GS3 PYQ (Mains Answer Writing): International Environmental Convention | Environment for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Q1: Explain the purpose of the Green Grid Initiative launched at World Leaders Summit of the COP26 UN Climate Change Conference in Glasgow in November, 2021. When this idea was first floated in the International Solar Alliance (ISA)? (UPSC MAINS GS3 )
The Green Grid or the One Sun One World One Grid (OSOWOG) initiative was announced at COP- 26, Glasgow by India and the UK. The initiative is aimed at accelerating the development and deployment of interconnected electricity grids across continents, countries, and communities, and improving energy access of the poorest through mini-grids and off-grid solutions. The idea for the single global solar grid was first outlined at the International Solar Alliance in 2018, by the Prime Minister of India.
The Green Grid Initiative aims
- To speed up the process of decarbonising energy production.
- To create an international network of global interconnected solar power grid to ensure 24×7 supply of green power.
- To help in increasing investment in R&D centers by pooling skill, technology and financial resources.
- Interconnected transnational grids are future.
- addressing the issue of reliability of supply from solar power plants
- addressing the issue of high cost of energy storage ! will reduce the costs of the energy transition
As good as it sounds, the implementation of the Green Grid has to counter the following challenges:
- The creation of global transmission infrastructure involves huge financing.
- For connecting with the Green Grid, a global cooperation between the countries is needed.
- As the grid will pass through several geographical locations, it will be sensitive to the security risks emanating from terror organisations.
The Green Grid initiative is a transformational new programme, with the goal of making universal access to renewable energy a reality. It will ensure that clean power is the most affordable and reliable option for all countries to meet their energy needs efficiently by 2030.
Topics Covered - Green Grid Technique
Q2: Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve these revised standards? (UPSC MAINS GS3 )
The WHO recently released an updated version of the Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs). The guidelines recommend new air quality levels to protect the health of populations, by reducing levels of key air pollutants.
Key Points:
- WHO’s new guidelines recommend air quality levels for six pollutants — particulate matter (PM 2.5 & PM10), ozone (O₃), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) sulfur dioxide (SO₂) and carbon monoxide (CO).
- The annual average for PM2.5 should not exceed 5 micrograms per cubic metre of air, while the 24-hour average should not exceed 15 micrograms per cubic metre.
- The annual average for PM 10 should not exceed 15 micrograms per cubic metre of air, while the 24-hour average should not exceed 45 micrograms per cubic metre.
- The ozone levels average should not exceed 100 micrograms per cubic metre over a 24-hour period.
- The nitrogen oxide levels should not exceed 25 micrograms per cubic metre over a 24-hour period.
- The sulphur dioxide levels should not exceed 40 micrograms per cubic metre over a 24-hour period.
- The carbon monoxide levels should not exceed 4 micrograms per cubic metre over a 24-hour period.
Global Air Quality Guidelines 2021 vs Global Air Quality Guidelines 2021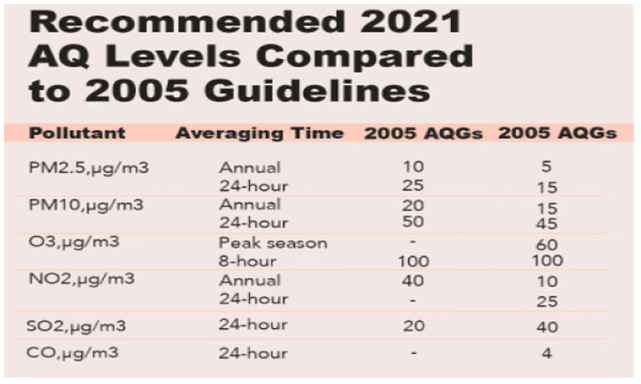 The centre has launched National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) to tackle air pollution in 122 cities by aiming for a 20-30 percent reduction in PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations by 2024, compared to 2017.
The centre has launched National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) to tackle air pollution in 122 cities by aiming for a 20-30 percent reduction in PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations by 2024, compared to 2017.
Changes required in India’s NCAP
- India’s air pollution standards are more relaxed in comparison to WHO’s prescribed guidelines. Thus, efforts are needed to make the guidelines more stringent with revised targets.
- Under the proposed new Mission – Clean Air for All, government tends to make targets of PM2.5 & PM10 more stringent.
- There is a need to adopt an airshed approach to take measures to deal with air pollution. Under this approach, the policymakers will have to plan actions keeping in view geographical, meteorological and other common factors which pollute air within the airshed.
Topics Covered - Global Air Quality Guidelines
Q3: Describe the major outcomes of the 26th session of the Conference of the Parties (COP) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). What are the commitments made by India in this conference? (UPSC MAINS )
The 26th UN Climate Change Conference of the Parties (COP26) was held in Glasgow, UK with the aim to finalise the rules and procedures for implementation of the Paris Agreement and to get all countries to commit to a net-zero target by a specific year.
Outcomes of COP-26
- For the first time, COP agreed upon phasing down coal power. A pledge to end coal power generation by 2040 was taken.
- Providing the long promised $100 billion annual support towards developing countries’ green transition.
- Supporting electric vehicles and a phase out of gasoline and diesel-powered motor vehicles by 2040.
- Reversing deforestation in an attempt to protect existing nature-based solutions to capturing emissions.
- The Paris Agreement rulebook was completed which kept the Paris targets alive of limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees celsius.
- The member countries agreed for the Glasgow Climate Pact, under which member countries will report their progress towards more climate ambition next year, at COP27 Egypt.
- A methane pledge, led by the United States and the European Union, by which more than 100 countries agreed to cut emissions of this greenhouse gas by 2030.
India’s commitment at COP-26
- India announced that its net zero target is to be achieved by 2070.
- The Government of India has launched ‘E-Amrit’, a web portal on electric vehicles (EVs), in COP-26. The portal will encourage adoption of EV and bust myth regarding it.
- India did not join methane pledge as it would have negatively impacted India’s agriculture.
- India will fulfil 50% of its energy requirement through renewable energy by 2030.
- India will reduce 1 billion tonnes of carbon emissions by 2030.
Although, COP-26 marked several breakthroughs in action towards climate change, yet the targets are not enough to control the rise of earth’s temperature by 1.5 degree at the end of century. Therefore, the countries should constantly strive to improve upon targets and adopt newer carbon neutral technologies.
Topics Covered- COP 26
|
95 videos|234 docs|52 tests
|
FAQs on GS3 PYQ (Mains Answer Writing): International Environmental Convention - Environment for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the purpose of international environmental conventions? |  |
| 2. How do countries comply with international environmental conventions? |  |
| 3. What are some key international environmental conventions? |  |
| 4. How do international environmental conventions impact global environmental governance? |  |
| 5. How do international environmental conventions contribute to sustainable development? |  |
















