Moon & its Phases | Physical Science for High School - Grade 9 PDF Download
Introduction
- The moon is the natural satellite of the Earth.
- It is also spherical in shape like the sun and eight planets.
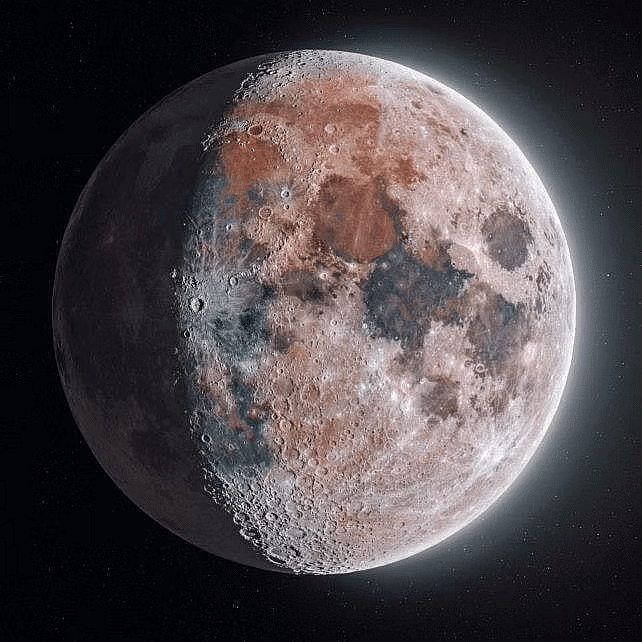

- The moon is made of rocks. There is no air on the moon. Thus, there is no atmosphere on the moon.
- So the side that receives sunlight is very hot and the other side away from the sun is very cold. No sound can be heard on the moon due to the absence of air.
- It is about 3,84,400 km away from the Earth.
- It does not have its own light. It shines because it reflects the sunlight that falls on it.
- The surface of the moon is covered with craters, mountains and valleys.
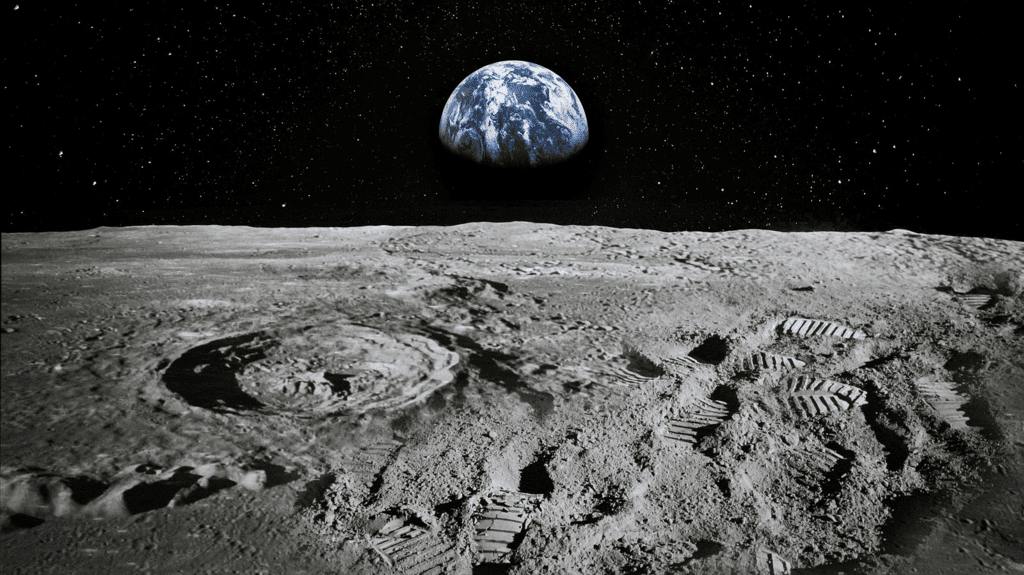 Outer Surface of Moon
Outer Surface of Moon
- Craters are big, round hollows that are formed when pieces of rocks called meteorites crash into the surface of the moon.
- The diameter of the moon is about 3500 km.
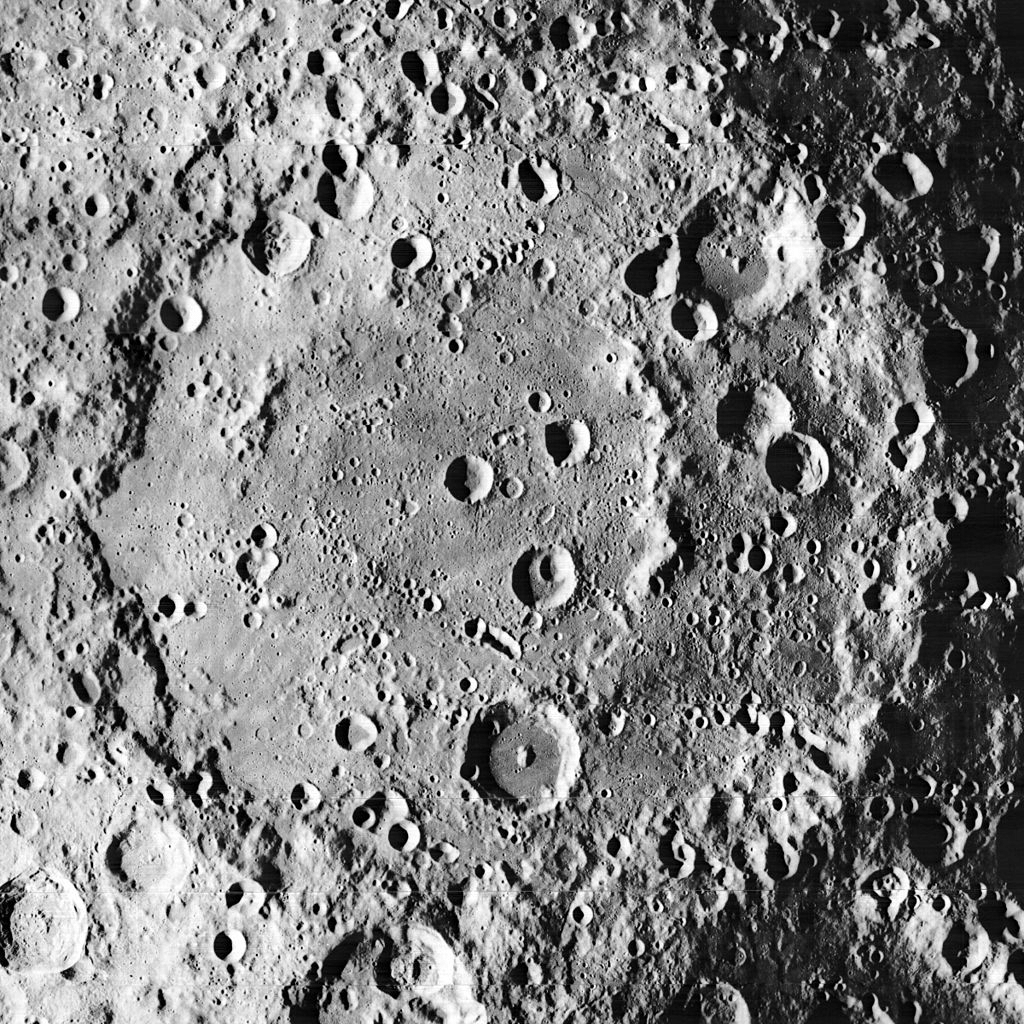 Craters on the Moon's Surface
Craters on the Moon's Surface
- The moon’s gravity is one-sixth of the Earth’s gravity. You can easily lift objects on the moon, that would be too heavy for you to lift on the Earth.
- If your weight is 36kg on the Earth, then it will be just 6kg on the moon.
Phases of the Moon
The moon takes about one month to revolve around the earth. As it revolves, it also rotates slowly. It takes the moon about one month to rotate. Since it revolves and rotates at the same speed, the same side of the moon always faces us. 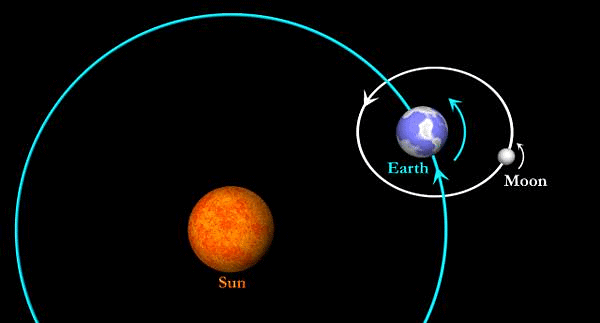 The Earth rotates around Sun and Moon rotates around The Earth
The Earth rotates around Sun and Moon rotates around The Earth
The moon does not give out its own light. It only reflects the light of the sun to us. Therefore, depending on the position of the sun, different areas of it reflect light to us on different days and the moon appears to change its shape every day. The different shapes of the moon, as visible to us on the earth, are called its phases.
 Phases of the Moon
Phases of the Moon
- The day when we cannot see the moon in the sky is called the New Moon day. The moon is not visible as side of the Moon facing us gets no sunlight at all.
- In the next couple of days a small portion of the side of the moon facing us gets sunlight and is visible to us. This is the Crescent Moon.
- In a week, the first quarter moon is visible.
- In the next three days from then, three-quarters of the Moon is visible to us. This is the waxing gibbous Moon.
- On the fourteenth day the entire side facing us gets sunlight and we can see the Full Moon.
- In the next fourteen days the moon progressively decreases in size, and the phases reverse.
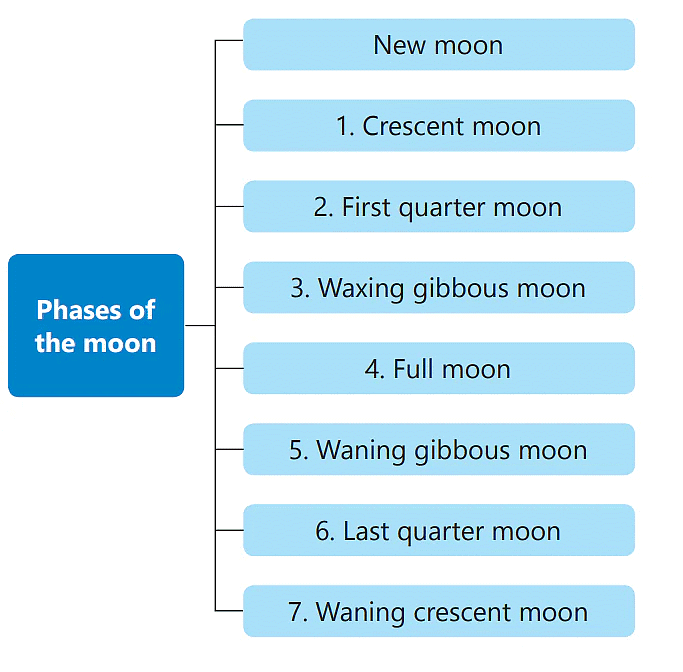
After the full moon is seen the waning gibbous moon, then the last quarter moon, the waning crescent moon and finally the new moon.
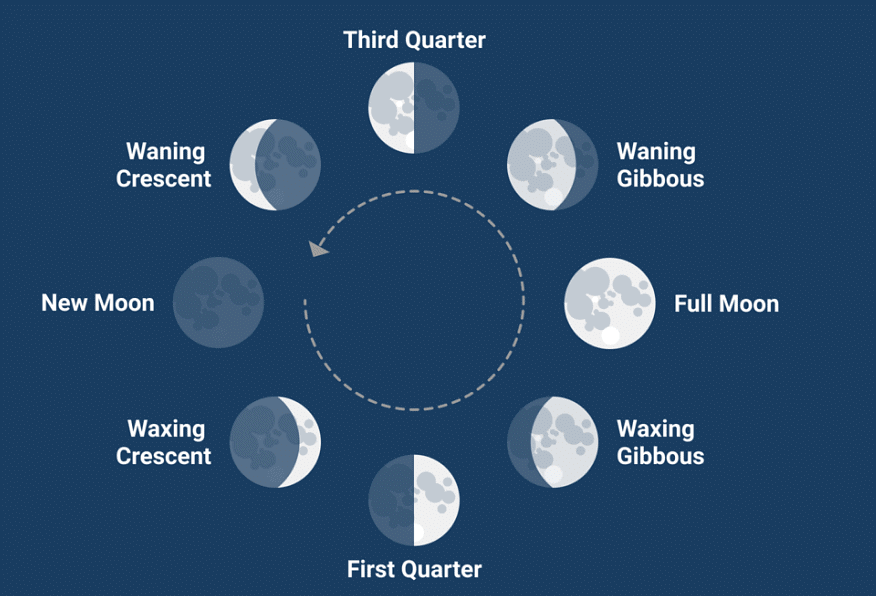 Moon's Phases
Moon's Phases
|
80 videos|359 docs|87 tests
|
FAQs on Moon & its Phases - Physical Science for High School - Grade 9
| 1. What are the different phases of the Moon? |  |
| 2. How long does each phase of the Moon last? |  |
| 3. Why does the Moon appear to change its shape? |  |
| 4. What is a New Moon? |  |
| 5. How does the Moon affect tides on Earth? |  |





















