Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Notes > Mathematics Olympiad Class 7 > Summary: Symmetry
Symmetry Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary Chapter 12
Line Symmetry
- A figure has a line symmetry, if there is a line about which the figure may be folded so that the two parts of the figure will coincide.
Lines of symmetry for regular polygons
- A polygon is said to be regular if all its sides are of equal length and all its angles are of equal measure.
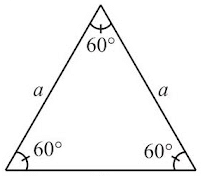
- An equilateral triangle is regular because each of its sides has same length and each of its angles measures 60°.
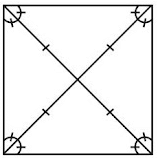
- A square is also regular because all its sides are of equal length and each of its angles is a right angle (i.e., 90°). Its diagonals are seen to be perpendicular bisectors of one another.
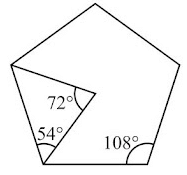
- If a pentagon is regular, naturally, its sides should have equal length. The measure of each of its angles is 108°.
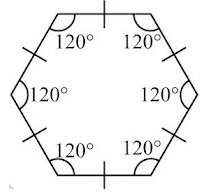
- A regular hexagon has all its sides equal and each of its angles measures 120°.
Rotational symmetry
- Rotation turns an object about a fixed point. This fixed point is the centre of rotation. The angle by which the object rotates is the angle of rotation.
- A half-turn means rotation by 180°; a quarter-turn means rotation by 90°. Rotation may be clockwise or anticlockwise.
- If, after a rotation, an object looks exactly the same, we say that it has a rotational symmetry.
- In a complete turn (of 360°), the number of times an object looks exactly the same is called the order of rotational symmetry. The order of symmetry of a square, for example, is 4 while, for an equilateral triangle, it is 3.
Line Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
- Some shapes have only one line of symmetry, like the letter E; some have only rotational symmetry, like the letter S; and some have both symmetries like the letter H.
Line Symmetry and Mirror Reflection
- A shape has line symmetry when one half of it is the mirror image of the other half.
- Mirror reflection leads to symmetry, under which the left-right orientations have to be taken care of.
The document Symmetry Summary Class 7 NCERT Summary Chapter 12 is a part of the Class 7 Course Mathematics Olympiad Class 7.
All you need of Class 7 at this link: Class 7
|
40 videos|118 docs|99 tests
|
Related Searches
















