Types of Communication - Communication Notes
Introduction
Communication can be defined as the process of exchanging information, ideas, thoughts, and feelings between individuals or groups through various channels such as verbal, non-verbal, written, or visual means.
- Communication involves sharing information and ideas between individuals or groups.
- It enables mutual understanding through various channels like speech, writing, or gestures.
- Communication is interactive and involves feedback.
- It occurs through verbal, non-verbal, written, and visual means.
- Context and culture influence the effectiveness of communication.
Types of Communication
On the basis of the number of participants
This classification of communication is based on ‘either a man communicate with himself, or two men communicate with each other, or more than two Men are indulged in this act.’
(i) Intra-personal Communication: When a man communicates with himself to develop useful ideas.
(ii) Interpersonal (Dyadic) Communication: When a person communicate his thoughts to another person.
(iii) Intra Group (Multiadic) Communication: A complex form of communication which occurs between more than two individuals.
(iv) Intergroup (Association) Communication: The communication which involves two groups
(v) Organisational (Institutional) Communication: The form of communication which is used in business enterprises.
(vi) Public Communication: The form of communication in which public (which can be heard and addressed) is involved.
(vii)Mass Communication: When a person or firm communicates with a very large group o people or society without meeting them in a conference hall or meeting room.
On the Basis of Direction of Flow
This classification is based on the guiding factors in a firm or institution. In a firm, orders can move down and reports and suggestions can move upwards.
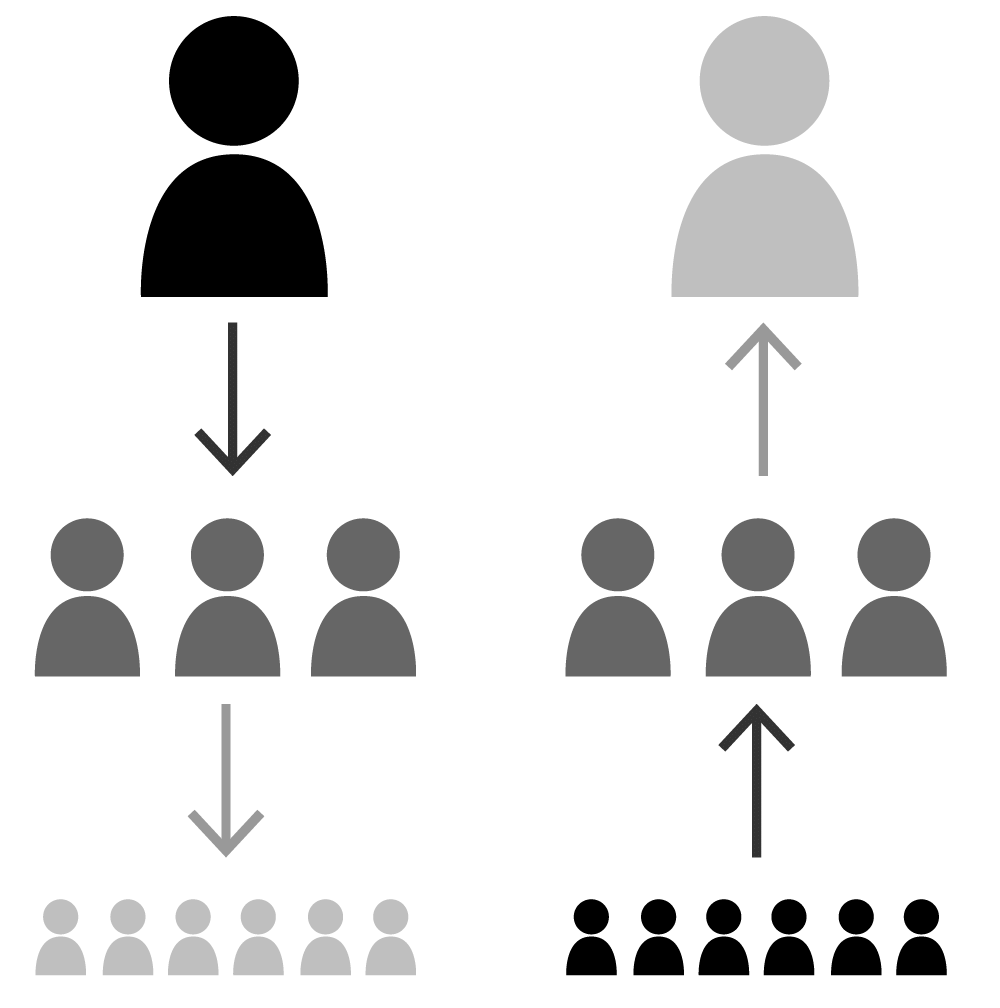
(i) Downward Communication: In this type of communication orders or information move down wards from superiors to subordinates.
(ii) Upward Communication: When information move upward from subordinates and continues up to the top of organisational hierarchy. It is an important type of communication which controls purposes.
(iii) Crosswise (Diagonal) Communication: This type of communication involves different people on the same organisational or different levels of the organisational hierarchy.
On the basis of way of expression
On the basis of way of expression, communication can be classified into six major groups.
(i) Written Communication: In this type of communication, message is sent/obtained through printed or hand-written texts.
(ii) Oral Communication: It may be of two types
- Audio: It refers to the movement message for ears, while the speaker is not present before the listener,
- Verbal: It refers to the transfer of message by words, while the listener is present before the speaker.
(iii) Visual Communication: When the communication involves the use of more visuals and less text.
 (iv) Audio visual Communication: When the information is obtained by the combination of pictures with voices.
(iv) Audio visual Communication: When the information is obtained by the combination of pictures with voices.
(v) Non-verbal Communication: This type of communication involves the use of face, gestures, attire, eyes etc. for the transfer of an information.
(vi) No Comm (No Communication): It refers to the total elimination of the response of the receiver to the message of the sender. The reason for this behavior could be psychological, unfavourable conditions or flaws in the business deal.
On the Basis of organizational structure
(i) Formal Communication: In this type of communication, informations are sent and authenticated by corporate firms, government departments, NGOs, social service groups etc. that have strict and rigid procedures to achieve their respective objectives.
 (ii) Informal Communication (Grapevine): It arises due to informal relations between persons and grows spontaneously from personal and group interests. Verbal discussion, a gesture, nod, smile or even silence can be the indium of this type of communication.
(ii) Informal Communication (Grapevine): It arises due to informal relations between persons and grows spontaneously from personal and group interests. Verbal discussion, a gesture, nod, smile or even silence can be the indium of this type of communication.
On the basis of Objective
Objectives of communication may be social, political, education, entertainment, business or news and views.
(i) Mass/Societal Communication: In this type of communication masses are communicated to be addressed certain burning issues
(ii) Socializing Communication: This type of communication involves individual talking, exchange of e-mail, Internet Relay Chat (IRC), video mail and newsgroup discussions.
(iii) Political Communication: Political speeches, meetings, conferences, rumours, propaganda, publicity and election campaigns are involved in this type of communication.
(iv) Educational Communication: When communication is done to educate the masses.
(v) Business Communication: When communication is used for business purposes.
(vi) Entertainment Communication: When communication is used to entertain people.
(vii) News and Views Communication: This type of communication is used to convey or obtain news and wide range views.
(viii) City Information Communication: It concerns data regarding city elements.
(ix) Data Collection Communication: It is used to collect useful data.
On the basis of environment of the firm
On the basis of environment of the firm, communication be classified in two groups:
(i) External Communication: If the information of communication is related to those elements that operate outside the organisation.
(ii) Internal Communication: When the information is related to those elements that are a part of the organisation.
On the basis of the modes of mediation
(i) Human Communication: According to DeFleur and Ball-Rokeach, “human communication begins when one person decides what he or she wants to arouse a specific set of internal meaning experience in another individual by initiating a significant symbol. The process of communication has been completed when the internal experiences of the receiving person are more or less paralleled to those intended by communication.
(ii) Mediated Communication: This type of communication involves the use of media to send the message across to the receiver. The media would be used when we plan to communicate with another person, a group of people, organisations, institutions, public and the masses.
|
6 videos|26 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Types of Communication - Communication Notes
| 1. What are the different types of communication discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. How are verbal and non-verbal communication different from each other? |  |
| 3. Can you provide examples of written communication? |  |
| 4. What is visual communication and how is it used in different contexts? |  |
| 5. How has digital communication changed the way we communicate in today's world? |  |
















