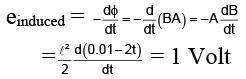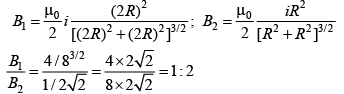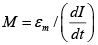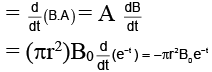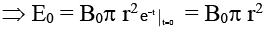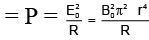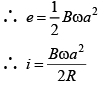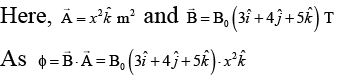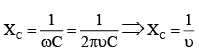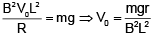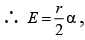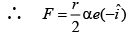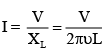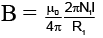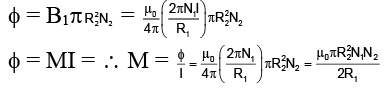JEE Advanced (Single Correct Type): Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Current | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. A square loop of side 1 m is placed in a perpendicular magnetic field. Half of the area of the loop lies inside the magnetic field. A battery of emf 10 V and negligible internal resistance is connected in the loop. The magnetic field changes with time according to the relation B = (0.01- 2t) tesla. The resultant emf of the circuit is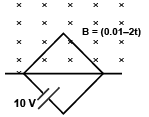 (a) 1 V
(a) 1 V
(b) 11 V
(c) 9 V
(d) 10 V
Correct Answer is Option (c)
∴ Resultant emf = 10 - 1 = 9V
Q.2. The direction of induced current in the right loop in the situation shown by the given figure is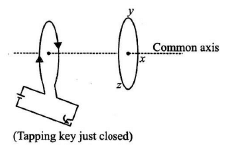 (a) along the common axis
(a) along the common axis
(b) along xzy
(c) along xyz
(d) none of these
Correct Answer is Option (c)
The induced current in the right loop will be along xyz.
Q.3. The variation of induced emf (e) with time (t) in a coil if a short bar magnet is moved along its axis with a constant velocity is best represented as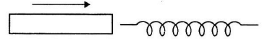
(a) 
(b) 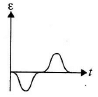
(c) 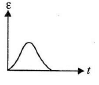
(d) 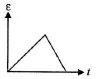
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The polarity of emf will be opposite in the two cases while the magnet enters the coil and while the magnetic leaves the coil. Only in option (B) polarity is changing.
Q.4. Figure shows two coils carrying equal currents. The ratio of magnetic field at P due to coil-1 to coil-2 is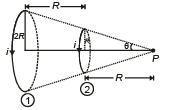 (a) 1/√2
(a) 1/√2
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 1/4
(d) (1/2)1/4
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.5. Two circular coils can be arranged in any of three situations as shown in the figure. Their mutual inductance will be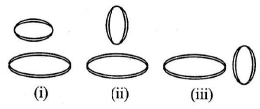 (a) maximum in situation (i)
(a) maximum in situation (i)
(b) maximum in situation (ii)
(c) maximum in situation (iii)
(d) same in all situations
Correct Answer is Option (a)
A mutual inductance occurs when the magnetic field generated by a coil induces a voltage in a secondary coil.
Since, in option (A), there is maximum emf is induced in secondary coil. So, mutual inductance is maximum.
Q.6. Shown in the figure is a circular loop of radius r and resistance R. A variable magnetic field of induction B = B0e-t is established inside the coil. If the key (K) is closed, the electrical power developed right after closing the switch is equal to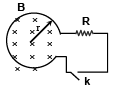 (a)
(a) 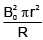
(b) 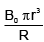
(c) 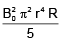
(d) 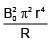
Correct Answer is Option (d)
The induced emf = E = dϕ/dt
∴ The electrical power developed in the resister just at the instant of closing the key =
Q.7. The arrangement shown here is a Faraday’s disc of radius a which is rotating in a uniform magnetic field B perpendicular to the plane of disc. The current passing through the resistance is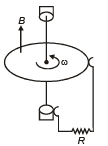 (a)
(a) 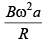
(b) 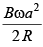
(c) 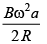
(d) 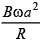
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Emf induced in the disc will be same as that induced in a rod rotating in a magnetic field.
Q.8. A square of side x m lies in the x-y plane in a region, where the magnetic field is given by B = 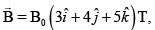 where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square
where B0 is constant. The magnitude of flux passing through the square
is
(a) 5B0x2Wb
(b) 3B0x2Wb
(c) 2B0x2Wb
(d) B0x2Wb
Correct Answer is Option (a)
∴ ϕ = 5B0x2Wb
Q.9. The phase relationship between current and voltage in a pure resistive circuit is best represented by
(a) 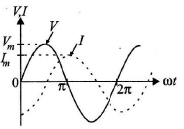
(b) 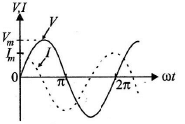
(c) 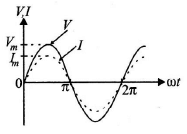
(d) 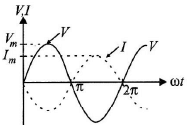
Correct Answer is Option (c)
In the pure resistive circuit current and voltage both are in phase. Hence graph (C) is correct.
Q.10. Which of the following graphs represents the correct variation of capacitive reactance XC with frequency?
(a) 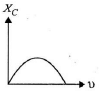
(b) 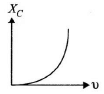
(c) 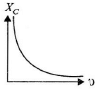
(d) 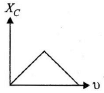
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Capacitive reactance,
With increase in frequency, XC decreases.
Hence, option (C) represents the correct graph.
Q.11. The natural frequency (ω0) of oscillations in LC circuit is given by
(a) 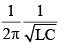
(b) 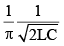
(c) 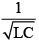
(d) 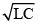
Correct Answer is Option (c)
Q.12. A rod PQ mass ‘m’ and length can slide without friction on two vertical conducting semi-infinite rails. It is given a velocity V0 downwards, so that it continues to move downward with the same speed V0 on its own at any later instant of time. Assuming g to be constant every where, the value of V0 is :-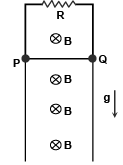 (a) mgr/2B2L2
(a) mgr/2B2L2
(b) mgR/2B2L2
(c) zero
(d) Any value
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Q.13. Alternating voltage (V) is represented by the equation
where Vm is the peak voltage
(a) V(t) = Vweωt
(b) V(t) = Vm sin ωt
(c) V(t) Vm cot ωt
(d) V(t) = Vm tan ωt
Correct Answer is Option (b)
The equation of the alternating voltage is V(t) = Vm sin ωt
Q.14. In the case of an inductor
(a) voltage lags the current by π/2
(b) voltage leads the current by π/2
(c) voltage leads the current by π/3
(d)voltage leads the current by π/4
Correct Answer is Option (b)
In an inductor voltage leads the current by π/2 or current lags the voltage by π/2.
Q.15. The magnetic flux linked with a coil of N turns of area of cross section A held with its plane parallel to the field B is
(a) NAB/2
(b) NAB
(c) NAB/4
(d) zero
Correct Answer is Option (d)
Magnetic flux linked with a coil
ϕ = NBA cos θ
Since the magnetic field B is parallel to the area A, i.e., q = 90°.
∴ ϕ = 0
Q.16. In the cylindrical region shown, magnetic field is diminishing at the rate of α(T/s). The force on the electron at a distance r along y-axis is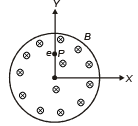 (a)
(a) 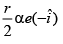
(b) 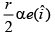
(c) 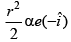
(d) 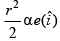
Correct Answer is Option (a)
E × 2πr = πr2.α
At P, E will be along
Q.17. An ideal inductor is in turn put across 220 V, 50 Hz and 220 V, 100 Hz supplies. The current flowing through it in the two cases will be
(a) equal
(b) different
(c) zero
(d) infinite
Correct Answer is Option (b)
An ideal inductor is in turn put across 220 V, 50 Hz and 220 V, 100 Hz supplies.
The current in the inductor coil is given by
Since frequency u in the two cases is different, hence the current in two cases will be different.
Q.18. An ac source of voltage V = Vm sin ωt is connected across the resistance R as shown in figure. The phase relation between current and voltage for this circuit is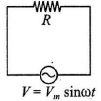 (a) both arc in phase
(a) both arc in phase
(b) both are out of phase by 90°
(c) both are out of phase by 120°
(d )both are out of phase by 180°
Correct Answer is Option (a)
The given circuit is a pure resistive circuit. In this circuit the voltage and current both are in phase.
Q.19. A coil of wire having finite inductance and resistance has a conducting ring placed coaxially within it. The coil is connected to a battery at time t = 0, so that a time-dependent current I1(t) starts flowing through the coil. If I2(t) is the current induced in the ring, and B(t) is the magnetic field at the axis of coil due to I1(t), then as a function of time (t > 0), the product I2(t) B(t)
(a) increases with time
(b) decreases with time
(c) does not vary with time
(d) passes through a maximum.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
i2(t) B(t) ∝ i2 (t)i1(t) ∝ (1–e–t/τ)e-t/τ
At t = 0, i1(t).i2 = 0
Also i1(t).i2 (t) → 0 as t → ∞
Q.20. Two circular coils of radii R1 and R2 having N1 and N2 turns are placed concentrically in the same plane. If R2 << R1, then the mutual inductance between them is
(a) 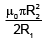
(b) 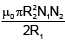
(c) 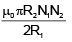
(d) 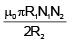
Correct Answer is Option (b)
Let I be the current through the coil of radius R1. The magnetic induction at the centre of the coil is
Magnetic flux linked with the coil of radius R1 is
|
481 docs|964 tests
|