Integer Answer Type Questions for JEE: Heat & Thermodynamics | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Q.1. 3000 J of heat is given to a gas at constant pressure of 2 x 105 N/m2. If its volume increases by 10 litres during the process find the change in the internal energy of the gas.
Ans. 1000
ΔQ = 3000 J
W = P Δ V = (2 x 105 N/m2) (10 x 10-3 m3) = 2 x 103 J
ΔU = ΔQ - W = 3000- 2000 = 1000 J.
Q.2. The specific heat of argon at constant volume is 0.075 kcal/kg K. Calculate its atomic weight,[R = 2cal/mol K]
Ans. 40
As argon is monatomic, its molar specific heat at constant volume will becal/mol K
Now as CV = McV with CV = 0.075 cal/gK
3 = M × 0.075Mw = 3/0.075 = 40 gm/mole
Q.3. The normal temperature of human body is 98.6ºF what is this temperature in Celsius degrees ?
Ans. 37
tºC = 5/9 (tºF – 32º)= 5/9 (98.6º – 32º) = × 66.6º
= 37ºC
Q.4. A closed container of volume 0.02 m3 contains a mixture of neon and argon gases at temperature of 27ºC and pressure of 1 × 105 Nm2. The total mass of the mixture is 28 g. If the gram molecular weights of neon and argon are 20 and 40 respectively, find the masses of the individual gases in the container, assuming them to be ideal. Given R = 8.314 J/mol/K.
Ans. 24
Let m g be the mass of neon. Then, the mass of argon is (28 – m)g.Total number of moles of the mixture,
…(A)
Now, μ =…(B)
Equating (A) and (B), (28 + m)/40 = 0.8
or 28 + m = 32
or m = 4g mass of argon = (28 – 4)g = 24 g
Q.5. For what value is the Fahrenheit temperature equal to the Celsius temperature?
Ans. 40
Let x ºF = x ºC , then using it in
t ºC = 5/9 (t ºF – 32º)x = 5/9 (x – 32) or 9x = 5x – 160
or x = – 40
Thus, – 40 ºC = 40 ºF
Q.6. A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in the Figure. If 3.6 calories of heat is given in the process, one calorie is equivalent to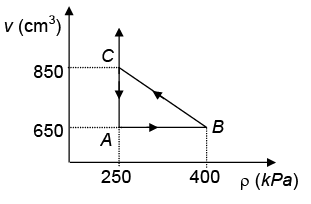
Ans. 4.17
∴ Heat given = Work done in the process
= 1/2 x (400 – 250) x 103 x (850 – 650) x 10–6
= 1/2150 x 200 x´ 10–3 = 15 J ≡ 3.6 cal.
⇒ 1 cal = 15/3.6 = 4.17 J.
Q.7. The average translational kinetic energy and the rms speed of molecules in a sample of oxygen at 300K are 6.21 x 10-21J and 484 m/s respectively. The corresponding values at 600K area nearly (assuming ideal gas behavior).
Ans. 684
∴ KE2 = 2KE1 = 2 x 6.21 x 10-21 = 12.42 x 10-21J
Q.8. A man got 100 Kcal heat from its lunch. Its efficiency is only 25% and mass of man is 60 kg. Calculate the height he can acquire.
Ans. 175
50/100 × 100 × 103 = Mgh
⇒ 25 × 103 =
⇒ h == 175m
Q.9. A 63 gm bullet moving velocity 200 m/s. Collides against a wall consequently two third of it's kinetic energy is converted into heat. Than what will be the heat developed by bullet in calorie. (Given: J = 4.2)
Ans. 200
Q =
= 200 cal
Q.10. The height of a water spring is 50m. The difference of temperatures at the top and bottom of the spring will be
Ans. 0.117
mgh = msΔθ= 0.117ºC
|
446 docs|930 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
 cal/mol K
cal/mol K …(A)
…(A) …(B)
…(B)


 = 175m
= 175m = 200 cal
= 200 cal = 0.117ºC
= 0.117ºC















