Transactional Model - Communication Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| 1. Barnlund’s Transactional Model |

|
| 2. Helical Model |

|
| 3. Becker’s Mosaic Model |

|
Introduction
The main drawback in the interactive model is that it does not indicate that communicators can both send and receive messages simultaneously. This model also fails to show that communication is a dynamic process which changes over time. The transactional model shows that the elements in communication are interdependent. In transactional model, senders and receivers both are known as communicators and both play equally important role in communication
There are three implications in the transactional model:
- Transactional” means that communication is an ongoing and continuously changing process. You are changing, the people with whom you are communicating are changing, and your environment is also continually changing as well.
- In any transactional process, each element exists in relation to all the other elements. There is this interdependence where there can be no source without a receiver and no message without a source.
- Each person in the communication process reacts depending on factors such as their background, prior experiences, attitudes, cultural beliefs and self-esteem.
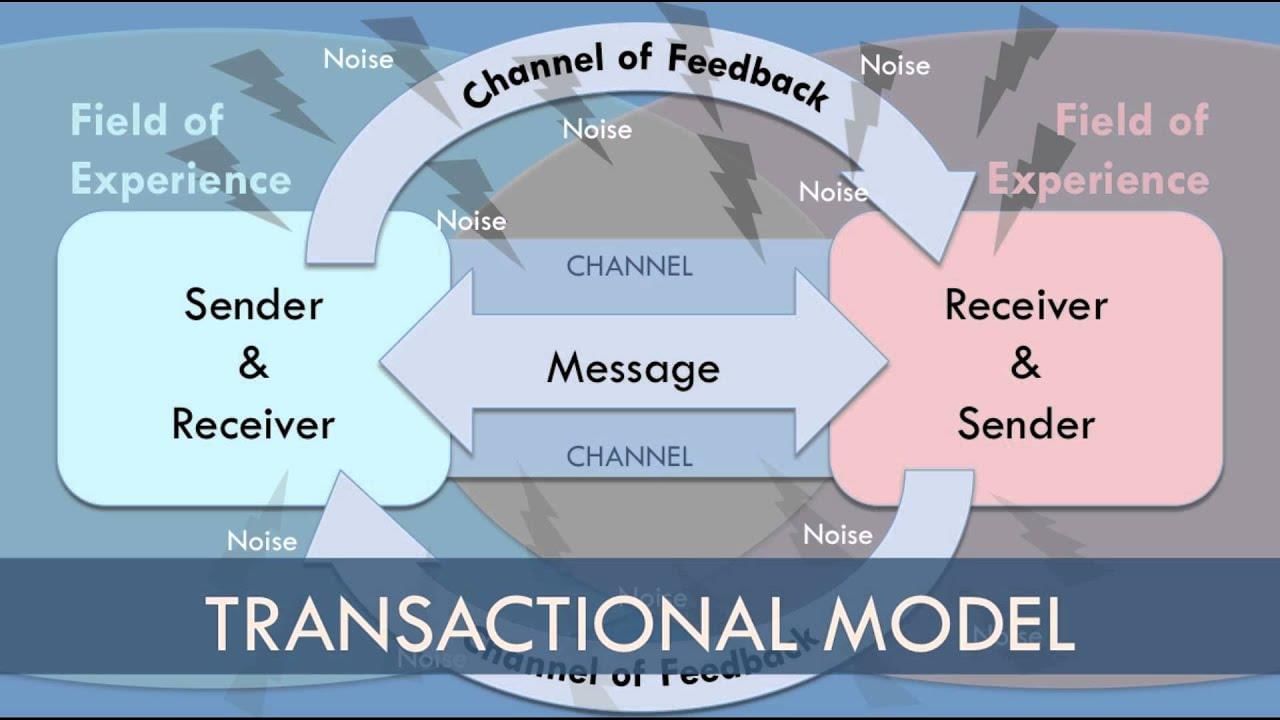
Transactional model relates communication with social reality, cultural up-bringing and relational context (relationships). Non-verbal feedback like gestures, body language, is also considered as feedback in this model.
1. Barnlund’s Transactional Model
- Dean Barnlund proposed a transactional model of communication in 1970 for basic interpersonal communication which articulates that sending and receiving of messages happens simultaneously between people which is popularly known as Barlund’s Transactional Model of Communication. Barnlund’s Transactional Model presents a multi-layered feedback system for all parties involved, and recognizes that anyone can be a sender and receiver at the same time. The layers of feedback consist of both verbal and non-verbal cues sent concurrently with the message itself. This further suggests that the feedback could take equal standing as the message itself. The model has been further adapted and reformed by other theorists as General Transactional Model.
Components of Barlund’s model
Cues refers to the signs for doing something. As per Barnlund there are: public cues, private cues and behavioral cues.
- Public cues (Cpu) are physical, environmental or artificial and natural or man-made.
- Private cues (Cpr) are also known as private objects of orientation which include senses of a person. Both these cues can be verbal as well as non-verbal. Another set of cues are behavioral cues.
- Behavioral cues can be verbal (Cbehv) as well as non-verbal (Cbehnv).
Advantages
- The model shows shared field experience of the sender and receiver.
- Transactional model talks about simultaneous message sending, noise and feedback.
- Barnlund’s model is taken by critics as the most systematic model of communication.
Disadvantages
- Barnlund’s model is very complex.
- Both the sender and receiver must understand the codes sent by the other. So they must each possess a similar “code book”. (The concept of code book is not mentioned in the model but understood.)
2. Helical Model
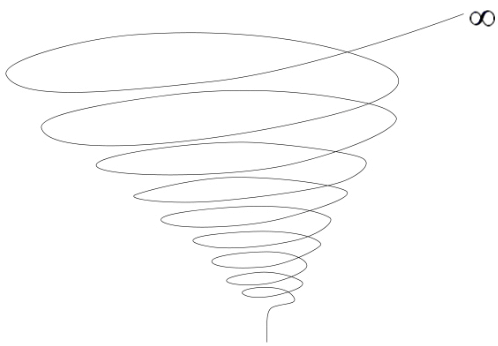
- In 1967, Frank Dance proposed the communication model called Dance’s Helix Model for a better communication process. The name helical comes from “Helix” which means an object having a three-dimensional shape like that of a wire wound uniformly around a cylinder or cone. He shows communication as a dynamic and non-linear process.
- Helical model of communication introduces the concept of time where continuousness of the communication process and relational interactions are very important. Communication is taken as a dynamic process in helical model of communication and it progresses with age as our experience and vocabulary increases. At first, helical spring is small at the bottom and grows bigger as the communication progresses. The same effect can be seen with communication of humans, where you know nothing about a person at first and the knowledge grows steadily as you know the person better. It considers all the activities of the person, from the past and present.
- Communication is affected by the curve from which it emerges which denotes past behavior and experiences. Slowly, the helix leaves its lower levels of behavior and grows upward in a new way. It always depends on the lowest level to form the message. Thus, the communicative relationship reaches to the next level in which people share more information.
Advantages
- The model assumes sender and receiver to be interchangeable and makes communication process to be two way.
- The model takes the communication process speculative and intellectual.
Disadvantages
- The model is taken as more simple than it should be.
- Some critics don’t take it to be a model as it has very few variables.
- It is not testable because it is abstract.
- It is not represent in a systematic and orderly way.
- Variables cannot be differentiated in this model.
- Continuity may not always be true for communication. There might be breaks in situations as well as events can be meaningless, forced or unproductive.
- The purpose of communication is not always growth.
3. Becker’s Mosaic Model
- Sam Becker presented a mosaic model of communication, arguing that traditional concept of the message has severely limited usefulness for understanding contemporary communication. The model explains the complexity of human communication. This mosaic consists of an immense number of fragments or bits of information on an immense number of topics.
- These bits are scattered over time and space and modes of communication. Each individual must grasp from this mosaic those bits which serve his needs, must group them into message sets which are relevant for him at any given time, and within each message set must organize the bits and close the gaps between them in order to arrive at a coherent picture of the world to which he can respond.
- Becker assumes that most communicative acts link message elements from more than one social situation. In the tracing of various elements of a message, it is clear that the items may result in part from a talk with an associate, from an obscure quotation read years before, from a recent TV commercial, and from numerous other dissimilar situations—moments of introspection, public debate, coffee-shop banter, daydreaming, and so on. In short, the elements that make up a message ordinarily occur in bits and pieces. Some items are separated by gaps in time, others by gaps in modes of presentation, in social situations, or in the number of persons present.”
- Becker links complex communicative events to the activity of a receiver who moves through a constantly changing cube or mosaic of information . The layers of the cube correspond to layers of information. Each section of the cube represents a potential source of information; note that some are blocked out in recognition that at any given point some bits of information are not available for use. Other layers correspond to potentially relevant sets of information.”
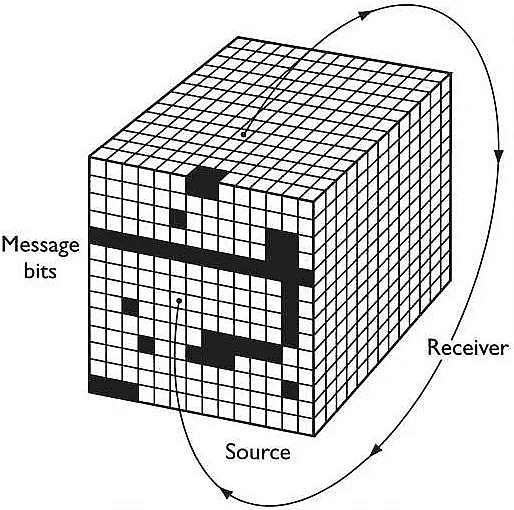
Components of Becker’s Mosaic Model of Communication
- Empty cells- Unavailable messages or sources
- Vertical layers- Set of similar messages
- Cells- Messages and sources
Advantages
- The mosaic model of communication shows the complexity of communication and says communication is dynamic.
- The model explains why the exposure to message varies.
- The model also talks about individual differences between people.
- The message is said to be interpreted in comparison to the information available and relationship of the bit of information.
Disadvantages
- The mosaic model of communication does not explain many dimensions like environmental and social.
- The new bits of information are useless if the last bits are lost.
|
6 videos|29 docs|5 tests
|
FAQs on Transactional Model - Communication Notes
| 1. What is Barnlund’s Transactional Model of communication? |  |
| 2. How does the Helical Model of communication differ from traditional linear models? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of Becker’s Mosaic Model of communication? |  |
| 4. How can understanding these communication models benefit students preparing for the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 5. In what ways can the application of these models impact real-world communication? |  |















