Idea of Development Planning and Mixed Economy | Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes) PDF Download
Introduction
India began its journey towards planned socioeconomic development after gaining independence. The various development schemes devised by the leaders of independent India aimed to address not just the economic aspect, but also education, population control, and political participation, among others. This demonstrates that India's focus is on sociocultural development rather than solely on economic growth.- The objectives of development have been enshrined in the Constitution and various planning documents. Following independence, the Constitution established the aim of building a socialist, secular, and democratic society. This meant creating a social order that guaranteed equality, freedom, and justice. To achieve these goals, the government developed institutional mechanisms and mobilized both human and material resources to fulfill the aims set forth by the Constitution. The Planning Commission has stated the following regarding the goal of development: To initiate a process of development that will raise living standards and open up new opportunities for a richer and more varied life for the people.
- While it is not possible to enumerate all the development schemes, let us mention some of them and examine how the principles of socialism, equality, social justice, and democracy have been integrated into these initiatives.
Socialist Path and Mixed Economy
India has adopted a mixed economy approach for its development, which incorporates elements of both socialism and capitalism. On one hand, India promotes private businesses and industries, while on the other hand, it maintains significant control over major entrepreneurial and business activities.- In accordance with its socialist principles, the Indian government plays a crucial role as an entrepreneur by establishing heavy industries such as steel production and power generation. Additionally, the public sector encompasses nationalized banks, railways, and postal services. This dominant control of the state over key economic sectors reflects India's commitment to socialist ideology.
- At the same time, India encourages private enterprises by reserving certain industries exclusively for the private sector. In industries like textiles and cement, both private and state-owned enterprises are permitted to operate. Moreover, sectors such as health, education, and transport witness the coexistence of private and state agencies, working independently or collaboratively.
- Critics argue that India's development path has, in practice, shifted towards capitalism, as privately managed industries have become more profitable and economic power has become concentrated in the hands of a few large private businesses. However, it is essential to acknowledge that India continues to strive for a balanced approach to development through its mixed economy model.

Rural Development in India: An Overview
India, with over 70% of its population residing in villages, has placed significant emphasis on rural development since its independence. Various programs and initiatives have been launched over the past few decades, with two main guiding principles: one derived from Mahatma Gandhi's vision of self-reliant and self-sufficient village communities, and the other from government policies. Despite these efforts, socio-economic disparities and the goal of establishing a social order based on equality and social justice remain unattained.- Gandhi's Vision: Gandhi envisioned village communities that were politically autonomous, economically self-sufficient, and characterized by harmony and cooperation. He believed that social equality would prevail in such communities, devoid of exploitation. Although his ideas have inspired various programs, not all have been incorporated into government policies for rural development.
- Community Development Programme (CDP): Launched as a method for transforming social and economic life in villages, the CDP focused on non-material aspects of community life. Its goals included increasing employment and production through scientific agricultural methods, establishing subsidiary and cottage industries, promoting self-help and self-reliance, and extending the principle of cooperation. However, the program was hindered by government structures and a divided rural society based on caste and land relations.
- Panchayati Raj: Following the Balwantray Mehta Committee's recommendations in 1957, Panchayati Raj was introduced to encourage local initiative and direction for rural development. While it attempted to devolve power to lower levels, the scheme did not achieve its desired results and was continually evaluated and revised through the 1970s and 1980s.
- Cooperative Institutions: Established as supportive institutions for the CDP and Panchayati Raj, cooperative institutions aimed to provide agricultural inputs, credit, essential commodities, and promote harmonious relations among rural people. While the cooperative movement grew, it primarily benefited large and middle farmers, with limited impact on landless and poorer groups.
- Target Group Planning: In the Fourth Five-Year Plan, the concept of rural development was redefined to focus on the rural poor as the 'target group' for ameliorative measures. Various programs were launched to cater to the needs of small and marginal farmers, tenants, agricultural workers, and the landless. However, these programs faced many challenges, including an overemphasis on bureaucratic control and a lack of local participation.
Planning : Five year plans
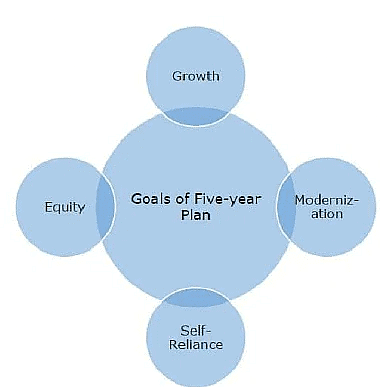
Five Year Plans have been the primary instruments for achieving India's development objectives. These plans have focused on various aspects, including economic growth, social justice, and poverty eradication. The Indian approach to planning is characterized by being comprehensive, balanced, and democratic. It aims to set up a socialistic pattern of society, considering both economic and social aspects of development.
The Indian approach to planning emphasizes the importance of human values and the pursuit of material advancement, striving to combine economic, technological, human, and institutional components of development. Some of the key features of India's approach to planning include:
- Comprehensive and balanced planning: Indian plans cover both public and private investment and encourage growth in all sectors of the economy.
- Democratic planning: India's planning approach differs from totalitarian planning in that it encourages active participation of people in organizing and developing their social life.
- Socialistic pattern of society: India's approach to planning aims to establish a socialistic pattern of society by considering both economic and social aspects of development.
- Combination of traditional and modern technology: India's approach to development focuses on improving and upgrading traditional technology used by village and cottage industries while also importing high technology to keep pace with global advancements.
- Reconciliation of planning with democracy and equitable distribution: India's development plans aim to balance increased production with equitable distribution, promoting the establishment of large industries alongside the development of cottage industries and traditional technology.
Despite these approaches, critics argue that India's planning strategies have only benefited a specific class of people, such as industrial and commercial groups, while disparities between different regions and groups have continued to increase. Moreover, fundamental problems such as land reform, modernizing village structures, and controlling population growth remain unsolved despite decades of planned social change. It is essential for India to address these issues and ensure that its planning strategies truly promote growth with equality and social justice.
Change in Relation to Caste, Rural society and Women
India has been on a journey of planned socioeconomic transformation since gaining independence. Social planning has played a significant role in driving these changes. However, to truly understand the process of social change in India, it is essential to consider numerous interrelated factors beyond planning, as well as the historical and internal processes that have shaped the rate, content, and direction of change.
- One such influential factor is the colonial rule, particularly the introduction of British ideas, science, and technology, which has played a crucial role in India's social transformation. This aspect must be considered in conjunction with the caste-based structure of Indian society to better comprehend the extent of change experienced by the nation.
- Many researchers who have studied social change in India have primarily focused on the transformations that have occurred in different aspects of life since British rule. Some argue that colonialism and the fight for independence, along with the pluralistic and caste-based stratification of Indian society, have significantly influenced the ideologies and strategies adopted by India regarding planned socioeconomic development since gaining independence.
- In summary, understanding social change in India requires examining a multitude of interconnected factors, including historical events like colonial rule, the introduction of British ideas, and the caste-based nature of Indian society, which have shaped the direction and rate of change in the country.
Conclusion
India's journey towards planned socioeconomic development since independence has been influenced by various factors, including its mixed economy model, rural development initiatives, five-year plans, and the interplay of historical events and social structures, such as colonial rule and the caste system. Despite considerable progress in many sectors, India still faces challenges in achieving its development goals, such as addressing socio-economic disparities, land reform, modernizing village structures, and controlling population growth. As India continues its development journey, it is crucial to ensure that its strategies remain focused on promoting growth with equality and social justice, in line with the guiding principles of its Constitution.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) of Idea of Development Planning and Mixed Economy
What is the primary goal of India's development schemes?
The primary goal of India's development schemes is to initiate a process of development that will raise living standards and open up new opportunities for a richer and more varied life for the people. This includes focusing on sociocultural development rather than solely on economic growth.
What is the mixed economy approach adopted by India?
India's mixed economy approach incorporates elements of both socialism and capitalism. The government promotes private businesses and industries while maintaining significant control over major entrepreneurial and business activities, and operating public sector enterprises in key economic sectors.
What are the key features of India's approach to Five Year Plans?
India's approach to planning is characterized by being comprehensive, balanced, and democratic. Key features include comprehensive and balanced planning, democratic planning, establishment of a socialistic pattern of society, combination of traditional and modern technology, and reconciliation of planning with democracy and equitable distribution.
How has India's focus on rural development evolved over the years?
India's rural development focus has evolved from programs inspired by Mahatma Gandhi's vision of self-reliant and self-sufficient village communities to government-led initiatives like the Community Development Programme, Panchayati Raj, cooperative institutions, and target group planning.
What factors need to be considered to understand social change in India?
To understand social change in India, it is essential to consider numerous interconnected factors, including historical events like colonial rule, the introduction of British ideas, the caste-based nature of Indian society, and the ideologies and strategies adopted by India regarding planned socioeconomic development since gaining independence.
|
112 videos|390 docs
|
FAQs on Idea of Development Planning and Mixed Economy - Sociology Optional for UPSC (Notes)
| 1. What is the concept of development planning in a mixed economy? |  |
| 2. How does a mixed economy differ from a purely capitalist or socialist economy? |  |
| 3. What are the key advantages of development planning in a mixed economy? |  |
| 4. What role does the government play in development planning within a mixed economy? |  |
| 5. How can development planning address issues of inequality in a mixed economy? |  |
















