Notes: Modal Verbs | Basic Grammar for IELTS PDF Download
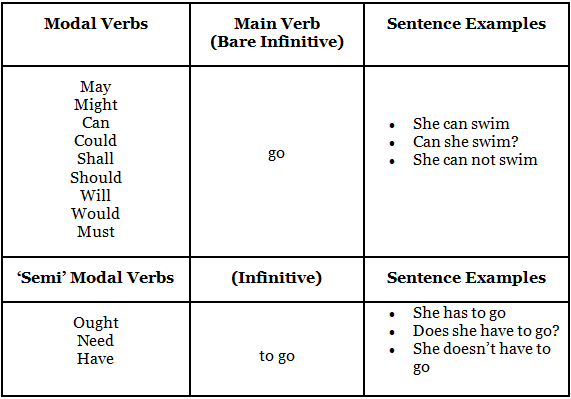
Modal Verbs are used commonly in English to add further information to the main verb.
They are auxiliary or 'helping' verbs, which means they cannot be used on their own but must be used with the main verb.
How are they used?
These verbs are used with a main verb and are followed by the bare infinitive (bare means no “to”)
The exceptions are ‘ought’,’ need’ and ‘have’ which are followed by the infinitive (with “to”).
Common Use in IELTS Task 2
Three important functions of modal verbs when you are writing or speaking for IELTS are:
- discussing degrees of certainty
- making suggestions.
- hypothetical situations
1. Degrees of Certainty
Will, may, might and could are common to make logical deductions about a situation or the future, which you often need to do in task 2:
Children with no father as a role model will become criminals. (100%)
Children with no father as a role model may become criminals. (Possible)
Children with no father as a role model could become criminals. (Possible)
Which of these sentences do you think is incorrect?
Hopefully you worked out that the first one is wrong. This is a common mistake to see in IELTS essays.
The grammar is ok, but it is not possible to conclude that all children with no father as a role model will become criminals!
Be careful when you are making assessments in this way.
‘Will’’ is 100% going to happen, so avoid using it to make generalizations about everybody/ everything unless you know it is 100% true. (There are other ways to make it less certain e.g. “will possibly”).
When you are writing IELTS essays, it's unusual that you will have evidence with you or that you can use to show 100% what you are saying is true.
So the second two are better in this situation.
2. Suggestions
Must, should, ought to, have to and could are often used to make suggestions for solving a problem. It is common in task 2 to get a question asking you to discuss a problem and suggest solutions.
Governments must/have to/need to take action to tackle global warming. (strong obligation)
Parents should/ought to stop their children watching too much television. (Strong suggestion) Individuals could recycle more (possibility).
Take a look at this model essay on global warming and note how modal verbs are used in the second body paragraph to discuss the solutions.
3. Hypothetical Situations
It is common to use would and could to discuss hypothetical situations.
If something is hypothetical, this means in effect it has not happened. You are discussing an unreal situation in the future or imagining something.
For example:
- If the government spent more money on hospitals, people would be healthier.
It is something that has not happened and you don't know if it will.
See this model essay on human cloning and notice the use of would and could throughout the essay.
Cloning of human beings has not happened yet, so it is a hypothetical situation.
|
18 videos|54 docs
|
FAQs on Notes: Modal Verbs - Basic Grammar for IELTS
| 1. What are model verbs in the English language? |  |
| 2. How are model verbs different from regular verbs? |  |
| 3. Can model verbs be used in all tenses? |  |
| 4. Can model verbs be used in passive voice sentences? |  |
| 5. Can model verbs be used to express probability or certainty? |  |
















