Solar Energy - People, Development and Environment Notes
| Table of contents |

|
| Solar Energy |

|
| Wind Energy |

|
| Soil Energy and Resources |

|
| Forest Energy and Resources |

|
| Renewable Energy in India |

|
Solar Energy
- Solar energy is one of the renewable energies, and it is defined as energy created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun.
- Sunlight that passes through the atmosphere is mostly in the form of visible light and infrared radiation.
- To convert solar energy into electricity, solar panels are used.

- Solar light coming from the sun is necessary for life on earth, and it is harvested for clean energy as well.
- Plants use solar energy to convert into sugar and starches, and this process of conversion is known as photosynthesis.
- China is the largest producer of solar energy, followed by the USA, Japan, Germany, and India.
India's INDC goals
- At the U.N. Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) Conference of the Parties (COP21) in Paris in December 2015, countries committed to reducing global warming through their initiatives called Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDCs).
- India's Intended Nationally Determined Contributions (INDC's) commitment is to reduce the emissions intensity of its GDP by 33 to 35 percent by 2030 from the 2005 level. Also, India aims to achieve about 40 percent of installed power capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030.
Technology
Solar Photovoltaic- Solar photovoltaic (SPV) cells convert solar radiation (sunlight) into electricity.
- A solar cell is a semi-conducting device made of silicon and other materials, which, when exposed to sunlight, generates electricity.
Solar power in India
- India's solar energy installed capacity reached 35.12 GW on 30 June 2020
- Indian government's initial target was 20 G.W. capacity for 2022.
- But, in 2015, the target was increased to 100 GW of solar capacity in which 40 G.W. would be from rooftop solar and 60 G.W. through the grid by 2022.
- Today, rooftop solar power accounts for 2.1 GW, of which 70% is industrial or commercial.
- India proposed International Solar Alliance (ISA) in the 2015 Paris summit
- ISA is headquartered in India.
- India has also initiated the concept of "One Sun One World one Grid" to harness abundant solar power on a global scale.
 Government initiatives
Government initiatives
- The Ministry of New and renewable energy is the nodal agency to tackle India's energy issue.
- To promote ecologically sustainable growth and address India's energy requirement, India proposed National Solar Mission.
- To provide loans for renewable energy and energy efficiency projects, requirement Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency (IREDA), a Non-Banking Financial Institution, is the main authority.
- The Ministry of natural resources and environment created the National solar energy institute as an autonomous research and development institution.
- The government also establishes solar parks to connect them with grid connectivity infrastructure.
- (SRISTI) scheme to promote rooftop solar power projects in India.
- Suryamitra program to prepare a qualified workforce.
- Renewable purchase obligation for large energy consumer customers.
- National green energy program and green energy corridor.
India's top 10 states by installed solar power capacity
1. Karnataka
2. Telangana
3. Rajasthan
4. Andhra Pradesh
5. Tamil Nadu
6. Gujarat
7. Madhya Pradesh
8. Maharashtra
9. Uttar Pradesh
10. Punjab
Top 10 Rooftop Solar States by Installed Capacity in India
1. Gujarat
2. Karnataka
3. Rajasthan
4. Maharashtra
5. Delhi
6. Tamil Nadu
7. Uttar Pradesh
8. Haryana
9. Punjab
10. Telangana
Top 10 States Have the Highest Solar Energy Potential in India
1. Rajasthan
2. Jammu & Kashmir
3. Maharashtra
4. Madhya Pradesh
5. Andhra Pradesh
6. Gujarat
7. Himachal Pradesh
8. Odisha
9. Karnataka
10. Uttar Pradesh
Wind Energy
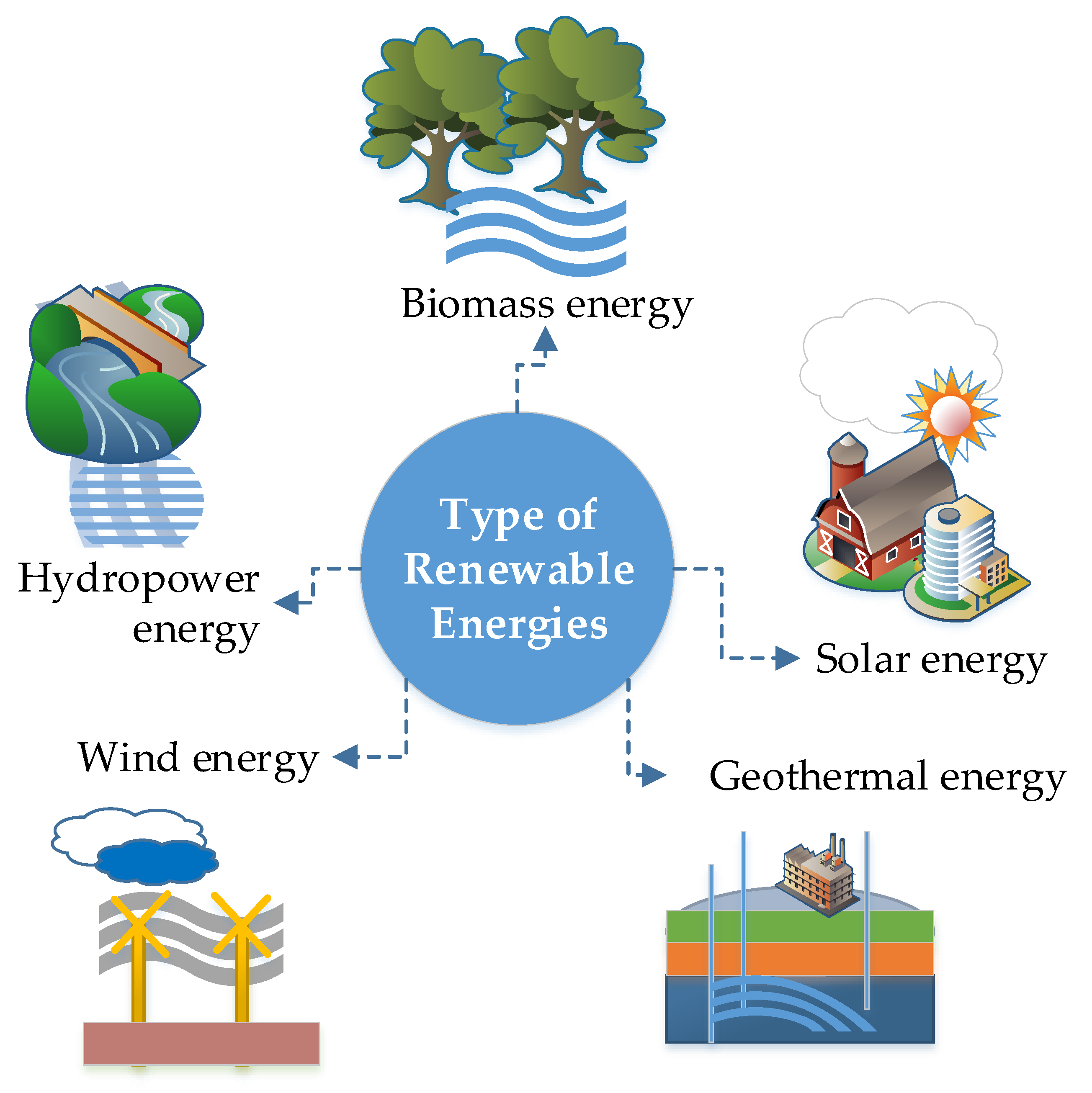
Wind energy is another renewable source that utilizes the kinetic energy of moving air to generate electricity. Wind turbines convert this kinetic energy into mechanical power, which is then transformed into electrical energy. The efficiency of wind energy depends on the location, wind speed, and atmospheric conditions. India has made significant progress in wind energy, ranking among the top wind power producers globally. States like Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Maharashtra lead in wind energy production.
Soil Energy and Resources
Soil plays a crucial role in supporting energy resources by acting as a medium for biomass production. Soil health directly influences the efficiency of bioenergy crops like sugarcane, corn, and jatropha, which are used to produce biofuels. Additionally, geothermal energy is another form of renewable energy that utilizes heat stored within the Earth’s crust, often accessed through soil and rock formations.
 Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is a significant non-fossil fuel-based power source. It is produced through nuclear fission, where atomic nuclei are split to release a tremendous amount of energy. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear power emits minimal greenhouse gases, making it an essential component of sustainable energy strategies. India has several nuclear power plants, including those in Tarapur, Kakrapar, and Kudankulam, with plans to expand nuclear energy production to meet its clean energy goals.
Forest Energy and Resources
Forests act as a natural energy source by providing biomass, a renewable source of energy derived from organic materials like wood, crop residues, and animal waste. Biomass energy is widely used for cooking, heating, and electricity generation in rural areas. Additionally, forests act as carbon sinks, helping reduce atmospheric CO2 levels. India’s commitment to expanding forest cover aligns with its climate change mitigation strategies, including the creation of a carbon sink of 2.5 to 3 billion tonnes of CO2 equivalent through afforestation and reforestation efforts by 2030.
Renewable Energy in India
India has been actively working on enhancing its renewable energy sector. The country has set ambitious targets, including 100 GW of solar energy, 60 GW of wind energy, and substantial contributions from biomass and small hydro projects. India proposed the International Solar Alliance (ISA) in the 2015 Paris summit, headquartered in India. The government has also introduced various initiatives such as the National Solar Mission, Suryamitra program, and Renewable Purchase Obligation to promote the adoption of renewable energy.
 Government Initiatives
Government Initiatives
National Solar Mission: Aims to increase the use of solar energy.
National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy: Promotes wind and solar hybrid energy projects.
IREDA (Indian Renewable Energy Development Agency): Provides financial assistance for renewable energy projects.
National Bio-Energy Mission: Encourages biomass and biofuel development.
Green Energy Corridor: Focuses on enhancing grid infrastructure for renewable energy integration.
SRISTI Scheme: Promotes rooftop solar projects.
India's top states leading in renewable energy production include Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. With continued investment in wind, solar, biomass, nuclear, and forest-based energy, India is on track to achieving a sustainable and energy-secure future.
|
25 videos|40 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Solar Energy - People, Development and Environment Notes
| 1. What is solar energy and how does it work? |  |
| 2. What are the advantages of using solar energy? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of solar energy technologies? |  |
| 4. How is solar energy relevant to the UGC NET exam? |  |
| 5. What policies support the adoption of solar energy in India? |  |















