Change of State | Science for Grade 6 PDF Download
You will learn about:
- Change of State of matter
- Melting
- Evaporation
- Condensation
- Freezing
- Expansion and contraction of matter
Introduction
Matter can change from one state to another on heating or cooling.
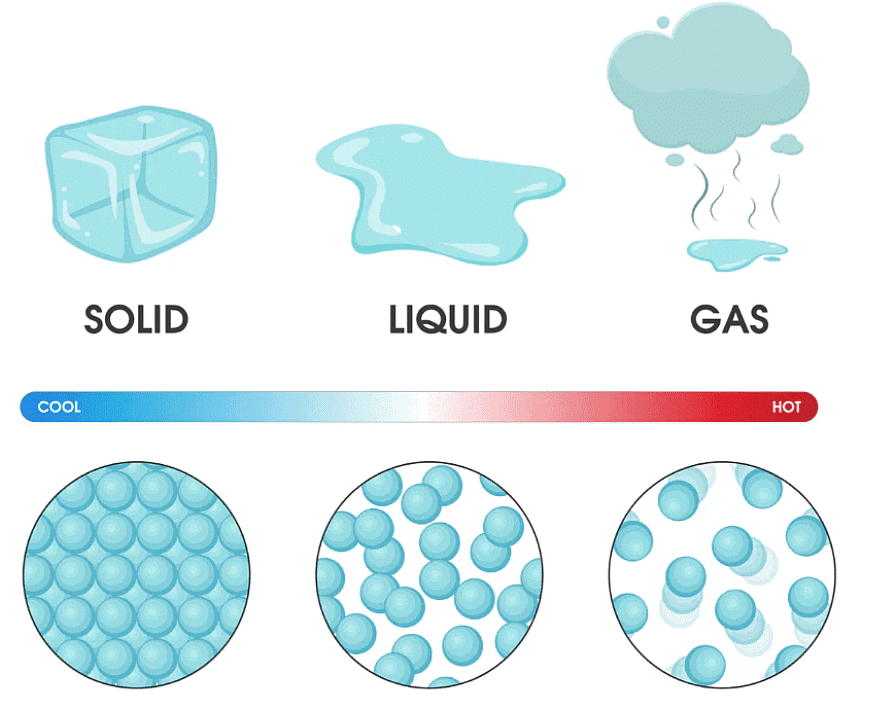
Melting

When ice is kept out of a refrigerator, it melts into water. The process of changing a solid into a liquid on heating is called melting.
When ice is kept in a warm place, the molecules of ice start vibrating faster and become free from the rigid form. They become loosely packed to form water.
Evaporation

When water is heated, it changes into water vapour. The process of changing of a liquid into a gas on heating is called evaporation. The molecules of water start vibrating faster on heating. They become free and escape into the air as gas. Molecules of a gas move much more freely.
Condensation

When the steam touches a cold surface, it changes into water. The process of changing a gas into a liquid on cooling is called condensation. When molecules of steam or water vapour touch a cold surface, their movement slows down. They become less free to move and form water.
Freezing
When water is kept in a freezer, it changes into ice. The process of changing a liquid into a solid on cooling is called freezing. On cooling water, the molecules slow down and come very close to each other. They pack themselves into a rigid form to make ice.
Expansion and contraction of matter
- When we heat a substance, the molecules start vibrating rapidly.
- Due to this intermolecular space between the molecules increases and the substance expands.
- Thus, expansion is the increase in size of matter on heating. For example, tight metal lid of a jar can be opened easily by dipping it in hot water.

- This happens because hot water causes the lid to expand a little and thus it opens out easily.
- Similarly, electric wires between electric poles hang loose in summer season.
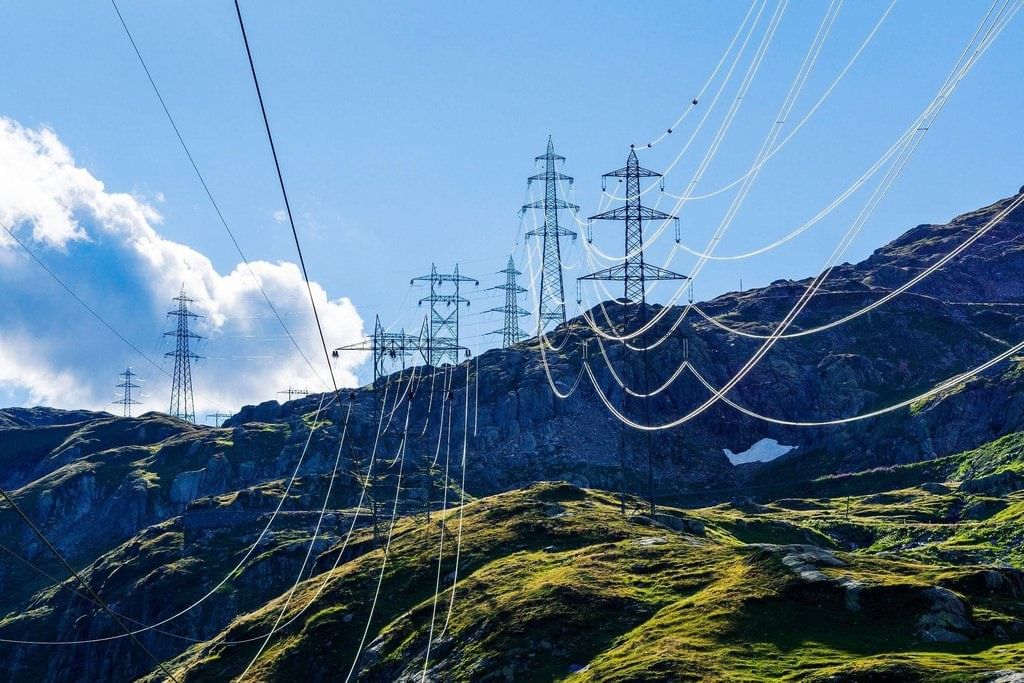 Pole wires in Summers
Pole wires in Summers - On the other hand when we cool a substance, the movement of molecules slows down.
- Due to this intermolecular space between the molecules decreases and the substance contracts.
- Thus, contraction is the decrease in size of matter on cooling. For example, electric wires do not hang loose between electric poles in winter season.
|
137 videos|271 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Change of State - Science for Grade 6
| 1. What is melting? |  |
| 2. What causes expansion and contraction of matter? |  |
| 3. How does the change of state occur? |  |
| 4. What factors affect the melting point of a substance? |  |
| 5. Can expansion and contraction of matter be reversible? |  |























