1) ? cout << "No solution"
: cout << "Start = " << start;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by supratik_mitra
C
// C program to find circular tour for a truck
#include <stdio.h>
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
struct petrolPump {
int petrol;
int distance;
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
int printTour(struct petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
int start;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Identify the first petrol pump from where we
// might get a full circular tour
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
// To store the excess petrol
int curr_petrol = 0;
int i;
for (i = start; i < n;) {
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance);
// If at any point remaining petrol is less than 0,
// it means that we cannot start our journey from
// current start
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
// We move to the next petrol pump
i++;
// We try to identify the next petrol pump from
// where we might get a full circular tour
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
// Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
// Move to the next petrolpump if curr_petrol is
// >= 0
i++;
}
}
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach the
// first petrol pump, it means no circular tour is
// possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < start; j++) {
curr_petrol += (arr[j].petrol - arr[j].distance);
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any point
// before we reach initial start, it means no
// circular tour is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
// If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
// means can get a circular tour from final_start, hence
// return it
return start;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
struct petrolPump arr[]
= { { 6, 4 }, { 3, 6 }, { 7, 3 } };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1) ? printf("No solution")
: printf("Start = %d", start);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by jainlovely450
Java
// Java program to find circular tour for a truck
public class Circular
{
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol
// pump
static class petrolPump {
int petrol;
int distance;
public petrolPump(int petrol, int distance)
{
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
static int printTour(petrolPump arr[], int n)
{
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Identify the first petrol pump from where we
// might get a full circular tour
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
// To store the excess petrol
int curr_petrol = 0;
int i;
for (i = start; i < n;) {
curr_petrol
+= (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance);
// If at any point remaining petrol is less than
// 0, it means that we cannot start our journey
// from current start
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
// We move to the next petrol pump
i++;
// We try to identify the next petrol pump
// from where we might get a full circular
// tour
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
// Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0;
break;
}
}
}
else {
// Move to the next petrolpump if
// curr_petrol is
// >= 0
i++;
}
}
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach
// the first petrol pump, it means no circular tour
// is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < start; j++) {
curr_petrol
+= (arr[j].petrol - arr[j].distance);
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any
// point before we reach initial start, it means
// no circular tour is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
// If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
// means can get a circular tour from final_start,
// hence return it
return start;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
petrolPump arr[]
= { new petrolPump(6, 4), new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3) };
int n = arr.length;
int start = printTour(arr, n);
System.out.println(start == -1
? "No solution"
: "Start = " + start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by jainlovely450
Python3
# Python program to find circular tour for a truck
# A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump:
def __init__(self, petrol, distance):
self.petrol = petrol
self.distance = distance
# The function returns starting point if there is a
# possible solution, otherwise returns -1
def printTour(arr, n):
start = 0
for i in range(n):
# Identify the first petrol pump from where we
# might get a full circular tour
if arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance:
start = i
break
# To store the excess petrol
curr_petrol = 0
for i in range(start, n):
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance)
# If at any point remaining petrol is less than 0,
# it means that we cannot start our journey from
# current start
if(curr_petrol < 0):
# We move to the next petrol pump
i += 1
# We try to identify the next petrol pump from
# where we might get a full circular tour
while(i < n):
if(arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance):
start = i
# Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0
break
i += 1
else:
# Move to the next petrolpump if curr_petrol is
# >= 0
i += 1
''' If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach the
first petrol pump, it means no circular tour is
possible '''
if(curr_petrol < 0):
return -1
for i in range(start):
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance)
''' If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any point
before we reach initial start, it means no
circular tour is possible '''
if(curr_petrol < 0):
return -1
''' If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
means can get a circular tour from final_start, hence
return it '''
return start
# Driver code
arr = [petrolPump(6, 4), petrolPump(3, 6), petrolPump(7, 3)]
start = printTour(arr, len(arr))
if start == -1:
print("No solution")
else:
print("Start = {}".format(start))
# This code is contributed by jainlovely450
C#
using System;
// C# program to find circular tour for a truck
public class Circular {
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol
// pump
public class petrolPump {
public int petrol;
public int distance;
public petrolPump(int petrol, int distance) {
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
static int printTour(petrolPump []arr, int n) {
int start = 0;
int i;
for ( i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Identify the first petrol pump from where we
// might get a full circular tour
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
// To store the excess petrol
int curr_petrol = 0;
for (i = start; i < n;) {
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance);
// If at any point remaining petrol is less than
// 0, it means that we cannot start our journey
// from current start
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
// We move to the next petrol pump
i++;
// We try to identify the next petrol pump
// from where we might get a full circular
// tour
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
// Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0;
break;
}
}
}
else {
// Move to the next petrolpump if
// curr_petrol is
// >= 0
i++;
}
}
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach
// the first petrol pump, it means no circular tour
// is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
for (int j = 0; j < start; j++) {
curr_petrol += (arr[j].petrol - arr[j].distance);
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any
// point before we reach initial start, it means
// no circular tour is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
// If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
// means can get a circular tour from final_start,
// hence return it
return start;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args) {
petrolPump []arr = { new petrolPump(6, 4),
new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3) };
int n = arr.Length;
int start = printTour(arr, n);
Console.WriteLine(start == -1 ? "No solution" : "Start = " + start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Javascript
<script>
// JavaScript program to find circular tour for a truck
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump {
constructor(petrol, distance) {
this.petrol = petrol;
this.distance = distance;
}
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
const printTour = (arr, n) => {
let start;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// Identify the first petrol pump from where we
// might get a full circular tour
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
break;
}
}
// To store the excess petrol
let curr_petrol = 0;
let i;
for (i = start; i < n;)
{
curr_petrol += (arr[i].petrol - arr[i].distance);
// If at any point remaining petrol is less than 0,
// it means that we cannot start our journey from
// current start
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
// We move to the next petrol pump
i++;
// We try to identify the next petrol pump from
// where we might get a full circular tour
for (; i < n; i++) {
if (arr[i].petrol >= arr[i].distance) {
start = i;
// Reset rem_petrol
curr_petrol = 0;
break;
}
}
}
else {
// Move to the next petrolpump if curr_petrol is
// >= 0
i++;
}
}
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 while we reach the
// first petrol pump, it means no circular tour is
// possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
for (let j = 0; j < start; j++) {
curr_petrol += (arr[j].petrol - arr[j].distance);
// If remaining petrol is less than 0 at any point
// before we reach initial start, it means no
// circular tour is possible
if (curr_petrol < 0) {
return -1;
}
}
// If we have successfully reached intial_start, it
// means can get a circular tour from final_start, hence
// return it
return start;
}
// Driver code
let arr = [new petrolPump(6, 4), new petrolPump(3, 6), new petrolPump(7, 3)];
let n = arr.length;
let start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1) ? document.write("No solution") : document.write(`Start = ${start}`);
// This code is contributed by rakeshsahni
</script>
Output
Start = 2
- Time Complexity: O(n)
- Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Another simpler approach is to store the value of the capacity in some variable whenever the capacity becomes less than zero.
In this case You have to traverse the array only once as compared to previous method which traverses the each index twice.
Here is the implementation of above idea:
C++
// C++ program to find circular tour for a truck
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump {
public:
int petrol;
int distance;
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
int printTour(petrolPump p[], int n)
{
// deficit is used to store the value of the capacity as
// soon as the value of capacity becomes negative so as
// not to traverse the array twice in order to get the
// solution
int start = 0, deficit = 0;
int capacity = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
capacity += p[i].petrol - p[i].distance;
if (capacity < 0) {
// If this particular step is not done then the
// between steps would be redundant
start = i + 1;
deficit += capacity;
capacity = 0;
}
}
return (capacity + deficit >= 0) ? start : -1;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
petrolPump arr[] = { { 6, 4 }, { 3, 6 }, { 7, 3 } };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int start = printTour(arr, n);
(start == -1) ? cout << "No solution"
: cout << "Start = " << start;
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by aditya kumar
Java
// Java program to find circular tour for a truck
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
static class petrolPump {
int petrol;
int distance;
petrolPump(int a, int b) {
this.petrol = a;
this.distance = b;
}
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
static int printTour(petrolPump p[], int n)
{
// deficit is used to store the value of the capacity as
// soon as the value of capacity becomes negative so as
// not to traverse the array twice in order to get the
// solution
int start = 0, deficit = 0;
int capacity = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
capacity += p[i].petrol - p[i].distance;
if (capacity < 0) {
// If this particular step is not done then the
// between steps would be redundant
start = i + 1;
deficit += capacity;
capacity = 0;
}
}
return (capacity + deficit >= 0) ? start : -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
petrolPump arr[] = { new petrolPump(6, 4),
new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3) };
int n = arr.length;
int start = printTour(arr, n);
if (start == -1)
System.out.print("No solution");
else
System.out.print("Start = " + start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
Python3
# Python program to find circular tour for a truck
# A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump:
def __init__(self,a, b):
self.petrol = a;
self.distance = b;
# The function returns starting point if there is a
# possible solution, otherwise returns -1
def printTour( p, n):
# deficit is used to store the value of the capacity as
# soon as the value of capacity becomes negative so as
# not to traverse the array twice in order to get the
# solution
start = 0;
deficit = 0;
capacity = 0;
for i in range(n):
capacity += p[i].petrol - p[i].distance;
if (capacity < 0):
# If this particular step is not done then the
# between steps would be redundant
start = i + 1;
deficit += capacity;
capacity = 0;
if(capacity + deficit >= 0):
return start;
else:
return -1;
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [petrolPump(6, 4),petrolPump(3, 6),petrolPump(7, 3)] ;
n = len(arr);
start = printTour(arr, n);
if (start == -1):
print("No solution");
else:
print("Start = " , start);
# This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
// C# program to find circular tour for a truck
using System;
public class GFG {
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
public class petrolPump {
public int petrol;
public int distance;
public petrolPump(int a, int b) {
this.petrol = a;
this.distance = b;
}
};
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
static int printTour(petrolPump []p, int n) {
// deficit is used to store the value of the capacity as
// soon as the value of capacity becomes negative so as
// not to traverse the array twice in order to get the
// solution
int start = 0, deficit = 0;
int capacity = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
capacity += p[i].petrol - p[i].distance;
if (capacity < 0)
{
// If this particular step is not done then the
// between steps would be redundant
start = i + 1;
deficit += capacity;
capacity = 0;
}
}
return (capacity + deficit >= 0) ? start : -1;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
petrolPump []arr = { new petrolPump(6, 4),
new petrolPump(3, 6),
new petrolPump(7, 3) };
int n = arr.Length;
int start = printTour(arr, n);
if (start == -1)
Console.Write("No solution");
else
Console.Write("Start = " + start);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
Javascript
<script>
// javascript program to find circular tour for a truck
// A petrol pump has petrol and distance to next petrol pump
class petrolPump {
constructor(a , b) {
this.petrol = a;
this.distance = b;
}
}
// The function returns starting point if there is a
// possible solution, otherwise returns -1
function printTour( p , n) {
// deficit is used to store the value of the capacity as
// soon as the value of capacity becomes negative so as
// not to traverse the array twice in order to get the
// solution
var start = 0, deficit = 0;
var capacity = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
capacity += p[i].petrol - p[i].distance;
if (capacity < 0) {
// If this particular step is not done then the
// between steps would be redundant
start = i + 1;
deficit += capacity;
capacity = 0;
}
}
return (capacity + deficit >= 0) ? start : -1;
}
// Driver code
var arr = [ new petrolPump(6, 4), new petrolPump(3, 6), new petrolPump(7, 3) ];
var n = arr.length;
var start = printTour(arr, n);
if (start == -1)
document.write("No solution");
else
document.write("Start = " + start);
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
Output
Start = 2













