Rajasthan during Mahajanpada Period | Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan) PDF Download
Mahajanpada Period
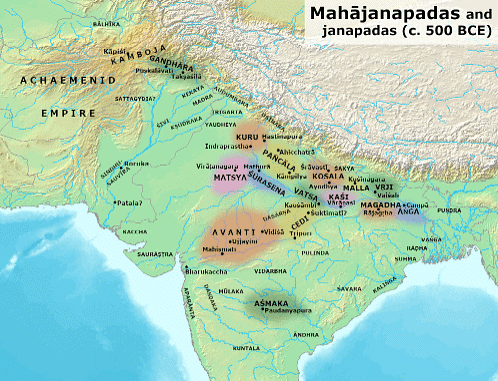 The term “Janapada” literally means the foothold of a tribe, in Pāṇini’s “Ashtadhyayi”, Janapada stands for country. The Pre-Buddhist north-west region of the Indian sub-continent was divided into several Janapadas demarcated from each other by boundaries. Each of these Janapadas was named after the Kshatriya tribe (or the Kshatriya Jana) who had settled therein. Ancient Buddhist texts like the Anguttara Nikaya make reference to sixteen Mahajanpadas and Janapada (Republics) which had evolved and flourished in Indian Sub-Continent. The region surrounding modern districts of Bikaner & Jodhpur was referred to as Jangaldesh during Mahajanpada period. Here, we first look at Mahajanpada’s and then at Republics of Rajasthan.
The term “Janapada” literally means the foothold of a tribe, in Pāṇini’s “Ashtadhyayi”, Janapada stands for country. The Pre-Buddhist north-west region of the Indian sub-continent was divided into several Janapadas demarcated from each other by boundaries. Each of these Janapadas was named after the Kshatriya tribe (or the Kshatriya Jana) who had settled therein. Ancient Buddhist texts like the Anguttara Nikaya make reference to sixteen Mahajanpadas and Janapada (Republics) which had evolved and flourished in Indian Sub-Continent. The region surrounding modern districts of Bikaner & Jodhpur was referred to as Jangaldesh during Mahajanpada period. Here, we first look at Mahajanpada’s and then at Republics of Rajasthan.
Rajasthan during Mahajanpada period (600 BCE -300 BCE)
The end of Vedic India is marked by linguistic, cultural and political changes. By the 6th century BCE, the political units consolidated into large kingdoms called Mahajanapadas. The age is also referred to as period of second urbanization. The modern state of Rajasthan was also part of several Mahajanpadas mentioned below: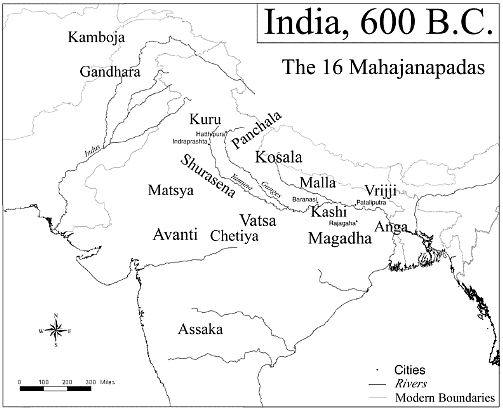
1. Matsya Mahajanpada
- The modern districts of Jaipur, Alwar & Bharatpur formed part of Mahajanpada of Machcha or Matsya.
- The capital of Matsya was at Viratanagari (present-day Bairat), which is said to have been named after its founder king, Virata.
- The kingdom came under the control of the neighboring Chedi Kingdom in the 5th century.
2. Saurasena Mahajanpada
- The capital of Saurasena janpada is located near modern day Mathura.
- It covers region of Alwar, Bharatpur, Dholpur & Karauli.
3. Kuru Mahajanpada
- The capital of Kuru Janpada was Indrapath.
- It covered parts of northern Alwar region.
Rajasthan after Alexander Invasion (326 BC)
In 326 BC Alexander invaded India, he never reached Rajasthan. However, his Indian incursion profoundly affected the course of its history. Weakened by his invasion republican tribes of South Punjab especially Malav, Shivi and Arjunayan migrated to Rajasthan. Punjab and Rajasthan became the nucleus of a number of oligarchies, or tribal republics whose local importance rose and fell in inverse proportion to the rise and fall of larger kingdoms.According to coins recovered, the politically most important republics of Rajasthan were the Audambaras, Arjunayanas, Malavas, Kunindas, Trigartas, Abhiras, Yaudheyas and Shibis (Shivi).
1. Arjunayana Janapada
- Arjunayanas had their base in the present-day Bharatpur-Alwar region.
- They emerged as a political power during the Shunga period (c. 185 – c. 73 BCE).
2. Rajnaya Janapada
Different scholars have ascribed different regions to Rajnaya janpada:
- Based on coins Cunningham suggested their region as near Mathura,
- Smith suggested former Dholpur state as original home of Rajnaya and
- Rapson ascribed them in same region as of Arjunayanas & Kings of Mathura.
3. Shivi or Sibi Janapada
- Shivi gana covered present districts of Udaipur & Chittorgarh.
- The Shibis (Shivi) migrated from the Punjab to Rajasthan and settled in areas adjoining modern day Chittaurgarh.
- Madhyamika (later Nagri) was the capital of Sibis
- Nagri was excavated in 1904 A.D by D. R. Bhandarkar.
4. Malavas
- The Malavas are actually mentioned in the Mahabhashya of Patanjali.
- According to D. R. Bhandarkar, they initially lived in the Punjab; later, they migrated to eastern Rajasthan (Jaipur & Tonk), and finally to region in Madhya Pradesh, which is known as Malwa after them.
- Their capital in Rajasthan was Nagar, located in Tonk.
5. Shalvya
- The Salvas were settled north of the Matsyas State.
- Salvaputras must have been a branch of these Salvas. Modern day Alwar is a corrupt form of Salvaputra mentioned in Maharabharata.
6. Yodheya or Yaudheyas
- Yaudheya or Yaudheya Gana was an ancient confederation who lived in the area between the Indus river and the Ganges river.
- Present Ganganagar & Hanumangarh districts formed part of their gana.
- They find mention in Pāṇini’s Ashtadhyayi and Ganapatha.
- Their Constitution has been regarded as quasi-monarch as in the Bijaygarh (Bharatpur) inscription, their chief is given title of Maharaja-Senapati and is said to be appointed to the post by Yaudheya-gana.
- In 2nd Century A.D. the Yaudheyas came into conflict with Rudradaman I (Saka ruler), who though defeated them but acknowledged the military might of the Yaudheyas as in the Junagadh rock inscription (c. 150 CE) of Rudradaman I .
FAQs on Rajasthan during Mahajanpada Period - Course for RPSC RAS Preparation - RPSC RAS (Rajasthan)
| 1. What is the Mahajanpada period in Rajasthan? |  |
| 2. How many Mahajanapadas existed in Rajasthan during the Mahajanpada period? |  |
| 3. What was the significance of the Mahajanpada period in Rajasthan? |  |
| 4. What were the main characteristics of the Mahajanpadas in Rajasthan? |  |
| 5. How did the Mahajanpada period in Rajasthan contribute to the overall history of ancient India? |  |
















