History of Banking in India | IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
Banking in India has a very long history starting from the late 18th century. The origin of modern banking started in 1770 in the name of the “Bank of Hindustan” by the English agency ‘House of Alexander & Co’ in Kolkatta however it was closed in 1832. Further in 1786 “General Bank of India” was started and it failed in 1791.
The term "banking" as we know it today originated in the Western world. The history of banking in India dates back to the 17th century when it was introduced by British rulers. Since then, a number of changes have occurred due to the evolution of the banking sector, and Indian banks are now among the best in emerging market economics, with a strong focus on globalisation.
Banks are regarded as the pillars of any economy. The Indian economy was experiencing a series of economic crises in the late 1980s, including the Balance of Payments crisis. From the near depletion of foreign reserves in mid-1991 to becoming the world's third-largest economy in 2011, India has come a long way. Banks have made significant contributions to this journey.
What is a Bank?
- A bank is a type of financial intermediary as it mediates between the savers and borrowers. It does so by accepting deposits from the public and lending money to businesses and consumers. Its primary liabilities are deposits and primary assets are loans.

- It essentially serves as a conduit between those with excess capital and those in need of those funds. In general, a country's banking system improves the efficiency of economic transactions.
- Banks are regulated by the country's central bank—in India, the RBI (Reserve Bank of India). The banking sector in India truly reflects a mixed economy, with public, private, and foreign banks.
Presidency Banks
These banks were funded by the presidential government at that time.The 3 presidential banks were
- Bank of Bengal- Established in 1806
- Bank of Bombay - Established in 1840
- Bank of Madras - Established in 1843

These three presidency banks were reorganised and amalgamated to form a single entity named “Imperial Bank Of India” on 27 January 1921. It was later transformed into the “State Bank Of India” in 1955.
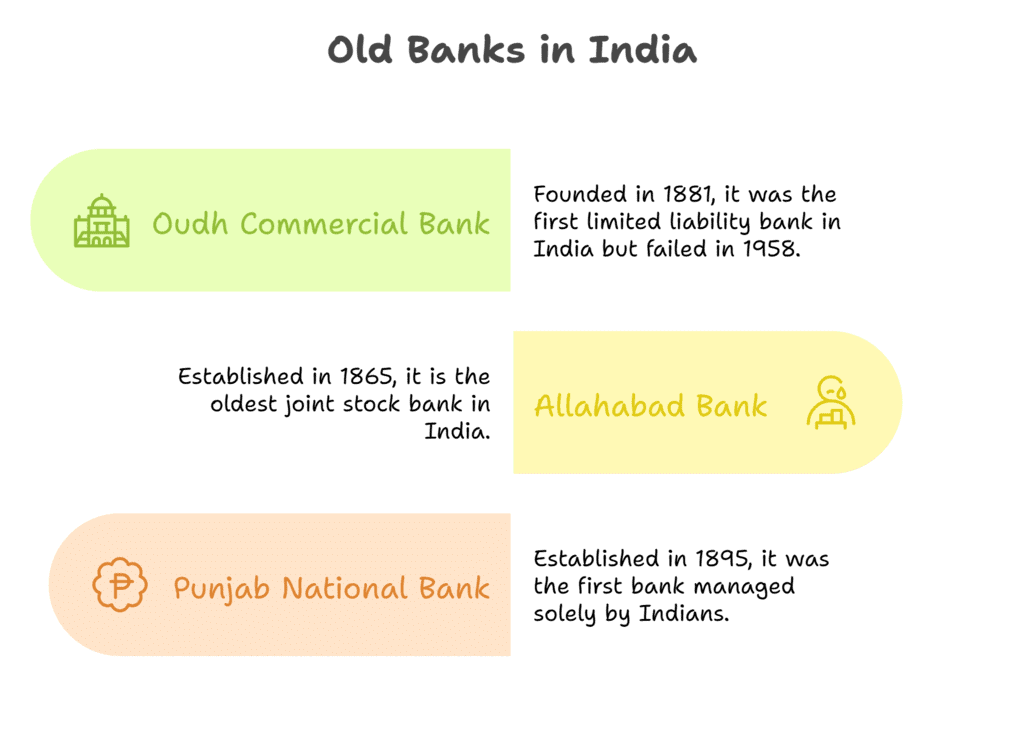
Some of the Old Banks
- Allahabad Bank was established in 1865 at Allahabad(Uttar Pradesh). It is the oldest joint stock bank of our country functioning till today.
- Oudh Commercial Bank was established in 1881 at Faizabad (Uttar Pradesh). It is the First limited liability Bank in India and also the first joint stock bank by Indians. However, it failed in 1958.
- Punjab National Bank was established in 1895 in Lahore(Pakistan) and it was also the first bank to be managed solely by Indians.
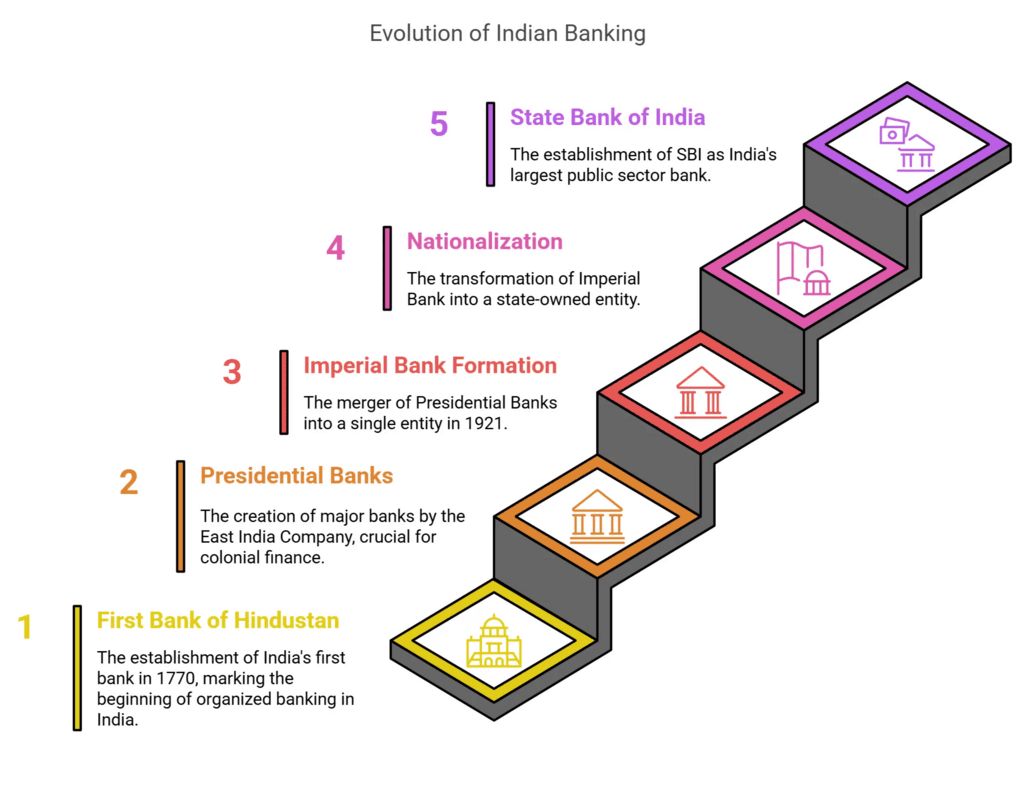
Stages of Evolution
Phase I – Pre-Independence Phase (1786-1947)
- The "Bank of Hindustan," established in 1770 in the then-Indian capital of Calcutta, was the country's first bank. However, this bank did not succeed and closed its doors in 1832.
- Over 600 banks were registered in the country during the pre-independence period, but only a few survived.
- During British rule in India, the East India Company established three banks known as the Presidential Banks: The Bank of Bengal, the Bank of Bombay, and the Bank of Madras.
- These three banks were eventually merged into a single bank in 1921, which was known as the “Imperial Bank of India.”
- The Imperial Bank of India was later nationalized and renamed The State Bank of India, which is now the largest public sector bank in India.
- In the history of Indian banking, the Oudh Commercial Bank was the country's first commercial bank.
- Other banks founded in the nineteenth century, such as Allahabad Bank (Est. 1865) and Punjab National Bank (Est. 1894), have withstood the test of time and continue to exist today.
Phase II – Post-Independence Phase (1947-1991)
- At the time of India's independence, all of the country's major banks were privately led, which was a source of concern because people in rural areas were still reliant on money lenders for financial assistance.
- To address this issue, the then-Government decided to nationalise the banks. The Banking Regulation Act of 1949 was used to nationalise these banks.
- The Reserve Bank of India, on the other hand, was nationalised in 1949.
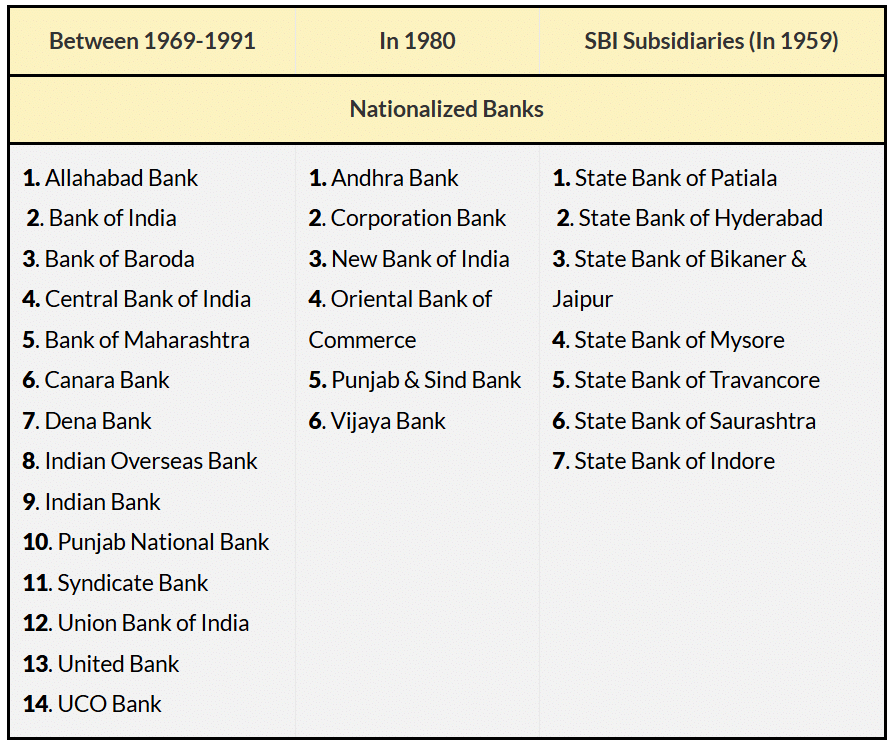
- Following the formation of the State Bank of India in 1955, another 14 banks were nationalised between 1969 and 1991. These were the banks with more than 50 crores in national deposits.
- Another six banks were nationalised in 1980, bringing the total to twenty.
- Aside from the aforementioned 20 banks, seven SBI subsidiaries were nationalised in 1959.
- Except for the State Bank of Saurashtra, which was merged in 2008, and the State Bank of Indore, which was merged in 2010, all of these banks were merged with the State Bank of India in 2017.
- The primary goal of this move was to reduce the concentration of power and wealth in the hands of a few families who owned and controlled these financial institutions.
- There were other reasons for nationalisation as well, such as:
- To assist India's agricultural sector
- To mobilise individual savings
- To grow India’s banking network by opening more branches
- To boost priority sectors by providing banking services
- In addition to nationalising private banks, the Indian government established a few financial institutions between 1982 and 1990 to achieve specific goals.
- EXIM Bank – a bank that promotes both imports and exports.
- The National Housing Board – It is responsible for funding housing projects across the country.
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) – for agricultural development.
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) – for lending money to small-scale Indian businesses.
Phase III – LPG Era (1991-Till Date)

- Once the banks have been established in the country, regular monitoring and regulations must be followed in order to maintain the profits generated by the banking sector.
- The final or ongoing phase of the banking sector's development is critical.
- To ensure the stability and profitability of the Nationalised Public Sector Banks, the Government decided to form a committee led by Shri. M Narasimham to oversee the various banking reforms in India.
- The introduction of private sector banks in India was the most significant development.
- The Reserve Bank of India granted licenses to ten private sector banks to establish themselves.
- Global Trust Bank
- ICICI Bank
- HDFC Bank
- Axis Bank
- Bank of Punjab
- IndusInd Bank
- Centurion Bank
- IDBI Bank
- Times Bank
- Development Credit Bank
- Other notable changes and developments during this time period included:
- Foreign banks such as Citibank, HSBC, and Bank of America established branches in India.
- The nationalisation of banks has come to a halt.
- The Reserve Bank of India and the government treated public and private sector banks equally.
- Payments banks were established.
- Small finance banks were allowed to open branches across India.
- Banks began to digitalize transactions and other banking operations.
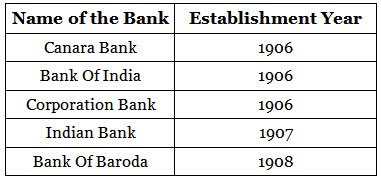
Impact of the “SWADESHI” Movement
Due to the “Swadeshi” movement, many banks were established between 1906 to 1911. Many local businessmen and strong political figures in India funded the banks for the Indian community. Some of the banks that were established are as follows:
“The Reserve Bank Of India”

- RBI was established on 1st April 1935 in accordance with the provisions of the RBI Act, of 1934.
- It was established under the recommendations of the “Hilton Young Commission” also known as “Royal Commission On Indian Currency And Finance”.
- Initially, it was set up in Calcutta and permanently moved to Mumbai in 1937.
- Initially, the RBI was started with private shareholders fully paid up capital of Rs.5 crores.
- It also acted as the central banking institute for Mynmar till 1948 and till 1947 for Pakistan.
- The RBI was nationalized on 1st January 1949 in accordance with the RBI(Transfer to Public Ownership) Act,1948.
- It empowered RBI to act as a central banking institution to control the monetary policy of the Indian Rupee and to control, regulate, monitor, and inspect banks in the country as mentioned in the 2nd schedule of RBI act1934.
Subsidiaries of RBI
- Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) was set up in 1978.
- Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Limited(BRBNMPL) was set up in 1995.
- Reserve Bank of India Information Technology Private Limited (ReBIT) was set up in 2014.
- Indian Financial Technology and Allied Services (IFTAS) was set up in 2015.
- Reserve Bank of India Innovation Hub (RBIH) was set up in 2022.
State Bank of India
 The State Bank Of India was formerly known as “The Imperial Bank Of India” during British rule.
The State Bank Of India was formerly known as “The Imperial Bank Of India” during British rule. - It was established on 1st July 1955 under the recommendations of the “Gorwala committee”.
- It was nationalized on 2 June 1956 with the majority of its share taken by the Government of India.
- The SBI acts as an agent where the Reserve Bank Of India has no branch offices.
- It has 5 associate banks, State Bank of Bikaner & Jaipur, Hyderabad, Mysore, Patiala and Travancore.
Conclusion
- In India, the banking sector is critical to the country's economic development.
- Numerous changes have occurred within this industry over the centuries, ranging from technological advancement to diversifying financial services and products.
- Over the last three decades, India's banking system has achieved a number of notable accomplishments. The most striking feature is its extensive reach.
- It is no longer limited to India's metropolises or cities. In fact, the Indian banking system has spread to even the most remote parts of the country. This is a key aspect of India's growth story.
|
670 videos|1101 docs|322 tests
|
FAQs on History of Banking in India - IBPS PO Prelims & Mains Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the history of banking in India? |  |
| 2. What are presidency banks? |  |
| 3. What were some of the old banks in India? |  |
| 4. How did the "SWADESHI" movement impact banking in India? |  |
| 5. What is the Reserve Bank of India and its subsidiaries? |  |






















