Audio & Video Conferencing - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
Networking
- A network is simply an interconnection of one or more computers for the purpose of sharing information and resources (printers, storage devices, and applications).
- Computer Networks are an interconnected set of an autonomous system that permits distributed processing to information.
Five Components of Networking
- Sender Computer
- Sender equipment (Modem)
- Communication Channel (Telephone Cables or wireless device)
- Receiver Equipment (Modem)
- Receiver Computer

Types of Network
Classification Based on Geographical Coverage:
- Local Area Network (LAN): A local area network is a relatively smaller and privately-owned network with a maximum span of 10 km.
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): MAN is defined for less than 50 Km and provides regional connectivity within a campus or small geographical area.
- Wide Area Network (WAN): A wide Area Network (WAN) is a group Communication Technology provides no limit of distance.
Classification Based on Channel:
- Point to Point Network: When a packet is sent from one router to another intermediate router, the entire packet is stored at each intermediate router, stored there till the output line is free and then forwarded. A subnet using this principle is called point to point or packet-switched network.
- Topologies for a point to point Subnet
(i) Star: Each device has a dedicated point to point link only to a central controller, usually called a
(ii) Tree: A tree topology is a variation of a
(iii) Ring: Each device has a dedicated point to point line configuration only with the two devices on either side of
(iv) Bus: One long cable act as a backbone to link all the devices in the - Broadcast Networks: Broadcast networks have a single communication channel that is shared by all the machines on the network.
Intranet
- An intranet can be an excellent method for sharing organizational information and creating internal communication channels. An intranet is an ideal way to communicate in a secure environment. An intranet provides a way to communicate with a common technology.
- A collection of resources to which only internal users have access.
- A private network inside an organization, similar to the Internet, but which is for internal use only, and is not accessible to the public.
- Users of an Intranet can exchange electronic mail (email), send files (FTP), browse web (WWW) pages, and connect to any other computer. Just like the normal internet, however, only people within an organization can use the intranet.
- Intranets are often separated from the Internet by using a firewall.
Advantages of Intranet
- Data can be stored centrally
- Allows easier maintenance of data
- Web-based interface for access o common technology for communication
- Ability to access from anywhere in the world

Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to link several billion devices worldwide. It is also known as “network of networks” that consists of millions of private, public, academic, business, and government networks.
Various applications of internet
- Exchange messages using e-mail (Electronic mail).
- Transfer files as well as software.
- Browse through information on any topic on the web.
- Communicate in real-time (chat) with others connected to the Internet.
- Search databases of government, individuals and organizations.
- Read news available from leading newsgroups.
The World Wide Web commonly known as the Web or “www” developed by Tim Berners – Lee in 1989, is a system of interlinked hypertext documents that are accessed via the Internet. These multimedia pages are ever-changing.
A web browser(commonly referred to as a browser) is a software application for retrieving, presenting and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. Ex. WorldWideWeb (First Web Browser), Netscape, Internet Explorer, Opera, Mozilla Firefox, Safari (Apple), Google Chrome, UC Browser etc.
Various Features of a Web Browser
A web browser has the following features:
- Menu bar: The menu bar, located at the very top of the screen, can be accessed using the mouse. Actions that are in black can be performed, while actions that cannot be performed will be in grey or lightened.
- Toolbar: The toolbar is located at the top of the browser; it contains navigational buttons for the Web. Basic functions of these buttons include:
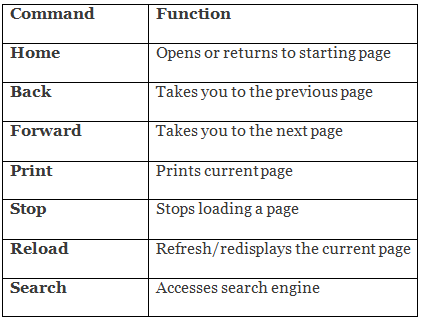
- Location bar: The location bar, below the toolbar, is a box labelled “Location,” “GoTo,” or “Address.” You can type in a site’s address and press the Return or Enter key to open the site.
- Status bar: The status bar is located at the very bottom of the browser window. You can watch the progress of a web page download to determine if the host computer has been contacted and text and images are being downloaded.
- Scroll bar: The scroll bar is the vertical bar located on the right of the browser window. You can scroll up and down a web page by placing the cursor on the slider control and holding down the mouse button.
- A website is a set of related web pages served from a single web domain.
- Uniform Resource Locator abbreviated as URL is the Address for web sites. Most of them begin with HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol), followed by a colon and two In most web browsers, the URL of a web page is displayed on top inside an address bar. An example of a typical URL would be “http://www.edurev.in“.
- A Hyperlink is a reference to data that the reader can directly follow either by clicking or by hovering or that is followed automatically.
- Downloading means to receive data to a local system from a remote system, or to initiate such a data
- Uploading refers to the sending of data from a local system to a remote system such as a server or another client with the intent that the remote system should store a copy of the data being
 |
Download the notes
Short Notes: Audio & Video Conferencing
|
Download as PDF |
Electronic Mail (e-mail)
Electronic Mail (e-mail) was invented by “John Von Neumann”. Electronic Mail transfers the data from one system to another system in the form of messages (test), pictures (images), multimedia messages.
An e-mail address normally consists of three parts.
- Name of the User
- “@” Sign
- It comes after @ sign and it is the name of the DNS.
Example: edurev@gmail.com
edurev (user name)
Gmail.com (Domain name System)
In the e-mail window, you can find “folder Pane” at the left side of the window. It has a set of folders named as Composed mail, Inbox, Out Box, Sent Items, Drafts, Trash, Spam etc.,
- Inbox: used to store incoming
- Sent Items: used to store mail that has already been
- Deleted Items (Trash): used to store deleted mail up to 30
- Draft folder: use to store mail that is not yet
- Spam: used to store unsolicited bulk e-mail up to 30
- Compose Mail: use to create a new
Important points of e-mail
- Hotmail, a free e-mail service provided by Microsoft which was established in 1995 was co-founded by an Indian American entrepreneur Sabeer Bhatia along with Jack Smith in July of 1996.
- An Internet Protocol address (also known as an IP address) is a numerical label assigned to each device (e.g., computer, printer) participating in a computer network. It acts as an identifier for a computer. It is a unique address for every computer.
- Top-level domain: Each part of a domain name contains certain information. The first field is the hostname, identifying a single computer or organization. The last field is the top-level domain, describing the type of organization and occasionally country of origin associated with the address.
For e.g. – .com – Commercial, .edu – Educational, .org – organisation, .net – Network, .in – India etc.
Protocols:
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- Internet Protocol (IP)
- Post Office Protocol (POP3)
- HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
- Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
Audio and Video Conferencing
Audio Conferencing
- Involves two or more people using a conference bridge to communicate.
- Participants dial into a central system instead of calling each other directly.
- Enhances collaboration with optional features like screen sharing.
Video Conferencing
- Uses the internet to conduct live visual meetings.
- Requires a webcam, desktop, laptop, or mobile device.
- Enables high-quality audio, video, and text communication.

Web Conferencing (Internet-Based)
- Online service for meetings, presentations, and training via the internet.
- Uses VoIP for audio and can include real-time communication.
- Features include:
- Whiteboard for annotations.
- Screen sharing for collaboration.
- Audio conferencing for voice-only communication.
- Webinars for controlled presentations.
- Online meetings with scheduling options.
- Mobile access for remote participation.
- Real-time chat for instant messaging.
|
24 videos|19 docs|8 tests
|
FAQs on Audio & Video Conferencing - Information and Communication Technology (ICT) Notes
| 1. What is audio and video conferencing? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of audio and video conferencing tools? |  |
| 3. How has audio and video conferencing impacted education? |  |
| 4. What are some popular audio and video conferencing platforms? |  |
| 5. What should I consider when choosing an audio and video conferencing tool? |  |