Threaded Binary Tree - Class 8 PDF Download
Threaded Binary Tree
Inorder traversal of a Binary tree can either be done using recursion or with the use of a auxiliary stack. The idea of threaded binary trees is to make inorder traversal faster and do it without stack and without recursion. A binary tree is made threaded by making all right child pointers that would normally be NULL point to the inorder successor of the node (if it exists).
There are two types of threaded binary trees.
- Single Threaded: Where a NULL right pointers is made to point to the inorder successor (if successor exists)
- Double Threaded: Where both left and right NULL pointers are made to point to inorder predecessor and inorder successor respectively. The predecessor threads are useful for reverse inorder traversal and postorder traversal.
The threads are also useful for fast accessing ancestors of a node.
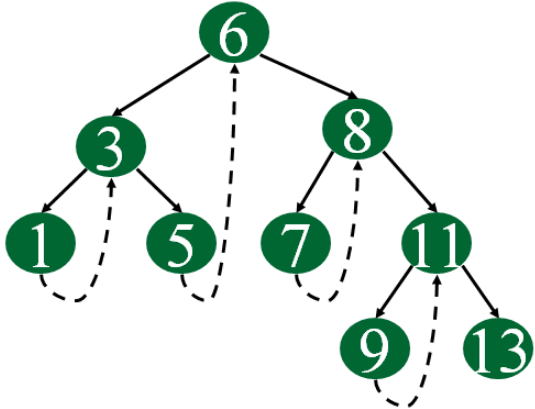
Following diagram shows an example Single Threaded Binary Tree. The dotted lines represent threads.
C representation of a Threaded Node
Following is C representation of a single-threaded node.
C
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *left, *right;
bool rightThread;
}
Java representation of a Threaded Node
Following is Java representation of a single-threaded node.
Java
static class Node
{
int data;
Node left, right;
boolean rightThread;
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data,rightThread):
self.data = data;
self.left = None;
self.right = None;
self.rightThread = rightThread;
# This code is contributed by umadevi9616
C#
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public bool rightThread;
}
// This code is contributed by aashish1995
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.rightThread = false;
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995
</script>
Since right pointer is used for two purposes, the boolean variable rightThread is used to indicate whether right pointer points to right child or inorder successor. Similarly, we can add leftThread for a double threaded binary tree.
Inorder Traversal using Threads
Following is code for inorder traversal in a threaded binary tree.
C
// Utility function to find leftmost node in a tree rooted
// with n
struct Node* leftMost(struct Node* n)
{
if (n == NULL)
return NULL;
while (n->left != NULL)
n = n->left;
return n;
}
// C code to do inorder traversal in a threaded binary tree
void inOrder(struct Node* root)
{
struct Node* cur = leftMost(root);
while (cur != NULL) {
printf("%d ", cur->data);
// If this node is a thread node, then go to
// inorder successor
if (cur->rightThread)
cur = cur->right;
else // Else go to the leftmost child in right
// subtree
cur = leftmost(cur->right);
}
}
Java
// Utility function to find leftmost node in a tree rooted
// with n
Node leftMost(Node n)
{
if (n == null)
return null;
while (n.left != null)
n = n.left;
return n;
}
// C code to do inorder traversal in a threaded binary tree
static void inOrder(Node root)
{
Node cur = leftMost(root);
while (cur != null) {
System.out.printf("%d ", cur.data);
// If this node is a thread node, then go to
// inorder successor
if (cur.rightThread)
cur = cur.right;
else // Else go to the leftmost child in right
// subtree
cur = leftmost(cur.right);
}
}
// This code contributed by aashish1995
Python3
# Utility function to find leftmost Node in a tree rooted
# with n
def leftMost(n):
if (n == None):
return None;
while (n.left != None):
n = n.left;
return n;
# C code to do inorder traversal in a threaded binary tree
def inOrder(root):
cur = leftMost(root);
while (cur != None):
print(cur.data," ");
# If this Node is a thread Node, then go to
# inorder successor
if (cur.rightThread):
cur = cur.right;
else: # Else go to the leftmost child in right
# subtree
cur = leftmost(cur.right);
# This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
C#
// Utility function to find leftmost node in a tree rooted
// with n
Node leftMost(Node n)
{
if (n == null)
return null;
while (n.left != null)
n = n.left;
return n;
}
// C code to do inorder traversal in a threaded binary tree
static void inOrder(Node root)
{
Node cur = leftMost(root);
while (cur != null)
{
Console.Write("{0} ", cur.data);
// If this node is a thread node, then go to
// inorder successor
if (cur.rightThread)
cur = cur.right;
else // Else go to the leftmost child in right
// subtree
cur = leftmost(cur.right);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
Javascript
<script>
// Utility function to find leftmost node in a tree rooted
// with n
function leftMost(n)
{
if (n == null)
return null;
while (n.left != null)
n = n.left;
return n;
}
// JavaScript code to do inorder traversal in
// a threaded binary tree
function inOrder(root)
{
let cur = leftMost(root);
while (cur != null) {
document.write(cur.data+" ");
// If this node is a thread node, then go to
// inorder successor
if (cur.rightThread)
cur = cur.right;
else // Else go to the leftmost child in right
// subtree
cur = leftmost(cur.right);
}
}
// This code is contributed by unknown2108
</script>
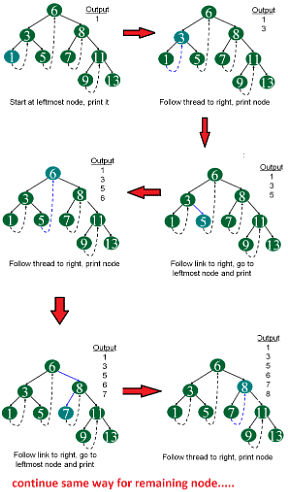
Following diagram demonstrates inorder order traversal using threads.
Advantages of Threaded Binary Tree
- In this Tree it enables linear traversal of elements.
- It eliminates the use of stack as it perform linear traversal.
- Enables to find parent node without explicit use of parent pointer.
- Threaded tree give forward and backward traversal of nodes by in-order fashion.
- Nodes contain pointers to in-order predecessor and successor.


















