Best Study Material for UGC NET Exam
UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Notes > Research Aptitude for UGC NET > Notes: Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics
Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics - Research Aptitude Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to Research Ethics |

|
| Major principles of Research ethics |

|
| I. Practices that are against Research Ethics |

|
| II. Steps to ensure ethics in research |

|
Introduction to Research Ethics
Ethics is the set of moral principles that a person is expected to follow irrespective of time and place. Research ethics focuses on the norms and values or code of conduct that researchers must follow so as to ensure responsible conduct of research. It treats values like honesty, social responsibility and integrity as the underlying tenets for conducting any form of research.
Major principles of Research ethics
- Minimising the risk of harm
- Obtaining informed consent
- Protecting anonymity and confidentiality
- Avoiding deceptive practices
- Providing the right to withdraw
 |
Test: Research Ethics
|
Start Test |
Start Test
I. Practices that are against Research Ethics
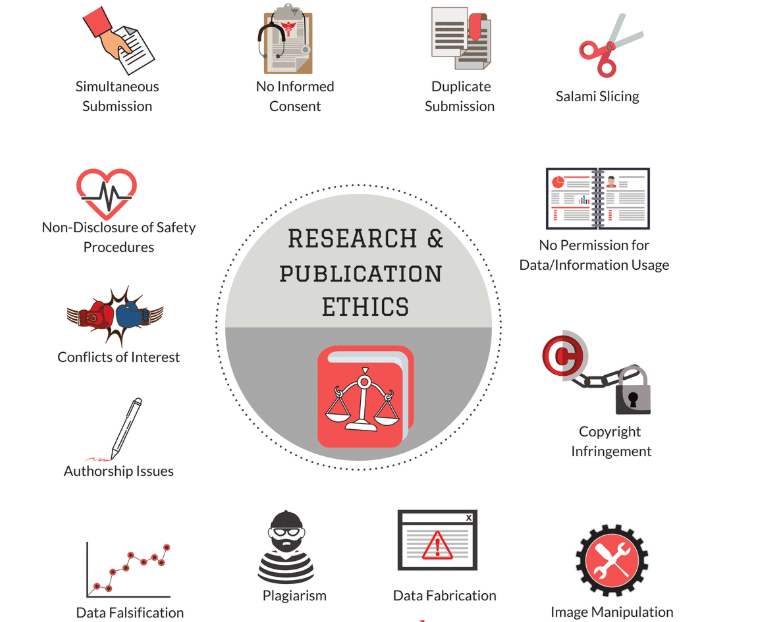
Practises against research ethics or Research Misconduct is defined as “the fabrication, falsification, plagiarism or deception in proposing, carrying out or reporting results of research or deliberate, dangerous or negligent deviations from accepted practises in carrying out research.” However, it is important to note that research misconduct does not include honest error or honest differences of opinion. Some of the major research misconducts are discussed in the following paragraphs.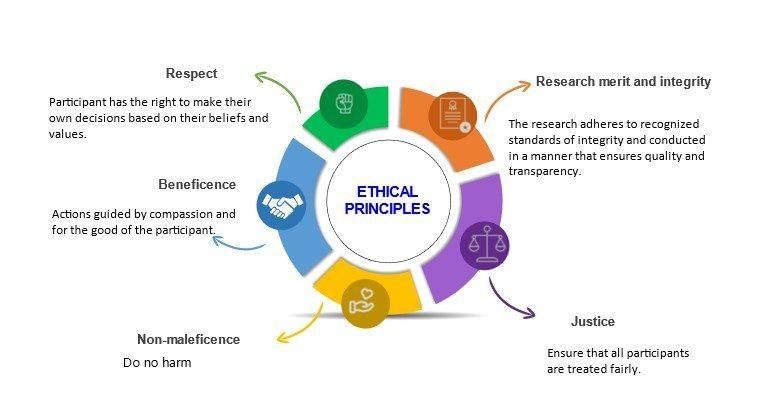
- Fabrication: Fabrication is making up data or results and recording or reporting them. It is the manipulation of research data with the intention of giving a false impression. It need not be a complete lie and may have an element of truth but mostly it is an exaggeration or downplay of the real situation so as to get the expected results.
Eg: Claims made on the basis of incomplete or assumed results - Falsification: Falsification is manipulating research materials, equipment or processes, or changing or omitting research data results such that the research is not accurately represented in the research record. Unlike fabrication, falsification doesn’t have an element of truth and is completely deliberate and untruthful manipulation of information
Eg: publishing untrue and manipulated facts associated with a study - Plagiarism: Plagiarism comprises the misappropriation or use of one’s own or other’s ideas, intellectual property or work (written or otherwise), without acknowledgement or permission.
Eg:- Direct Plagiarism: occurs when a person copies the text of another person, without any changes and doesn’t use quotation marks or attribution.
- Self-plagiarism: reuse of one’s own work without suitable acknowledgement.
- Mosaic Plagiarism: involves copying phrases, passages and ideas from different sources and putting them together to create new content.
- Paraphrasing Plagiarism: It involves the use of someone else’s writing with some minor changes in the sentences and using it as one’s own.
- Breach of duty of care: Breach of duty of care is serious misconduct of research as it shows the inability and carelessness on the part of the researcher to ensure the protection and safety of the respondents.
Eg: Disclosing improperly the identity of individuals or groups involved in research without their consent or any other breach of confidentiality or anonymity - Fraudulent information: Misleading or fraudulent behaviour includes acts contributing to or associated with lying. It takes on any form of fabrication, falsification or misrepresentation
Eg: Taking credit for accomplishments achieved by another researcher. - Tampering: Tampering is the unauthorized removal or alteration of documents, software, equipment, or other academic-related materials. It should be noted that tampering may also be classified as a criminal activity.
Eg: Sabotaging another Researcher’s work intentionally - Copyright violation: Academic integrity prohibits the making of unauthorized copies of copyrighted material, including software and any other non-print media. Individuals, however may make a copy of an article or small sections of a book for personal use.
Eg: Making or distributing copies of a copyrighted article in a group. - Misrepresentation: Misinterpretation refers to an interpretation of the results that is not consistent with the actual results of the study. It is the manipulation of the results of the study so as to get the desired outcome.
Eg: suppression of relevant findings, or knowingly, recklessly or by gross negligence presenting a flawed data interpretation
Question for Notes: Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics
Try yourself:
What is one major principle of research ethics?View Solution
II. Steps to ensure ethics in research
Ethical research can be ensured by strictly following the five major concepts also known as the 5 ‘R’s in Research ethics. They are:- Respect: One of the basic qualities of a good researcher is to respect the respondent’s opinion and their confidentiality. People who contribute their views to research need to feel comfortable about what will happen to the information they give. Thorough research and preparation must be done prior to data collection so as to ensure that the respondent’s time is not wasted.
- Risk: There should be a proper assessment of personal risk as well as potential risks to other people involved in the research. Necessary steps should be taken to mitigate these risks.
Eg: are you putting your respondents in a situation of potential job loss because of your research? You have to limit the risk for the respondent, by ensuring confidentiality and convince them that they won’t lose their job because they helped you with your project. - Rights: It is the responsibility of the researcher to make the respondents and other people involved in the research understand what is expected of them, their rights including the right to withdraw from the research, our obligations towards them and what happens to the data collected from them. It is very important to obtain informed consent from respondents before data collection and moving forward with the research process.
- Routes: Most universities have a pre-existent process that offers a guided pathway through the various issues surrounding the research that need to be addressed. This process should be strictly followed by the researcher. It is also necessary to get the approval of the concerned authority before taking further steps. In case of any misconduct on the part of the researcher, they are also liable to accept the consequences and face disciplinary action.
- Record keeping: The researcher must document all consent forms and maintain the records containing details of how the information is collected, whether it is confidential or not, how it will be used, stored and the disposal method. Record keeping not only helps to keep a systematic track of your research process but it also helps the researcher to collect proof in case if they are later sued by any of the respondents.
Question for Notes: Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics
Try yourself:
What is one of the five major concepts in research ethics that emphasizes the importance of respecting respondents' opinions and confidentiality?View Solution
The document Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics - Research Aptitude Notes is a part of the UGC NET Course Research Aptitude for UGC NET.
All you need of UGC NET at this link: UGC NET
|
17 videos|30 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Practices against Research Ethics & Steps to ensure Ethics - Research Aptitude Notes
| 1. What are the major principles of research ethics? |  |
| 2. What practices are considered against research ethics? |  |
Ans. Practices against research ethics include fabrication, falsification, and plagiarism. Fabrication refers to making up data or results, falsification involves manipulating research materials or processes to misrepresent findings, and plagiarism is the act of using someone else's work or ideas without proper attribution.
| 3. What steps can researchers take to ensure ethics in their research? |  |
Ans. Researchers can ensure ethics in their research by obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality and privacy, conducting thorough ethical reviews, adhering to regulations and guidelines, and fostering a culture of integrity and accountability in their research practices.
| 4. Why is informed consent important in research ethics? |  |
Ans. Informed consent is crucial in research ethics as it ensures that participants are fully aware of the nature of the research, its purpose, potential risks, and their rights. This process respects the autonomy of participants and protects them from exploitation or harm.
| 5. How can ethical breaches in research affect the scientific community? |  |
Ans. Ethical breaches in research can undermine public trust in scientific findings, damage the credibility of researchers, and lead to harmful consequences for society. They can also result in retractions of published papers, loss of funding, and legal repercussions for the individuals involved.
Related Searches



















