Notes: Stages Of Language Development | Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET PDF Download
Introduction
The stages of language development are one of the essential parts of linguistics. Language plays a vital role in communicating with each other, from one country to another. Every language has its characteristics and objectives. Now the question is how a language is developed in children?
A child acquires a language or mother tongue through different stages. After finishing all the stages, the child can achieve their mother tongue. Let us see the stages of language development. We mainly analyze the four stages of child language acquisition. The four stages of language development in children are demonstrated in the table below:
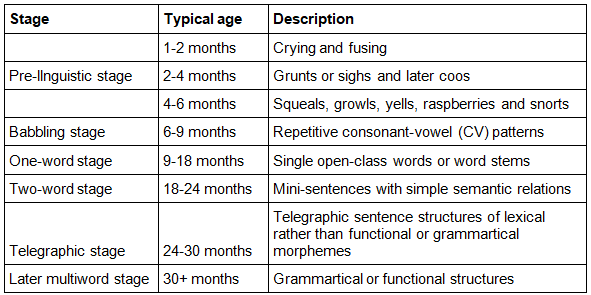
4 Stages Of Language Development
The 4 significant stages of language development are given below:
1. Pre-Linguistic Stage
The pre-linguistic stage is the core of child language acquisition. This stage begins from a child’s birth to his to her seven months. During childbirth, the baby’s vocal tract is here and there more like that of a chimp than that of a grown-up human. Specifically, the tip of the velum reaches or covers with the tip of the epiglottis. As the newborn child develops, the tract, bit by bit, reshapes itself in the grown-up example.
At the first or two months of life, a newborn child articulates distress with crying. Some non-reflexive, non-trouble sounds are delivered with a brought down velum and a shut or almost shut mouth, giving the impression of a syllabic nasal or a nasalized vowel.
At 2 to 4 months, the newborn child starts expressing alleviation sounds. The soonest alleviation sounds possibly snorts or moans, with the later forms being vowel-like ‘coos’. A child can laugh around three or four months later from birth.
At the age of 4 to 7 months, newborn children usually participate in ‘vocal play.’ They can produce different types of sounds such as friction noises, nasal murmurs, etc.
2. Babbling Stage
The babbling stage starts at the age of six months of a baby. At this stage, a child can produce sounds by using their speech organs. Not only that, those children begin to make extended sounds by oral articulations into syllable-like arrangements, opening and shutting their jaws, lips, and tongue.
At this stage, children often produce fricatives, affricates, and fluids rarely. In any event, at the outset, vowels will, in general, below and open. Sometimes they produce [bababa] or [nanana] etc.
In the Babbling stage, children produced random sounds with their speech organs. Vocal play and Babbling are both produced when they interact with their parents or relatives. In this stage, a child randomly grows a variety of sounds, and sometimes these sounds partly match their mother tongue.
3. Two-Word Stage
The two-word stage begins when a child becomes one year or one and a half-year-old. In this stage, children pronounce from one word to two words. At the same time, children start developing their sound production capability.
In the two-word stage children naturally, follow some grammatical rules in their sentences subconsciously. We can find some inflections at the end of the two-word stage of a child, and they can be able to describe an event by grammatical functions. This is how a child finishes their two-word stage by producing many sounds and combining them into sentences.
4. Telegraphic Stage
At the age of 24 months to 30 months seems to be a child’s telegraphic stage. In this period, children start producing expressions with more than two elements, and the expressions of children are longer than two words and have meaningful characteristics.
For example, the little capacity words, too, the a, can, is, and so on, are missing; just the words that convey the primary message, that is, the substance words are utilized. The expressions like feline stand up the table, what that, no stay here, etc., do not have the capacity words. These expressions are called the telegraphic stage.
The telegraphic stage incorporates just morphemes and words that convey essential semantic substance.
|
66 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|
FAQs on Notes: Stages Of Language Development - Child Development and Pedagogy for CTET Preparation - CTET & State TET
| 1. What are the stages of language development? |  |
| 2. How do children develop language skills? |  |
| 3. What is the role of parents in language development? |  |
| 4. Are there any milestones to track language development in children? |  |
| 5. How can teachers support language development in the classroom? |  |
|
66 videos|63 docs|36 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for CTET & State TET exam
|

|


















